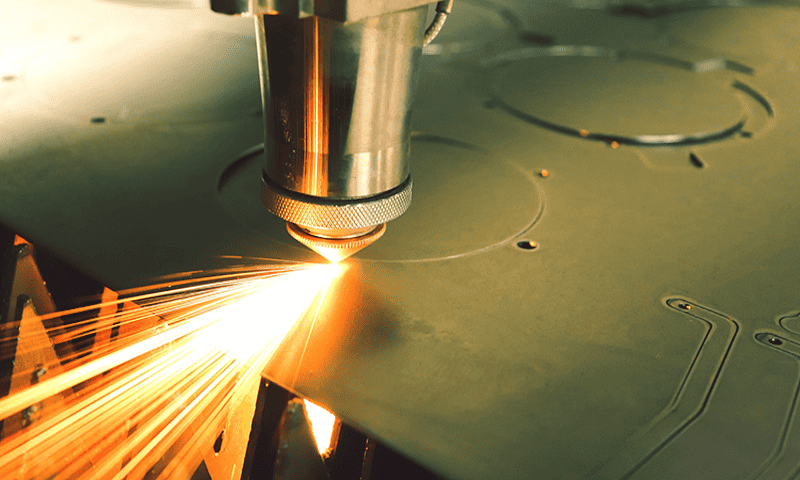
Laser cutting is an incredibly versatile manufacturing technology that has revolutionized many industries. It can transform a diverse range of materials with pinpoint accuracy. From wood and acrylic to fabric and metal, there is a laser cutter for every application.
In this article, we compile the ultimate laser cutting materials list and highlight some hazardous ones you should avoid.
What Materials Can Be Cut With a Laser Cutter?
Modern laser cutters support a diverse range of materials. As long as you have the necessary laser power, you can cut through anything, from thin sheets of acrylic to thick metal plates.
Here is a complete list of all the materials compatible with a laser cutter.
1. Metals & Alloys

Metals are some of the most popular laser-cutting materials. Traditionally, manufacturing techniques are slow, expensive, and require hours of hands-on training. Laser cutting is a more accessible technology that allows anyone with basic know-how to cut through the toughest metal parts.
Laser cutting machines can process thin metal sheets with incredible speed and accuracy. However, you will need to reduce the cutting speed for thicker metal materials to ensure complete laser depth penetration.
Here are some of the most popular metal materials used in laser cutting.
Alloys of these metals are also compatible with laser cutting. Aluminum and nickel are always used as alloys and rarely in their pure form.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
2. Wood

Laser-cutting wood has seen a steady rise in recent years. The modern furniture industry has already shifted to laser-cut wood design for its catalog. A drawback of laser cutting wood is accidental burning. Wood is flammable, and laser cutting often leaves char marks on cut edges.
Wood veneers are a popular choice for many designers. They use laser cutting to create veneer stickers that go on top of other inexpensive materials.
We can divide laser cutting wood materials into three categories.
Softwoods
- Alder
- Basswood
- Cedar
- Balsa
- Pine
- Popular
Hardwoods
- Cherry
- Maple
- Oak
- Walnut
- Birch
Synthetic Wood Materials
Most beginners should start with MDF and plywood, as these are inexpensive laser cutter materials that are widely available.
3. Plastics

Plastics are generally very soft and thus very difficult to cut and shape with traditional processes. Sawing, drilling, and milling result in the plastic melting and deforming. Hence, laser cutting plastic has grown in popularity with the wide availability of low-wattage laser cutters.
Here are the most popular plastic-based laser cutting materials.
- Acrylic
- Styrene
- Nylon
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyethylene (PE)
Acrylic is by far the most popular plastic material for laser cutting. It’s stiff, lightweight, affordable, and acts as a shatterproof glass alternative.
4. Textiles

