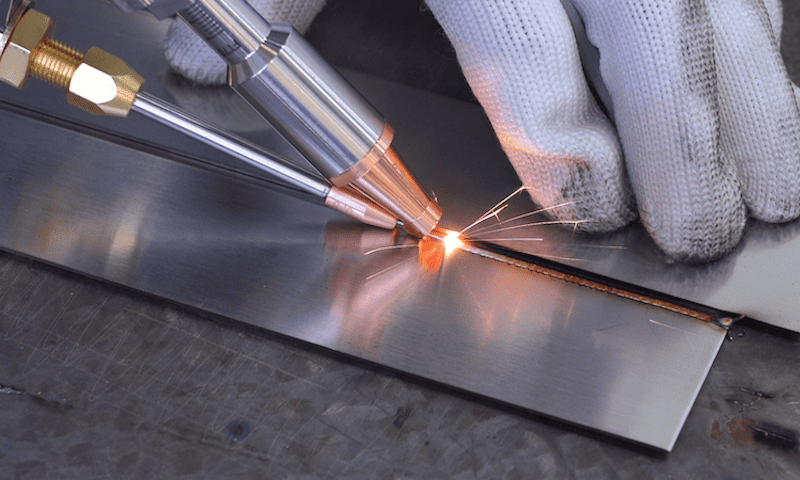
An in-depth understanding of wire feeding allows you to create your desired weld characteristics. In this blog post, we’ll share the basics of wire feeding in laser welding. You’ll also explore the problems associated with wire feeding and their solutions.
Basics of Laser Welding
Laser welding is a precise welding technique that employs highly focused laser beams for joining metal workpieces. A laser source creates a high-energy laser beam directed at the spot between workpieces you want to weld.
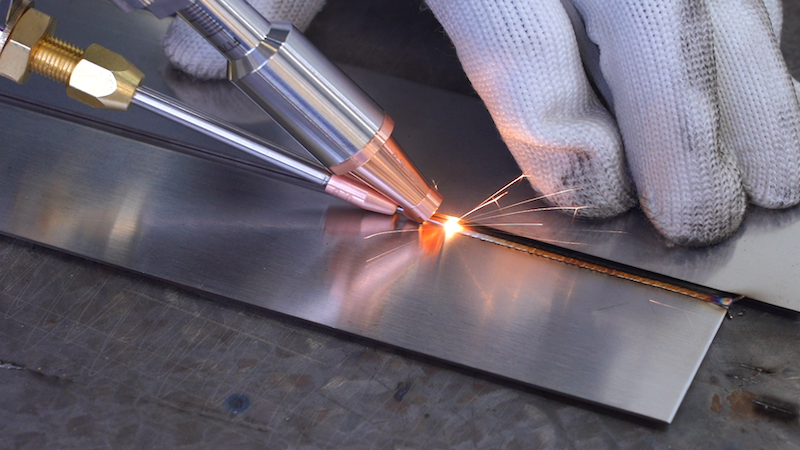

According to Academia, the laser beam creates a localized heat buildup that melts the metal. The molten metal fuses the two workpieces, creating a strong weld.
Several types of laser welding processes are employed today. The following are some common laser welding methods that involve wire feeding:
1. Deep Penetration Welding
This laser welding process is utilized for welding thicker materials and creating strong welds. It employs a high-power laser beam to achieve deep weld penetration. The high-powered laser beam vaporizes the material, creating a cavity referred to as a keyhole. The keyhole penetrates within the workpieces, resulting in a thicker weld. A molten filler is added to the trailing edge of this hole for weld formation.
