There are several reasons why hand welding is a valuable skill to learn. Firstly, it enables one to perform precise and accurate repairs on metal objects that cannot be easily replaced, such as cars or bicycles. Secondly, an individual can develop practical and artistic skills and grow personally by mastering hand welding.
This article has mentioned some of the most useful hand welding tips and techniques, along with their benefits and troubleshooting issues.
Where Are Hand Welding Techniques Used?
Hand welding involves manually attaching two or more metallic objects with a welding gun or torch.
There are many industries that use hand welding, including automotive, construction, aerospace, and shipbuilding, among others. Hand welding fabricates steel structures such as bridges and buildings in the construction industry.
Engine components and aircraft parts are repaired or upgraded utilizing this technology in the automotive and aerospace industries.

Importance of Mastering Hand Welding Techniques
It is imperative for experienced welders to master hand welding techniques as it:
- Offers a wide range of opportunities: For welders and DIY enthusiasts alike, this field offers many possibilities.
- High-quality welding: Welding that is consistent and precise produces high-quality products.
- Increases efficiency: Hand welding technique helps the welder finish their work faster and more accurately.
To maintain professional standards, you must master the hand welding technique in order to achieve accurate and efficient fabrication.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Benefits of Hand Welding
The following three reasons motivate businesses to invest in hand-welding equipment:
1. Portability
Hand welding has the advantage of allowing operators to carry the equipment, tools, and machines around. Fast jobs and repairs are possible with this level of responsiveness.

2. Cost Effectiveness & Convenience
A hand welder requires much less investment than a robot cell welder or multi-head welding machine. Furthermore, no glue, screws, or fasteners are necessary, which further reduces costs.
3. Speed & Flexibility
The hand welder is capable of achieving fast cycle times compared to existing joining methods. A full welding cycle, including cooling, can usually be completed within 5 seconds.
Techniques of Hand Welding
A variety of welding methods are available for people with varying levels of experience and for a variety of applications. Some methods of welding are limited to ferrous metals, whereas others can be used on a broader range of materials.
1. TIG Welding
In tungsten inert gas (TIG) arc welding, the welding electrode is non-consumable. This method of welding allows the welder to accurately regulate the gas flow and current. TIG welding, which is best suited to sensitive materials, can be used to join ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
If you want to make a choice between TIG and hand held laser welding, please look through the article we’ve written “Laser Welding vs. TIG Welding: Which Option is Best for You?“.

2. MIG Welding
Metal inert gas (MIG) welding utilizes solid wire electrodes and inert metal gases to create a weld. During welding, electrodes are heated and fed into welding guns. This technique of welding is the easiest weld to learn for beginners.
If you want to know the difference between MIG and laser welding, please look through the article we’ve written “Laser Welding vs. MIG Welding: Which One to Choose?“
3. Stick or Arc Welding
In the process of stick welding, a flux-coated consumable electrode is used to create the weld. This approach produces dependable welds and is effective on heavy materials. Also, this stick welding’ method is adaptable, quick to set up, and easy to utilize.
How to Prepare for Hand Welding?
We’ll now give you a thorough overview of setting up for hand welding so that all of your projects turn out well.
1. Use Different Welding Techniques
To determine which welding method best suits your needs, you should experiment with a few different methods (e.g. TIG, Stick, OR MIG welding).

