Whether it’s shipping materials, furniture production, wall insulation, or goods packaging, we see complex foam inserts everywhere around us. With the demand for foam parts growing exponentially, so must the production capabilities. Laser cutting gives businesses an excellent solution to improve foam product quality and production capacity.
In this article, we discuss in detail, how to laser cut foam, its material compatibility and its benefits over conventional cutting methods.
Basics of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a modern manufacturing technique that uses CNC (computer numerically controlled) technology to guide a laser beam precisely and accurately for cutting various materials. The laser inputs large amounts of heat into a very small contact point, instantly melting the material along a desired path.

You can cut thicker and tougher materials by slowing down the movement speed of the laser. So it has more time to make contact with the workpiece and deposit more energy (heat). Alternatively, a higher-wattage laser source that produces more heat per second can be used.
Laser cutting machines also come in at various price points. Most laser foam cutting machines start at $500 and go up to $5,000, with larger industrial models costing even more.
Types of Laser Cutter
Today, you can choose from a wide range of laser sources for your laser cutting machine.
- Gas Laser (CO2 Laser)
- Fiber Laser
- Solid State Laser (Nd: YAG Laser)
- Diode Laser
CO2 gas-based laser cutters are cheaper but, overall, less precise and accurate. Solid-state lasers like Nd: YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet) are primarily limited to medical devices.
Fiber and Diode lasers are generally a good option for cutting foam and similarly soft materials. Diode laser cutters are smaller and less powerful but easy to use and beginner-friendly. Fiber laser cutters can be seen as the bigger brother to diode lasers. Offering a lot more power, precision, and versatility in material choice and application.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
6 Advantages of Using Lasers to Cut Foam
Foam and similar materials are rather difficult to cut using traditional methods. You either have to invest in expensive punch-and-die setups or train workers to manually cut foam by hand.
Laser cutters, with their CNC precision, have several benefits over these older foam cutting techniques.
1. Faster Production
The production rate of laser-cut parts is heavily dependent on the workpiece material. Harder materials need to be cut at a slower speed and thus take longer to process. Softer materials like foam, plastic, and plywood are laser cut at a much faster rate, significantly increasing production efficiency.
Foam inserts that typically require hours of manual cutting can now be processed in just a few seconds.
2. More Complex Designs
Cutting hand-crafted complex designs is always going to be a difficult and time-consuming process. Small mistakes can ruin the entire foam sheet and undo hours of work in a split second. With CNC laser cutting, designers can work on creating the most complex and intricate designs without worrying about the processing challenges.
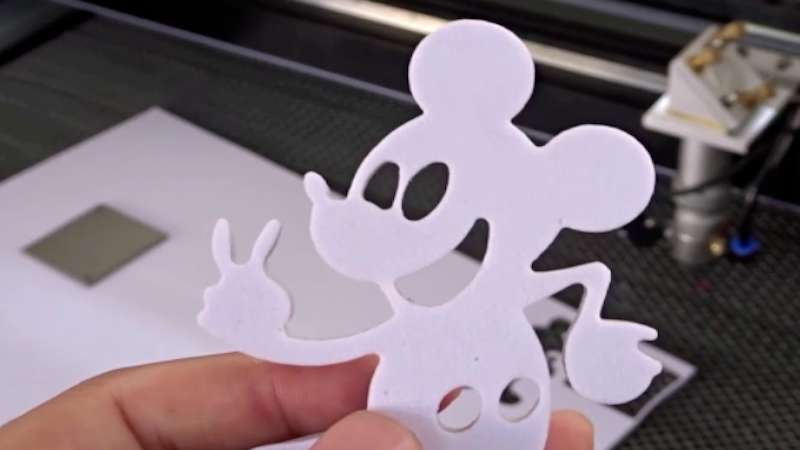