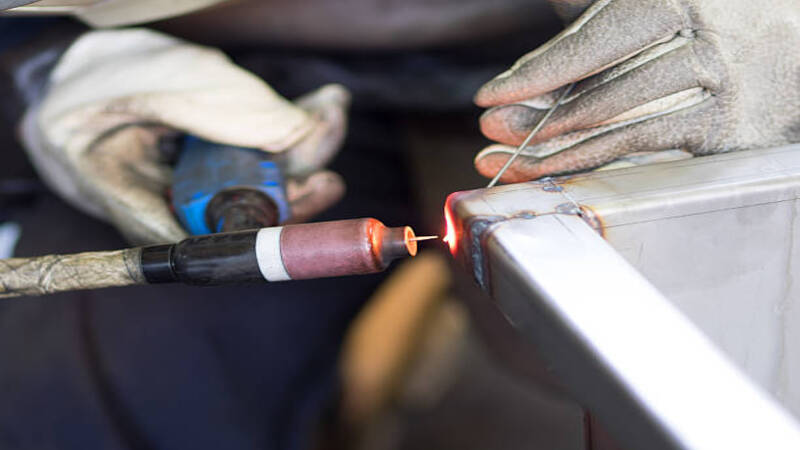

2. Laser Seam Welding
This laser welding approach creates a continuous welding seam between two metal workpieces. A high-energy laser beam melts the filler rods to make fillet joints using controlled motion. Continuous welds add strength to the final product as the laser beam moves along the workpieces.
3. Hybrid Welding
This welding process combines laser welding technology with MIG or TIG techniques. The combination of advanced and traditional approaches helps you create a robust weld. The laser offers sufficient energy to heat the metal, and the MIG and TIG processes supply the filler metal. This approach offers you the advantages of both types of welding.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Understanding Wire Feeding in the Laser Welding
Wire feeding refers to the intricate process of accurately positioning a metal wire relative to a laser beam for adding filler during welding. Wire feeding speed is also a crucial aspect of this process. A laser beam heats the metal wire, transforming it into a liquid state. This molten metal serves as a filler metal during welding, filling the contact point between the two workpieces.
1. Material Selection
Selecting the right welding wire material is crucial for smooth wire feeding. Compatibility of the wire with the base material is necessary in this process. Different materials have variable metallurgical and thermal characteristics. If the material of the wire is not compatible with the base material of the workpieces, you’ll be left with a weak weld.
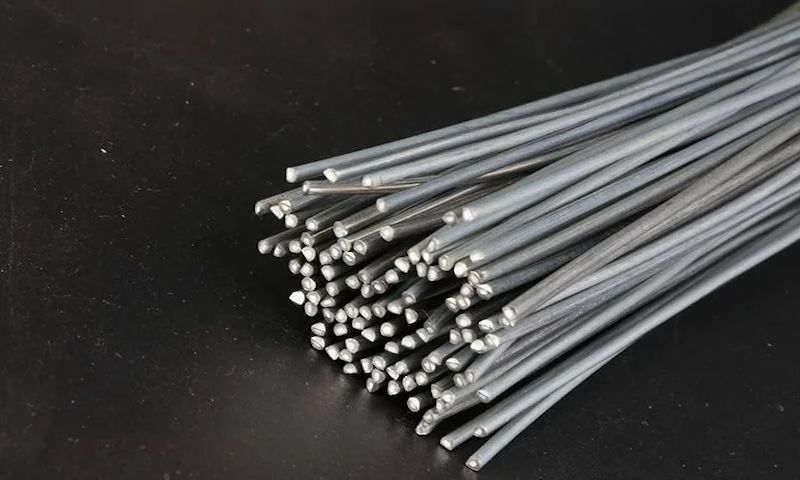

The following two types of wires are used for laser welding.
- Hard wires are used for wire-feeding various metal pieces, making it a versatile choice. Stainless steel and silicone bronze are commonly used hard wires. Stainless steel is used in applications where you have to weld various materials.
- The other type of wires are soft wires. Aluminium is a commonly used soft wire for welding materials using a handheld laser welding machine. It is used for materials having the same properties as aluminum.
2. Wire Diameter

Wire diameter is another significant factor influencing laser welding. It impacts the size of the weld pool generated by laser welding equipment. It also affects the overall quality of the weld.