2. Current Setting in Machine
Various electrode manufacturers sell numerous different electrode types, so the voltage setting will vary depending on the device you are going to utilize.
You can select multiple voltages, depending on your settings and which electrode you choose. Electrodes must be chosen in accordance with machine specifications and compatible weldability because different machine models can be welded in one mode or another.
3. Selecting Welding Accessories
You must carefully choose your welding accessories to tailor the experience. Successful welding and safety are guaranteed by welding accessories that have been set up properly.
- Power source: The first step in setting up welding equipment is to choose the best power source for your job.
- Wire feeder: Feeding wire to your gun so the weld bead is precisely placed without interrupting the welding process.
- Metal thickness gauge: Thickness gauges are used to ensure consistency across projects by adjusting settings according to material thickness.
- Safety gear: Leather aprons, gloves, earplugs, a helmet with proper lenses, and safety shoes are all essential safety items to weld securely.
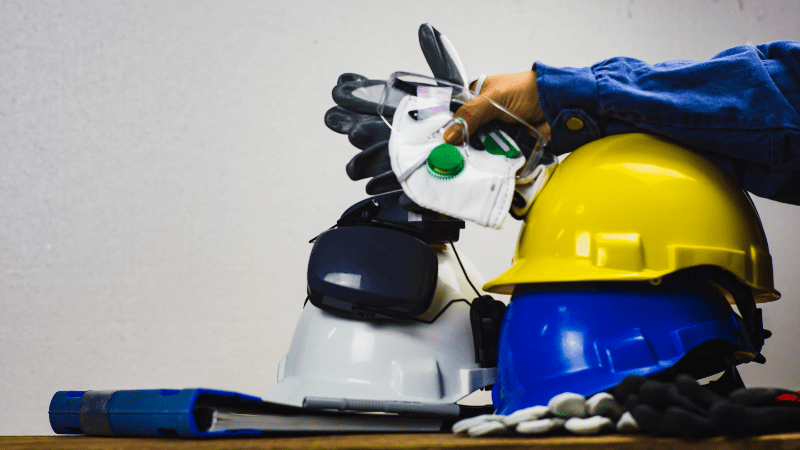

4. Preparing the Work Surface
It is crucial to prepare the work surface before hand welding. You need to consider the following things when setting up your hand-welding area:
- Ensure proper ventilation: Handwelding produces fumes that can be hazardous, so it is imperative to ensure adequate ventilation at all times.
- Clear all flammable objects: Make sure that nothing flammable is near your work area.
- Fire extinguisher: Keep one at hand in case an emergency arises.
5. Cleaning the Workpiece
When the workpiece is properly prepared, it will be less likely to warp or crack during welding. Clean welded joints to remove dirt, rust, or other contaminants that weaken future welded joints.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Basic Hand Welding Process
In gas metal arc welding (“GMAW”), a metal electrode and shielding gas are fed to the joint through a welding gun.
1. Proper Electrode and Filler Welding Rod Handling
Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) uses direct current electrodes with positive polarity. Therefore, the work clamp is connected to the negative terminal and the MIG torch to the positive terminal. The wire serves as an electrode and filler for metal during MIG welding. Moreover, metal is deposited into the joint through arc welding.
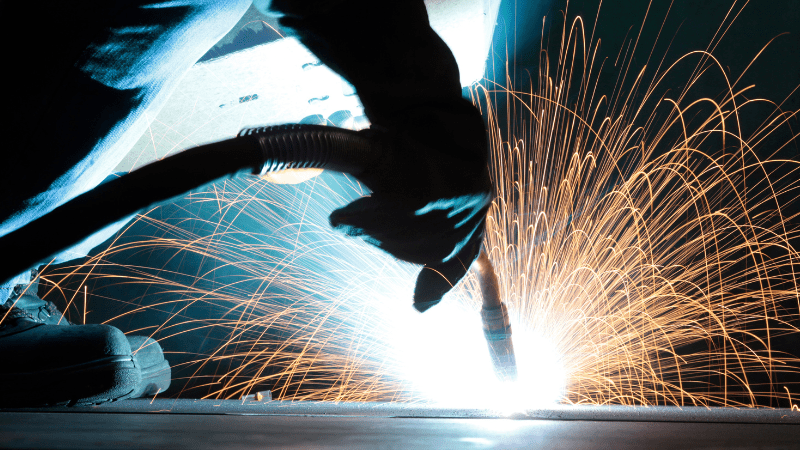