3. Cleaner Edges
Soft foam bends and stretches under the slightest pressure, making clean edges difficult to achieve. Laser cutters make precise cuts by selectively melting the foam sheet, ensuring clean and accurate edges. Unlike traditional cutting methods, there is no physical cutting tool (knife, blade, etc.).
4. Minimizing Material Waste
Cutting is an inherently destructive process. You lose a lot of material while cutting shapes and patterns out of a flat sheet. The more complex a design, the more material you waste cutting it out.
Luckily, you can first layout your designs digitally using CAD (computer-aided design) software and then have them cut by a laser machine. CAD helps pre-plan your designs and patterns so you can make the perfect cuts on the first try.
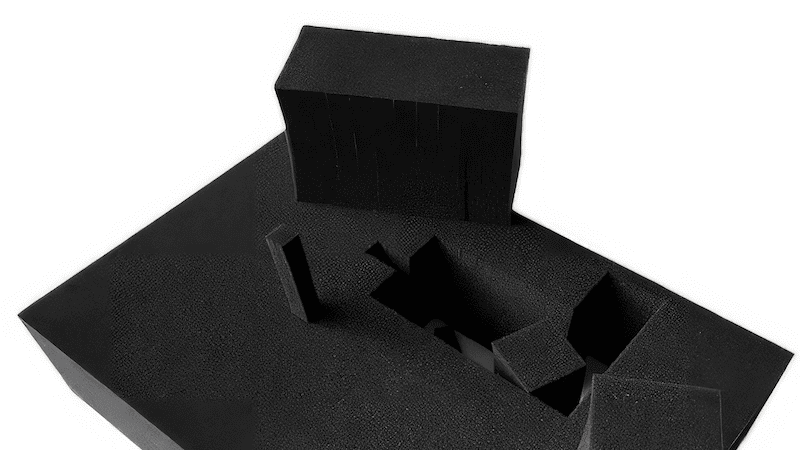
5. Improved Safety
Laser-cutting foam is also considerably safer than other cutting techniques. Foam cutting uses low-power laser beams, which are easier to manage and contain. These lasers are way less dangerous than heavy punch and die machines and keep workers’ hands away from sharp cutting tools.
Safer and more reliable equipment means fewer accidents on the factory floor and a higher production rate.
6. Versatility and Flexibility
Finally, we can never understate the versatility and flexibility of a laser cutting machine. Laser-cut foam is used for everything from packaging industrial products to making props and costumes for the film industry.
Laser cutting is also not limited to foam inserts and decorative pieces; it can also be used to create high-quality metal, plastic, wood, and fabric designs that come to life.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
Laser Cutting Foam – In 7 Easy Steps
Laser cutting foam is actually quite a simple process, especially if you have a basic understanding of laser components.
Step 1 – Designing Using Vectors
Laser-cut designs are divided into Images (also known as Rasters) and Vectors. Images are your standard photo-based designs, usually in the PNG format. Whereas, vectors are mathematical design coordinates that define your design’s geometry.
The standard CAD software outputs DXF, STL, and SVG files, which are compatible with most laser cutting machines.
Step 2 – Identify Your Foam Type
Next, you want to identify your base foam material. Foam is just the basic material shape, and the underlying chemical base determines its compatibility with laser cutting. Some foam materials melt and deteriorate under heat and are incompatible with laser cutting.
Common laser-cutting foams include the following materials.
- Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
- Polyethylene (PE) Foam
- Polyurethane (PU) Foam
- Polyester (PES) Foam
- etc.