Laser cutting supports various materials, including several fabric options. Fabrics tend to fray at the edges and require additional post-processing to stop the material from unraveling. The threat of fraying limits intricate pattern designs.
Laser cutting cauterizes the edges as it cuts through the fabrics, making it a more effective solution for textile design. As fabrics burn easily, you will need to fine-tune your laser-cutter settings. Keep the laser power low and the cutting speed high to get the best results.
Here are some common textile materials for laser cutting.
- Leather
- Denim
- Linen
- Felt
- Satin
- Silk
- Polyester
- Cotton
- Fleece
Leather is a very difficult material to handle. It requires years of training with traditional tools to master leather manufacturing. Luckily, modern CNC laser cutting can simplify the process and give newcomers a helping hand.
5. Rubber
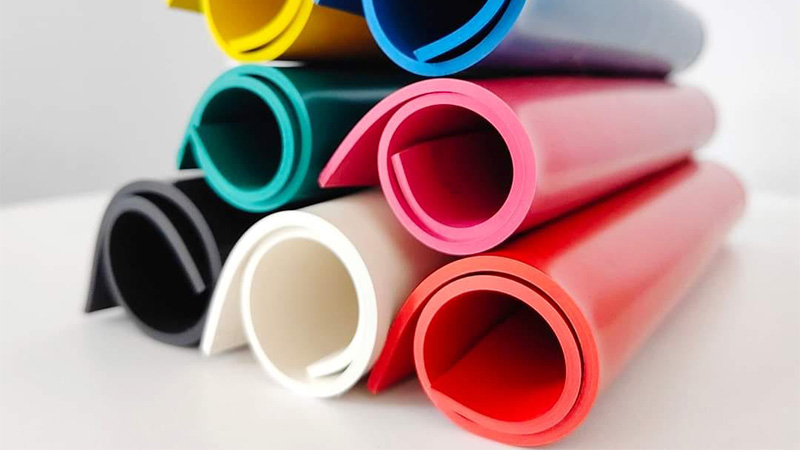

Rubber materials share some key traits with plastic and textiles, such as softness and flexibility, that make traditional cutting more difficult. Laser cutting can precisely cut thick and thin rubber sheets in seconds.
High-performance rubber gaskets and seals benefit from the excellent CNC precision of laser cutters. Most of today’s rubber gaskets are made from synthetic materials. Natural rubber is very durable, but the labor and processing costs limit its use cases.
Modern laser cutters can support the following rubber materials.
- Natural Rubber
- Silicone
- Neoprene
- Latex
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
6. Foam
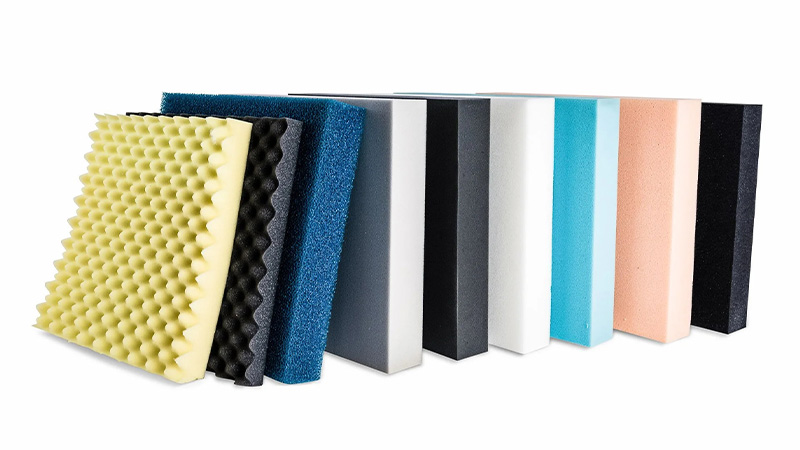

Fiber lasers are excellent at processing any material that is soft and delicate. A laser beam can cut through the most delicate materials without melting, bringing, or deflating. Hence, laser cutting foam is a natural fit for most manufacturers.
Precision-cut foam is used for various packaging, shock-proofing, and soundproofing applications. Laser cutting foam is compatible with various thicknesses of polymers. It can easily cut foams up to 2″ but at the cost of some dimensional accuracy.
Here are the five best materials for laser foam cutting.
- EVA Foam
- Polyethylene Foam
- Polyester Foam
- Polyurethane Foam
7. Paper & Cardboard

