We are familiar with the drawbacks of traditional industrial cutting. Material loss, rough edges, weakened structures—quite frustrating, right? But what if there’s a cutting-edge laser technique that not only erases these issues but also strengthens materials?
Enter Zero-Width Laser Cutting – a true game-changer! Let’s dive into this revolutionary method, uncovering its working, benefits, and unmatched potential.
What is Zero-Width Laser Cutting?
Zero-width laser cutting (ZWLC) is a non-contact cutting process for brittle materials like glass and quartz that works on the principle of rapid heating and cooling of the material, introducing thermal stresses on a molecular level. The stress on the glass surface causes crack progression, separating the material into ultra-fine quality without the need for any physical contact.
Similar to how a glass or a tumbler shatters when you pour a boiling beverage into it. The same phenomenon happens in zero-width cutting but in an extremely controlled environment.
It’s called “Zero-Width Cutting” because no cutting wedge is present, and no material is lost, as you commonly see in traditional processes like when diamond scribes cut the glass. Since there is no actual contact, the edges are free from chips, glass dust, and protrusions.
Furthermore, the edge quality is five times stronger than traditional methods and requires no further processing, like polishing and grinding.
It also goes by the name Laser Shearing, Laser Separation, and Laser Controlled Thermocracking (LCT).
You’ll find zero-width laser cutting mainly in the bio-, micro- and opto-electronics industries. Other than that, it’s the most practical solution for Flat display Panel (FDP) cutting.
However, zero-width laser cutting is a relatively new technology and quite rare. The research and development of machinery is primarily happening in Russia, America, and Taiwan. Zero-width laser cutters are the most efficient glass-cutting machines in the world.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Working Principle of Zero-Width Laser Cutting
Zero-width laser cutting is a pretty unconventional method to approach the cutting of brittle materials. So, we have broken down the basic working principles into a few easy steps.
1. Laser Heating
In traditional laser cutting, the laser beam melts and evaporates the material, which gives us the desired results. But in zero-width laser cutting, the laser radiation heats up the glass substrate along the non-dimensional cutting line.
The laser is not hot enough to melt the glass. However, it raises the temperature significantly, causing the heated area to expand. This introduces extreme compressive stresses from the surrounding cold glass, initiating cracks on a molecular level. During the controlled heating stage, there is no surface damage.
That’s why it’s called non-contact cutting because there is no mechanical cutting involved, just the changes in the material’s structure. The CO2 lasers between 100-500 W range are most suitable for zero-width laser cutting.
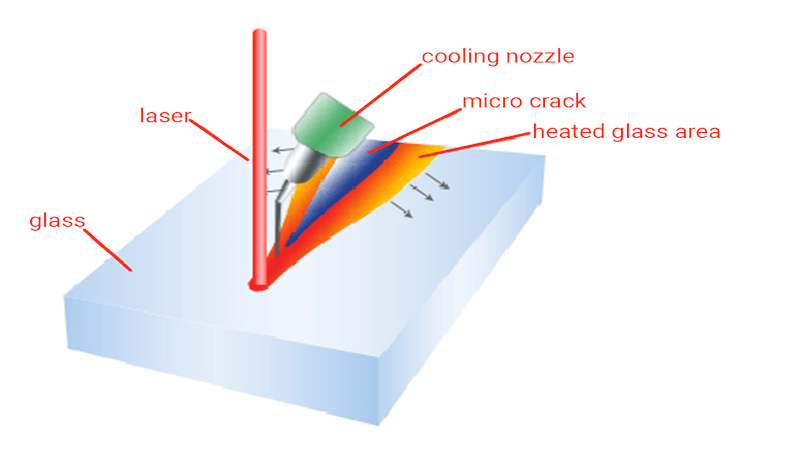
2. Rapid Cooling
Next, the heated non-dimensional scribe line (zero-width) is rapidly cooled using an atomized water jet or any suitable coolant. It cools the heated area, which creates extreme tensile internal stresses from colder glass. The material succumbs to the internal stresses, a crack starts propagating, and the substrate separation process starts.
All of this is possible because of the steep temperature gradient and correct power density profile on the cutting line, which generates huge thermal stresses beneath the surface, initiating a crack propagation that quickly separates the surface. A shallow crack occurs and starts propagating approximately at 1/6th of the thickness of the plate just below the surface.
Technically, no cutting is involved, just the substrate separating on a molecular level, making the process free from material loss, chips, and rough edges.