Step 3 – Dial in Your Cutting Parameters
Laser cutter parameters include the laser head’s moving speed, the laser beam’s power output, and the operation mode (continuous or discontinuous/dot).
You can fine-tune your cutting parameters based on the type of foam, its thickness and density, and your design tolerances.
Step 4 – Perform a Test Cut
Although optional, it is always recommended that you perform a test cut on a rough material to test the laser cutting parameters. Test cuts become more important as you work on more complex designs or with premium materials.
This step can help you optimize your laser cutting process and enhance the quality of your cuts.
Step 5 – Set the Foam Material into the Machine
Carefully place the foam material onto the laser-cutting bed. Ensure that the work material stays within the laser cutting zone and the focal length of the laser beam.
Most laser cutter nozzles have a focal length of 2.5-4″. Outside this range, the beam becomes unfocused, leading to loose cutting tolerances and lower material penetration.
Step 6 – Use the Computer Interface to Initiate the Cut
Once you have everything ready, upload your CAD design into the laser cutter through the attached computer interface or a personal computer/laptop.
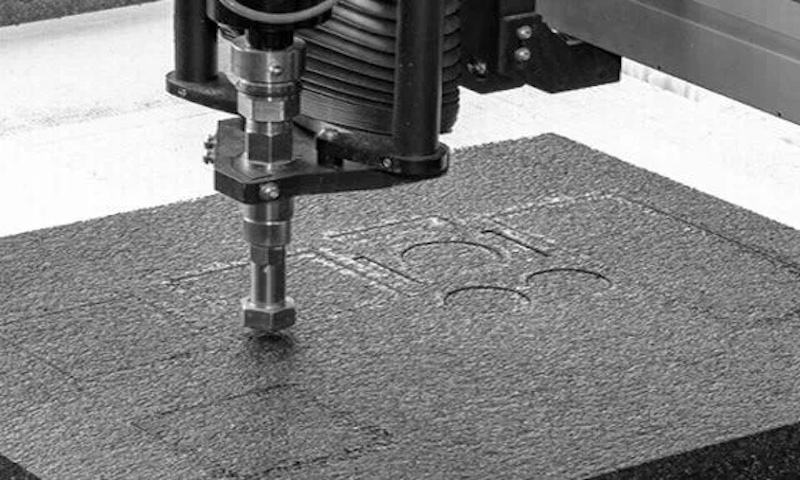

Now, you wait until the cutting process is finished. During this time, make sure you keep an eye on the laser cutter, as minor errors can lead to botched cuts.
Step 7 – Post Processing
Laser-cut foam typically doesn’t require any sort of post-processing. The cut edges are clean and accurate but may get charred by the laser beam. Post-processing consists of gluing, painting, and bending the foam parts.
Types of Foam That Can Be Laser Cut
Laser cutting supports a wide range of foam materials, ranging from soft to stiff. Each material is best suited to a specific application, which makes the decision-making process quite easy.
Here are the most popular foam materials for your laser cutting projects.
1. EVA Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a high-density and high-elasticity material. It is best suited to interior design and wall insulation applications. EVA foam maintains its shape and is easy to glue together, making it ideal for creative design projects.
2. Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is a low-density material with decent elasticity. The lower weight makes it ideal for packaging and shock absorption applications.
Additionally, PE foam is often laser cut for high-precision gasket and sealing applications.
3. Polyester Foam
Polyester foam is a lightweight, flexible, and low-cost material that is widely used in the packaging, furniture, and insulation industry.
Laser-cut polyester foam cushions are excellent for shock-resistant packaging and soundproofing applications.

4. Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is available in both flexible and rigid varieties and offers great versatility. Soft PU foam is used for car seats, while rigid PU is used as insulation in refrigerator walls.
Custom PU foam insulation is commonly found in electronic enclosures to seal the sensitive components, prevent shock damage, and prevent water ingress.
5. Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene is a rare food-safe foam material with low elasticity and material density. It is a general all-purpose material used for food packaging and shock absorption.
Aside from the food industry, laser-cut polystyrene form is commonly used in safety equipment like helmets and infant car seats.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
Common Foam Cutting Problems and Solutions
Laser cutting is a convenient and effective foam processing method. However, foam is a difficult material to cut, because of its soft and porous nature.
Here are some common problems that arise when laser cutting foam and their simple solutions.
1. Material Melting and Charing
Cause: Excessive laser power or slow cutting speeds and lead to greater energy deposition into the foam material, causing melting and charring.
Solution: Set the laser to a lower power output and increase the cutting speed. Test the changes on scrap materials and optimize your laser parameters.
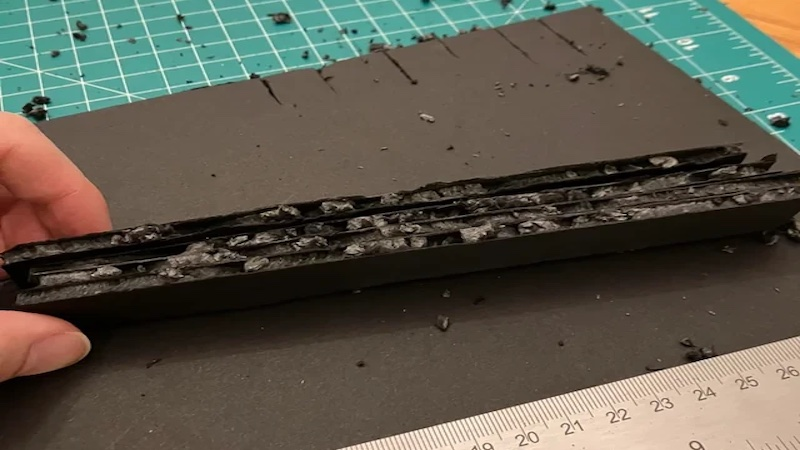