Paper and paper-based products are a big part of hobbyist laser cutting. They are inexpensive and easily accessible, perfect for your next arts and crafts project. On the industrial scale, laser cutting cardboard is generally limited to the packaging industry.
While you can easily cut paper and cardboard with a blade, laser cutting simply offers a more convenient and precise solution that can cut complex designs faster than any mechanical cutting tool.
- Paper (up to 150 g/m²)
- Cardboard
- Corrugated Cardboard
- Card Stock
- Foam Board
Laser cutting cardboard is a big trend in wedding decorations as a greener alternative to plastics.
8. Ceramics and Stones
Ceramics are stone-like materials that have high toughness and are very brittle. Laser cutting machines are commonly used as laser engravers. Modern ceramic markings are primarily done using high-power laser cutting.
Even though the process is difficult to manage, many ceramics materials can be cut using specialized processes, such as zero-width laser cutting.
Here is a list of common laser cutting materials.
- Glass
- Tiles
- Stone
- Marble
- Granite
| Metals | Wood | Plastics | Textiles |
|---|---|---|---|
Carbon/Mild Steel Stainless Steel Aluminum Copper Nickel Titanium | Softwoods Hardwoods MDF Plywood Particle Board | Acrylic Styrene Nylon Polypropylene (PP) Polyethylene (PE) | Leather Denim Satin Silk Polyester Cotton Felt & Fleece |
| Rubber | Foam | Paper | Ceramics |
| Natural Rubber Silicone Neoprene Latex | EVA Foam Polyethylene Foam Polyester Foam Polyurethane Foam | Paper (up to 150 g/m²) Cardboard Corrugated Cardboard Card Stock Foam Board | Glass Tiles Stone Marble Granite |
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
What Materials Shouldn’t Be Cut With a Laser Cutter?
Laser cutters can cut through almost any type of material with enough power. However, certain materials react negatively to the strong laser energy. Weaker materials like plastic tend to burn under excess heat and release toxic gas (fumes).
Several laser-cutting materials fall under a separate sensitivity category. These materials can be laser cut with proper care and precaution but are very dangerous.
Most plastic materials are generally not recommended for laser cutting. Following is a short list of laser-cutting materials that you shouldn’t use.
1. PVC Materials
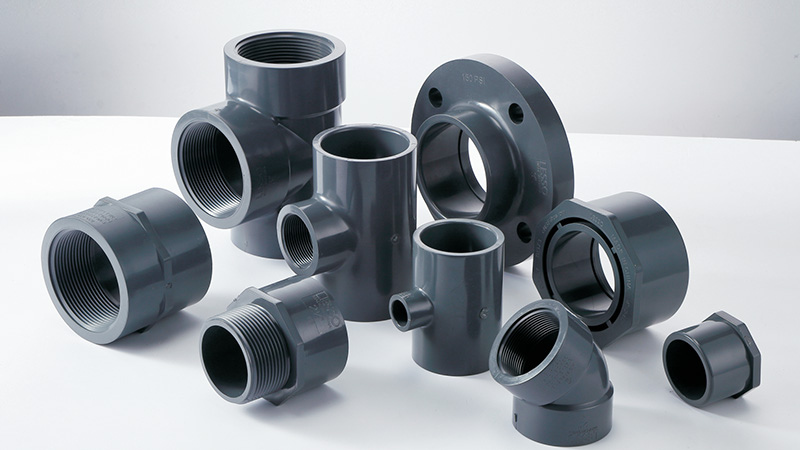

PVC (Poly Vinyl Chloride) is a durable thermoplastic that is useful for a wide range of applications. However, as this material is made using chlorine gas, excess heating can melt the PVC, releasing toxic chlorine gas into the air.
Even with a fume hood, laser-cut PVC is very dangerous.
2. Polycarbonate

Polycarbonate (PC) is a tough, clear plastic that absorbs most of the laser light. Thus, cutting polycarbonate requires more energy, making the process highly inefficient. It will also discolor from the laser heat.
3. Coated Carbon Fiber

Carbon fiber is compatible with laser cutting. However, the resin that coats and adheres to carbon fiber is unstable and releases toxic fumes on heating. Epoxy resin fumes, in particular, cause serious respiratory damage.
4. Fiberglass Sheets
Glass fiber sheets are bonded with resin as well, making them unsuitable for laser cutting. Additionally, the refractive properties of glass fibers inhibit the laser cutter’s full potential.
5. Galvanized Metal

Galvanization is the process of coating a metal component in a layer of zing to prevent rusting. As the laser beam cuts a galvanized metal, the zinc coating vaporizes and turns into zinc oxide.
Inhaling zinc oxide causes serious long-term damage to your health. Thus, it’s better to laser cut the raw metal first and galvanize it later during post-processing.
6. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)