Mind you, both heating and cooling are happening simultaneously and can achieve a fantastic cutting speed of one meter per second (1000 mm/sec).
The zero-width laser cutting can achieve extremely high cutting speeds in a straight line but requires tedious adjustments when many curves and contours are involved.
As you can see, this process is directionally sensitive, so highly advanced sensors are required to keep the positional accuracy and all the related parameters in check.
Key Features of Zero-Width Laser Cutting
Zero-Width Laser Cutting is a state-of-the-art technology, and it’s especially important to understand its features.
1. High Strength Edge
Zero-width laser cutting produces 5.5 times stronger edges than traditional diamond scribe cutting or wire sawing. This results in highly durable edges, especially in the case of flat panel displays.
Amazingly, that is due to the “Thermal Glass Tempering” effect that naturally occurs during the zero-width laser cutting process. The rapid heating and cooling compresses the edges, making it stronger than traditional glass materials. It saves a lot of resources, making this cutting process exceptionally efficient.
Higher edge quality is the need of modern manufacturing, considering the devices are getting thinner and smaller in size without compromising the strength and durability of the product.
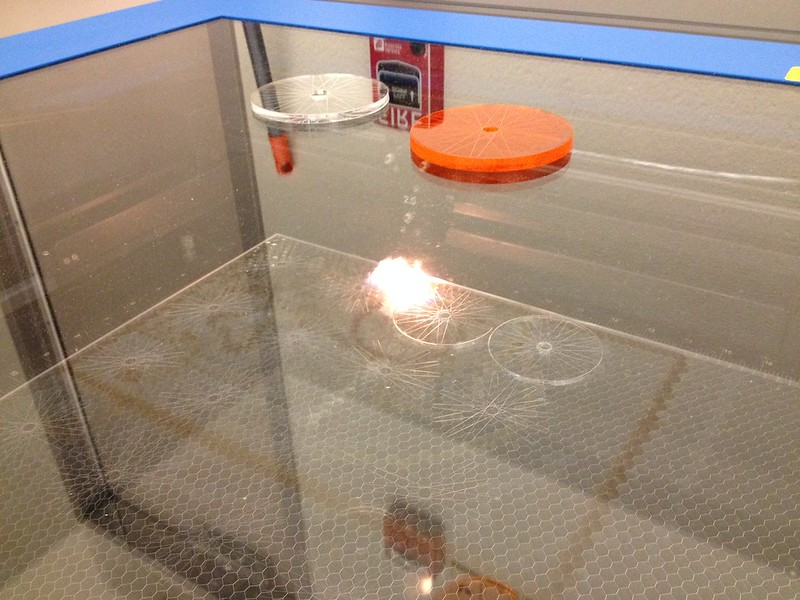

2. High Cutting Speed
The maximum cutting speed possible using zero-width laser cutting is one meter per second (3.28 ft/ sec), which is phenomenal. It’s one of the major key features of this cutting technology.
However, the cutting speed is inversely proportional to the penetration depth as the laser power is constant. This means for thicker materials, the cutting speed reduces and averages about 0.5m/s, which is still remarkable.
Zero-width laser cutting technology is best suited for 1 mm thickness of materials, but it can be optimized to cut as low as 0.3 mm thickness.
3. No Post-processing
Lastly, the most appealing feature of zero-width laser cutting is that no post-processing is required. Traditionally, cutting brittle materials leaves rough edges, chips, hooks, and protrusion.
So, for rectification, finishing processes like grinding and polishing are necessary to get smooth edges and regain the lost strength of the material edge. However, there is no such need for zero-width cutting as the cut has no width, and the material separation is ultra-fine.
Additionally, the edges are hardened due to natural heat treatment killing two birds with one stone.
It’s estimated that zero-width laser cutting saves approximately 70% of manufacturing costs, a huge economic and ecological benefit for the industry.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Pros and Cons of Zero-Width Laser Cutting
I’m sure you have concerns about the pros and cons of Zero-Width Laser Cutting. Don’t worry! Let’s get into them now.
Pros
Zero-Width Laser Cutting has a number of compelling benefits, which we’ve outlined below.
1. Zero Material Loss
There is no material loss during zero-width cutting, making it highly profitable. Since the material remains intact, there is no dust or debris, making the cutting process possible in clean room conditions.
Clean room conditions for production are necessary in most electronics and optics manufacturing, where the slightest impurity can negatively affect the product.
So, zero-width cutting eliminates the need for separate cutting space introducing a production line concept with multiple manufacturing processes that can done under a single roof, making it highly efficient.