2. Establishing the Arc
Pull the MIG torch trigger and attach the work clamp to the welded piece to create an arc. An arc length is formed when a wire contacts a grounded metal, which closes the circuit and shortens it.
3. Controlling the Heat
The arc length generates heat, and a small amount of the wire’s base metal also melts. The wire feeder constantly pushes a solid wire into the joint, resulting in yet another short circuit. Here, heat control is crucial to avoid overheating. The balance of heat can be achieved through several welding techniques. In this article, we will discuss two of them:
- Electrode Force: Shift heat away from contact areas by increasing force, and shift heat towards contact areas by decreasing force. Based on where the electrical resistance is, this technique evenly distributes heat within the workpiece.
- Upslope: The upslope time should be increased to shift heat away from contact areas, and the upslope time should be decreased to shift heat into contact areas. As the weld current increases gradually at the beginning of the weld pulse, the electrodes and parts have time to sit together.
4. Maintaining a Consistent Speed
Travel speed is the speed of the torch as it moves across the surface. Insufficient thermal energy will be produced at too high speeds, resulting in weak joints, while too little speed will cause burn-through holes in thin materials.
Types of Hand Welding
I. Welding Materials of Different Thicknesses
Stick welding is a highly versatile process for welding metals of different thicknesses. Stick welding requires you to adjust your settings appropriately whenever you weld different types of metals with varying thicknesses. Generally, the thicker the weld material, the higher the heat input required.
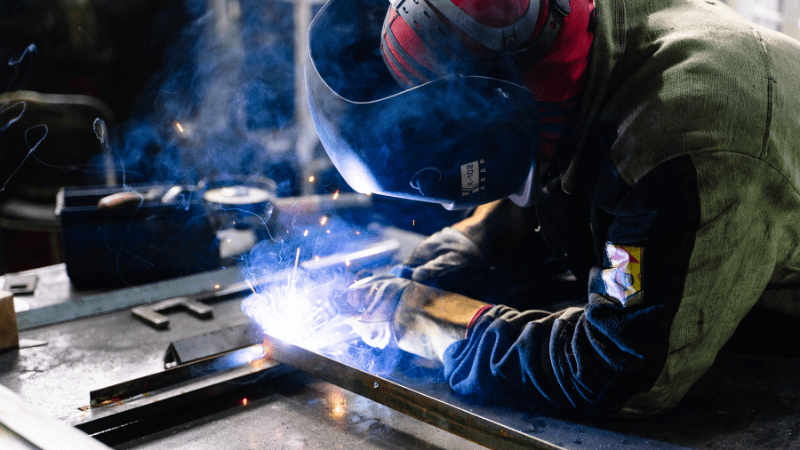

II. Welding in Different Positions
Each welding position requires a separate set of procedures, specifications, and preparations. Knowing the proper welding positions can help you choose the best filler metal used and enhance your welding technique. Welding positions can be classified into four categories:
- Flat welding position. The flat welding position is the easiest position to work in, as the joint is in a horizontal plane and the welder can work from above. This position is often used for welding large plates or sheets, and it allows for good visibility of the weld pool. To weld in the flat position, the welder typically uses a drag or backhand technique, moving the welding torch along the joint in a straight line.
- Horizontal welding position. The horizontal welding position is used when the joint is in a horizontal plane, but the welder must work from the side. This position is often used for welding pipes, and it can be challenging because gravity can cause the weld pool to sag or drip. To weld in the horizontal position, the welder typically uses a weaving technique, moving the welding torch back and forth along the joint in a zigzag pattern to build up the weld.
- Vertical welding position. The vertical welding position is used when the joint is in a vertical plane, and the welder must work from the bottom up. This position is often used for welding beams or columns, and it can be challenging because gravity can cause the weld pool to run down the joint. To weld in the vertical positions, the welder typically uses an uphill technique, moving the welding torch upwards along the joint to prevent the weld pool from running down.
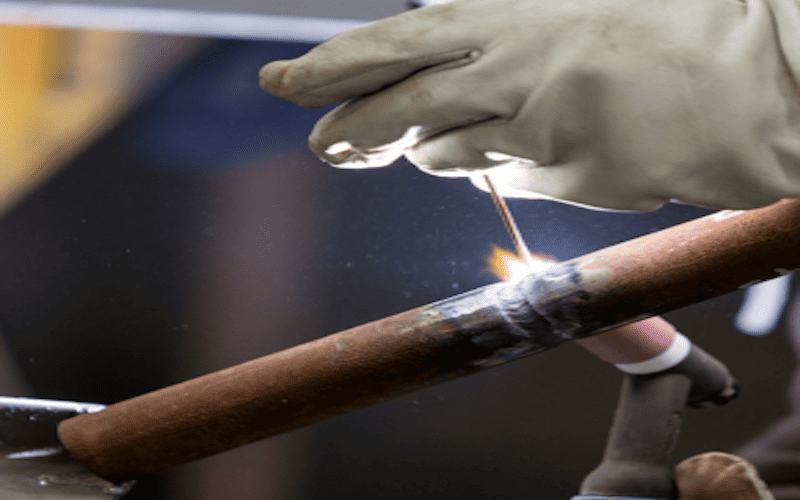