While choosing the wire diameter, you need to consider the gap you want to fill. Deep and wide gaps require thicker wires to fill them. Thin wires might take too long to feed metal pieces with larger gaps. You can employ thin wires to fill small spaces precisely and create intricate welds between metal workpieces.
2 Different Wire Feeding Technologies
Two types of wire-feeding technologies are used to weld metals using laser welding machines. One is hot wire feeding, and the other is referred to as cold wire feeding. Here is an overview of the two wire feeding methods.
1. Hot Wire Feeding
This type of wire feeding technique utilizes a heated filler wire. A customized power supply heats the wire. The power supply is controlled and heats up the wire to a particular temperature to facilitate the welding process. It also prevents the wire from transforming into the arc. The heat from the laser beam melts the wire. Combining two heat supplies improves the welding results, offering you a localized weld.
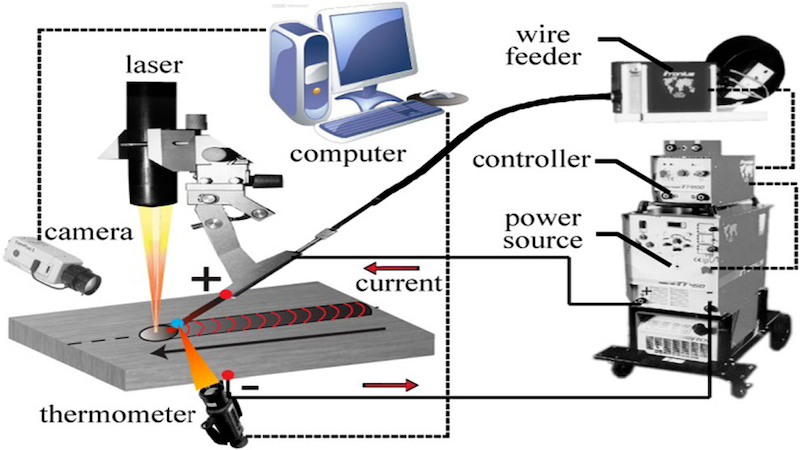
Hot wire feeding offers better deposition of the weld on the required spot. It involves lower heat input that minimizes the distortion of the weld. These factors help improve the weld quality.
2. Cold Wire
Cold wire doesn’t involve a preheating of the filler wire. It relies only on a laser beam to provide energy for heating as well as melting the wire. Wire feeding using a cold wire is time-consuming as the filler wire needs more energy to reach the melting point than a hot wire.
However, handling a cold wire is easier. It allows you to work with heat-sensitive materials for wire feeding conveniently. You can also wire feed components that are prone to distortion.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
How Does Wire Feed Affect Weld Quality?
Wire feeding is a prominent technique in fiber laser welding as well as traditional welding methods. It influences the weld formation. Here is an overview of how it affects the weld quality:
1. Enhancing Joint Fit-Up Tolerance
Joint fit-up refers to the accuracy in the alignment of welded components. The welding process often leaves air gaps between the workpieces. Sometimes, welding results in mismatched components that deteriorate the structural integrity of the product.
Wire feeding has a major role in improving the joint fit-up of welded components. You can have better control over the weld pool by precisely feeding the wire between the metal workpieces.
2. Preventing Solidification Cracking
Whether you are using laser beam welding or shielded metal arc welding, the risks of solidification cracking remain a major concern. According to Nature, it is a defect that significantly influences the structural integrity of the weld.