2. Exceptional Cuts for Brittle Materials
Zero-width laser cutting is best suited for cutting brittle materials. In fact, it’s the only cutting technique in the world with a non-dimensional cutting line and near-perfect efficiency. It also has an accuracy of up to 10 microns (0.01 mm).
3. Economic Benefits
A substantial budget goes into rectifying rough edges when it comes to traditional cutting, not to mention time and manpower. With zero-width laser cutting, almost two-thirds of cutting costs are reduced.

4. Longer Life Expectancy
We know by now that Zero-width laser cutting increases the edge strength, but that’s not all. It also enhances the impact strength of the overall component by 80%. This improved strength prevents damage during the production phase as well as in practical use.
So, it allows the machining of thinner and lighter materials without any risk, resulting in a longer lifespan and greater durability.
Cons
Inevitably, Zero-Width Laser Cutting has some drawbacks.
1. Material Compatibility
Zero-width laser cutting is only suitable for brittle materials, rendering it ineffective for most metals and non-metals. This technology is most suitable for cutting thin glass panels typically used in phones, tablets, and computer screens (FDPs).
2. Contours and Curvilinear Cutting Lines
Zero-width laser cutting inherently struggles while cutting contours and curvilinear lines. That’s because it’s challenging to keep the linear positioning of the laser source and coolant along the curves.
However, researchers are improving the technology by calibrating the cooling spot to move in a linear line relative to the laser beam, even on curves. As time passes, we hope for better and more effective cutting solutions.
What Materials Can ZWLCT Cut?
Zero-width laser cutting technology (ZWLCT) primarily works for brittle and non-metallic materials like glass, sapphire, silicon, microcrystalline quartz, and gallium arsenide typically used in opto- and microelectronic devices. But soda lime or alkali glass is most commonly used since it’s the most versatile material.
Here is a brief information about types of glass used for zero-width laser cutting and their applications.
| Glass type | Industry Type | Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| Alkali glass | Automotive | 1 |
| Borosilicate | Electronics | 0.05 – 0.5 |
| Borosilicate | Flat panel displays | 1.6 - 4 |
| Alkali glass, Borosilicate | Medical | 4 -10 |
| Alkali glass | Architectural | 0.3 – 1.1 |
Comparison of ZWLCT With Traditional Cutting Methods
Since ZWLCT is only applicable to brittle materials, we will discuss the alternatives currently used in the industry. This includes methods ranging from modern laser cutting to conventional mechanical cutting.
I. CO2 Laser Cutting
CO2 laser cutting is the most readily available laser-cutting solution for non-metals and brittle materials. It works on a simple vaporization principle, which means the hot laser beams melt the materials and cut them.
The secret lies in the 10.6 um wavelength of the laser beam, which reflective materials like glass can easily absorb. This laser-cutting technology is better than ZWLCT in terms of practicality and availability.
Advantages
- Highly precise and accurate, suitable for intricate designs.
- Fast and efficient for production.
- Readily available.
Disadvantages
- Expensive machinery

II. Fracture-controlled Cutting
It’s similar to Zero-width laser cutting as it’s non-contact. But instead of rapid heating and cooling, the material is heated in such a controlled manner that it introduces extreme thermal stresses on its own, propagating the crack in the substrate without any cooling. It’s a much faster process. Also called the full-body separation method.
Advantages
- Highly precise and accurate.
- Fast and efficient.
Disadvantages
- Rare technology and limited availability.
- Low material compatibility
III. Diamond Scribing
It’s a simple cutting method that utilizes a diamond-tipped tool to cut or scribe the glass.
Advantages
- Suitable for intricate designs and low-volume work.
- Works well with various glass thicknesses.
- Low cost
Disadvantages
- Slower compared to some other cutting methods.
- Rough edges and material loss

IV. Wire saw cutting
Wire saw cutting involves using a wire equipped with abrasive materials such as diamond particles to cut through the material.
Advantages
- Highly precise cuts in thick glass.
- Can cut various material types and thicknesses.
- Reduces waste due to thin wire.
- Produces clean edges
Disadvantages
- It might not be as fast as some other cutting methods.
- Complex setup
V. Water-jet Cutting
High-pressure water jets mixed with an abrasive substance can effectively cut through glass. This method is suitable for thicker glass or materials where precision is critical.
Advantages
- Versatile, capable of cutting various shapes and thicknesses.
- Produces minimal to no mechanical stress on the glass.