2. Material Ignition
Cause: Flammable materials like polystyrene and polyethylene foam ignite under excess laser power.
Solution: Set your laser to a lower power state and increase the cutting speed. Alternatively, you can use non-flammable foams like EVA or polyurethane.
3. Fumes and Odors
Cause: Most foam materials are plastic-based and thus release unpleasant and hazardous fumes on melting.
Solution: Place your laser cutter in a well-ventilated space, install a fume hood, and exhaust systems, or get an air filtration system.
4. Poor Edge Quality
Cause: Dirty optics and out-of-focus laser beams can result in uneven foam cutting, leading to poorer edge quality.
Solution: Regularly clean the laser optics, especially after long cutting sessions.

5. Inconsistent Cutting Depth
Cause: Uneven material surface or inconsistencies in the foam density can result in uneven laser penetration.
Solution: Ensure the foam material is lying completely flat on the workbench. Buy high-quality foam materials that have a more even density across the board.
6. Poor Cutting Tolerances
Cause: Reflective material surface or leftover adhesive residue will disrupt the laser focal point, reducing cutting accuracy.
Solution: Cut shiny foam sheets from the underside (non-reflective side) or mark the cutting surface with tape and account for the thickness change. Also, be sure to properly wash the material surface, removing all unwanted residue and impurities.
FAQs
1. What Kind of Foam is Best for Laser Cutting?
EVA foam is the go-to option for laser cutting. It is a laser-safe material available in a wide range of thicknesses and densities. EVA is also a low-cost option that is widely available in most regions.
2. Is Laser Cutting Foam Safe?
Yes. Using low-wattage (<50W) lasers to cut foam sheets is perfectly safe. Some materials, like polystyrene foam, are more sensitive and end up with charred or burnt edges after laser cutting.
3. Which Laser Cutter is Best for Cutting Foam?
CO2 laser cutters are cost-effective and the fastest at cutting different thickness foam shapes. Diode lasers are good for thin foam sheets, and Fiber lasers are an expensive general-purpose solution for foam and other materials.
4. What is the Minimum Wattage Required to Laser Cut Foam?
Foam materials vary by density and thickness. As a general rule, a 10-20W CO2 laser will cut most foam material under 10 mm of thickness. However, a higher wattage, 40-60W unit, is generally recommended for foam cutting.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
Conclusion
Although traditional cutting methods are still viable for low-volume simple designs, laser cutters are the way to go for businesses looking to improve their foam part design complexity and production volume. Laser-cutting foam is simple, inexpensive, and versatile. It is compatible with various foam materials, ensuring maximum production efficiency.
Get the Best Laser Cutting Precision with Baison!
Baison is a state-of-the-art laser solutions manufacturer. We serve as a one-stop shop for manufacturers in over a hundred countries and regions. Our CO2 and Fiber Laser Machines are the perfect solution for all your foam-cutting needs.
Let our team of experts help you get the best laser system for your business via our Free Application Evaluation program. Baison also offers Free Customer Training programs to help you get your business up and running in no time.
So don’t miss out on industry-leading precision. Contact us Now!