ABS is a very popular plastic material as it can be heat-molded after laser cutting. However, it is generally not recommended for laser cutting as it releases hazardous fumes on melting. It releases one of the most toxic compounds on melting, cyanide gas.
7. HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene)
HDPE is another one of those common materials that is easy to laser cut but is very volatile. It melts at a low temperature and has the risk of catching fire.
8. Polystyrene Foam

Polystyrene foam is durable and food-safe, making it one of the most widely used materials in the packaging industry. However, it is a very soft material that quickly catches fire. Using a laser cutter on polystyrene foam is dangerous and strongly condemned by professionals.
| Laser Cutting Materials to Avoid | Reason |
|---|
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
Types of Laser for Different Materials
Laser technology can be divided into four general types based on the laser source. Each laser type has its pros and cons that help it adapt to different materials.
I. Gas Laser

Gas lasers work by passing an electric current through a gas mixture to exceed the atoms. These atoms radiate light, which gets amplified into a laser beam. CO2 is the most popular gas option for laser cutters.
CO2 laser cutting has the broadest material compatibility. It can be used on metals, fabrics, plastics, wood, and more. The only limitation here is reflective surfaces, such as polished bronze or copper sheets.
II. Solid State Laser

Solid-state lasers use a crystal as a gain medium for the laser amplification. The most popular crystal option is Nd:YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet).
Nd:YAG lasers are low-power options that are primarily used for medical applications such as tattoos or hair removal. Outside of medical use, they are primarily limited to thin metal sheets.
III. Fiber Laser

Fiber lasers are a special type of solid-state laser that uses optic fiber cables to amplify and concentrate the laser source. They combine the energy efficiency of Nd:YAG lasers with the raw power of CO2 lasers for the ideal balance.
Fiber lasers are an excellent option for metal and non-metal cutting applications. It has greater compatibility with reflective surface metals but limited compatibility with rubber and wood materials.
IV. Diode Laser
Diode lasers use semiconductor materials to amplify the light beam into a laser. They are by far the most efficient laser technology at low wattages.
Due to their low power output, diode lasers are generally limited for fabrics, woods, and plastics.
We have also prepared a comparison article of these lasers: fiber laser vs. diode laser, CO2 vs. fiber laser, YAG vs. fiber laser.
| Materials | Fiber Laser | CO2 Laser | Nd:YAG Laser | Diode Laser |
|---|
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
What Are the Laser Cutting Settings for Different Materials?
The exact settings for laser cutting different materials will vary by manufacturer and machine model. We can set basic cutting rules for these different materials based on their properties.
| Material | PowerLaser Wattage | Cutting Speed | Number of Passes | Cutting Depth |
|---|
FAQs
1. Is It Safe To Laser Cut Flammable Materials?
You should always avoid laser cutting flammable material. However, you can safely cut such materials with proper precautions and the right laser setting.
2. What Wattage Laser Cutter Should I Get?
A sub-20W laser cutter is good enough for most non-metal applications. A 1kW-2kW laser can cut through most materials including metals up to 10 mm of thickness. You should only get 6kw or higher wattage lasers if you cut materials like titanium or thick stainless steel plates.
3. Are Laser Cutters Expensive?
Laser cutters start at $2000 for entry-level 20-40W machines and go up to 500,000 for multi-kilowatt industrial units.
Conclusion
Lasers can cut through any material, given enough power and time. The trick to a productive manufacturing process is to optimize your material choices. Diode lasers are excellent for cutting softer non-metal material, CO2 is an inexpensive option for metal cutting and engraving, and fiber lasers are the best laser cutting technology, although a bit expensive.
Identify your application and choose a laser cutter that best suits your needs.
Cut Through the Toughest Materials with Baison Lasers!
Baison is an industry leader with over 20 years of experience manufacturing laser cutting machines. Our exceptional fiber laser systems result from our commitment to quality, attention to detail, and dedication to perfection.
Take advantage of our FREE Application Evaluation program to help you get the best laser cutter for your business. We are committed to delivering the best products at the best prices. Get Instant Quotes tailored to your specific needs.
For more information, Contact Us Now!