Disadvantages
- Equipment maintenance can be high.
- It is not as precise as laser cutting for intricate designs.
| Cutting Method | Precision and Accuracy | Versatility | Cost Efficiency | Speed and Efficiency | Complexity of Cuts | Surface Quality | Material Integrity | Equipment and Skill Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZWLCT | High | Moderate | High | High | Moderate | High | High | High |
| Diamond Scribing | High | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | High | High | High | Moderate |
| Water Jet Cutting | Moderate | High | Moderate | High | High | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Laser Cutting | High | Moderate | Low | High | High | High | Moderate | High |
| CNC Machining | High | High | Moderate | Moderate | High | High | High | High |
| Wire Saw Cutting | Low | Low | High | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
Applications of Zero-Width Laser Cutting
Zero-Width Laser Cutting is being used in more and more industries, and we’ve learned about some of them below.
1. Flat Panel Display (FPD)
ZWLC is primarily designed for cutting thin display wafers or panels. Basically, all the display screens in modern mobile phones, TV screens, and similar devices fall under this category.
Since they’re mostly of very small thickness, the traditional cutting methods with a large cut width of the cutting line waste a high amount of raw material. With this modern zero-width laser cutting, thinner and finner cuts are obtained at significantly lower costs.
2. Micro Electronics
Microelectronics is a manufacturing industry of really small electronic devices. Typically, examples include transistors, inductors, diodes, and capacitors.
Such microfabrication requires extreme precision and delicacy to avoid damage during manufacturing, making ZWLC an extremely powerful cutting tool. Microelectronics also need clean room conditions for production, which is easily achieved because it creates no cutting dust or impurities.
3. Optoelectronics
Optoelectronics is an emerging technology that involves light-emitting and light-detecting devices. The most groundbreaking inventions in this field are optical fiber systems, photodiodes, and solar cells. ZWLCT’s highly efficient cutting of up to 10 microns makes it an excellent machining process for this industry.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
How to Get Zero-Width Laser Cutting?
Zero-width laser cutting is a relatively newer technology, even though the concept was first introduced in the 1980’s. As we discussed in the previous section, it’s not readily available. There is ongoing research going on to make ZWLCT a more practical and economical solution in countries like America, Russia, China, and Taiwan.
Right now, Fonon Corp., an American company, is the leading international manufacturer of zero-width laser cutting machines. Similarly, Foxconn Technology Group in Taiwan also has patents for curvilinear zero-width laser cutting.
Challenges and Limitations
Zero-width laser cutting technology is still a work in progress, and only a few companies hold the patent for its production. This simply means the research and development of these machines is still ongoing, and it will take time for them to become mainstream.
Additionally, laser-controlled thermos-cracking requires laser surface heating followed directly by a cooling nozzle, which needs high-end synchronization, only possible advanced sensors and control systems. This poses a challenge when cutting intricate designs.

Future of Zero-Width Laser Cutting
The FDP industry is estimated to reach about $218.98 Billion by 2031. It’s a massive increase compared to the $90 billion in 2007.
So, with the market rapidly growing and the demand for paper-thin gadgets ever increasing, it’s only natural that glass manufacturing companies worldwide want to move away from conventional glass-cutting methods that cause material loss and poor-quality edges.
Laser separation cutting machines (ZWLCT) are not industrialized yet, but companies are pouring revenue into their R&D to get better cutting solutions. The chip-free and reinforced cut edges, along with zero material loss, are the main attraction of zero-width laser cutting.
Sure, there are conventional CO2 laser cutting machines and mechanical cutting machines, but they have reached their potential, and there is a need for new and revolutionary technology to meet the production demand.
Conclusion
Zero-width laser cutting technology is still in the development phase, and minimal information about it is available online.
However, we’ve compiled all the available information regarding its working principle, benefits, limitations, and where you can obtain a ZWLC machine. Additionally, you can explore a comparison with conventional methods to witness the potential this technology holds.
Redefine Manufacturing: Baison Laser, Your Partner in Advanced Laser Cutting Technology!
Discover the power to transform your business with Baison – the leading manufacturer of cutting-edge laser machine systems. Trusted by companies across 100+ countries and regions, our advanced laser technology, from cutting to marking, exceeds industry standards.
Elevate your manufacturing with our expertly crafted Fiber and CO2 laser machining solutions. Gain a competitive edge with a Free Application Evaluation and comprehensive Customer Training.
Invest in Baison today and optimize your production capabilities now!