- Overhead welding position. The overhead welding position is used when the joint is above the welder, and they must work from below. This position is often used for welding the underside of bridges or other structures, and it can be challenging because gravity can cause the weld pool to drip or fall onto the welder. To weld in the overhead position, the highly skilled operator typically uses a backhand technique, moving the welding torch along the joint in a straight line while keeping a close eye on the weld pool to prevent any drips or sagging.
III. Welding Dissimilar Metals
A process of welding that connects materials composed of different alloys is known as dissimilar welding. The welder typically uses fusion welding to join dissimilar metals.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Troubleshooting Common Hand Welding Problems
You’re likely to encounter some difficulties learning hand welding. Here are some of the most common weld defects you may encounter:
1. Porosity
The porosity nature of weld pools is created by absorbing air elements while they are still molten. After the metal solidifies, these gases become trapped, causing holes in the weld. That is why it is imperative to clean the surface area before welding thoroughly. You should also look for any leaks in the gas supply.
2. Cracks
A crack may not appear right away, and it may take days, months, or years for the metal to crack. Cracks in welds can’t be filled in by simply filling them. If you want to repair the weld, you must remove that part of it, or the entire weld, and start over.
3. Burn-through
Basically, burn-through is the process of burning through metal and leaving a hole, or in more extreme cases, a protruding filler on the other side.

Techniques for Finishing and Post-Welding Clean-Up
An effective welding operation relies on proper cleaning. Some of the techniques are given below.
1. Polishing: Electropolishing is an effective technique for cleaning stainless steel following welding. Besides post-welding cleaning, the process is also useful for cleaning metal surfaces of rust, cross-contamination, and other impurities.
2. Cleaning: Chemical welds are most commonly cleaned with “pickling paste ”. Metal surfaces contaminated with rust, stains, and heat tint scales can be easily cleaned with this technique.
3. Inspecting the welds: The process of inspecting welds involves checking for quality, strength, safety, and other factors. Welding inspectors look for undercutting, porosity, and lack of fusion, which can all weaken a weld’s strength if ignored.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Conclusion
Hand welding requires patience and practice but can be successfully accomplished if you follow the various welding tips and techniques in the article above. Safety should always be the first priority when starting any project! With the advanced ideas and techniques presented in this article, you should be able to develop further and improve your hand welding skills significantly.
Welcome to Baison Laser – Your Trusted Solutions Provider for Fiber Laser Systems
Boost your productivity and efficiency today by partnering with Baison Laser for cutting-edge fiber laser systems that deliver unmatched results.
Are you looking for laser equipment that will enhance your production processes and add unparalleled efficiency to your manufacturing operations? Then, look no further than Baison Laser – the ultimate provider of top-tier fiber laser systems designed with durability at heart.
We have perfected the art of creating laser machines that enable you to easily craft precise, consistent, and intricate designs for various materials. Our products boast exceptional durability, low maintenance requirements, and unmatched performance, making them the ideal investment for businesses of all sizes. You can get free sample proofing from us!