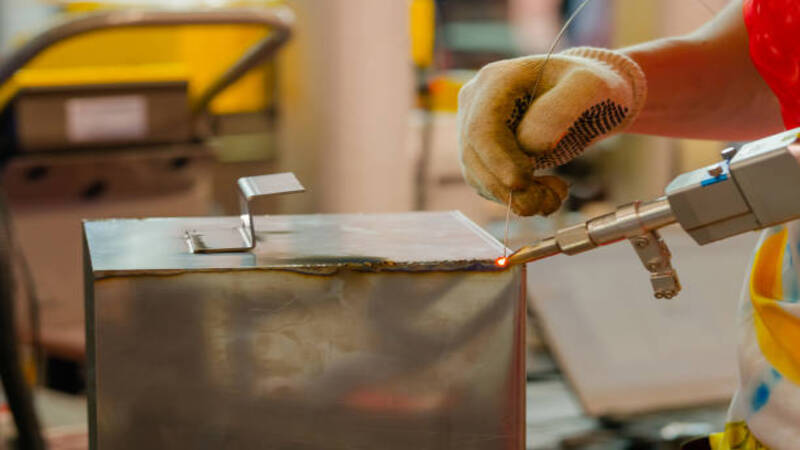

Choosing the right material for the filler wire and controlling the speed of the wire feed enables you to eliminate the chances of solidification cracking. Accurate wire feeding also boosts the mechanical properties of the welded components, improving the durability of the end product.
3. Improving Weld Profile
The weld profile is a major contributor to the structure of the welded workpieces. Wire feeding offers filler material that creates the weld bead.
Perfectly feeding wire impacts the precision in the deposition of the weld bead. It also eliminates the undercuts from the weld bead, reducing the stress and improving the external geometry of the weld. Moreover, it boosts the mechanical properties of the weld, giving you a better-quality product.
The Setting of Wire Feed Parameters
Setting of wire feed parameters can significantly impact the quality of the welding. The following are some crucial parameters of wire feeding and their setting:
1. Wire Feed Rate
The wire feed rate for a particular air gap between two workpieces. It controls the deposition of filler wire between the air gap. It depends on the welding speed and the cross-section area of the gap between the joint face. It is also influenced by the cross-sectional area of the filler wire.
Wire feeding limits the welding speed as a significant amount of laser energy is used to melt the wire. Too low a wire feeding rate affects the wire and the workpieces you are welding. The laser beam might melt a larger section of the wire. It damages the liquid metal bridge and results in a drop formation at the end of the filler wire. It deteriorates the appearance and the integrity of the weld.
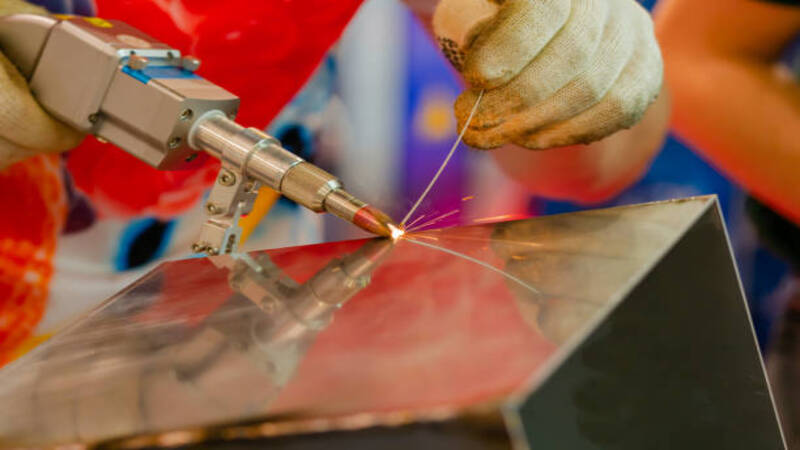

On the other hand, too high a wire feed rate results in insufficient energy supply for melting. It increases the volume of liquid metal in the liquid metal bridge and at the end of the wire. Moreover, the non-melted wire piece might also enter the weld pool and push out the liquid metal. It results in hump formation on solidification. It can also lead to porosity at the depth of the weld.
A precise balance of wire feed rate is necessary to ensure deep penetration of filler wire. You need to maintain a moderate welding speed to ensure deep penetration of filler wire. A precise balance of wire feed rate is also required for the creation of the right bead height.
2. Laser Beam-Filler Wire Interaction
The interaction between the laser beam and the filler wire is another considerable parameter that influences wire feeding in several welding techniques. Exposing a short length of wire to a laser beam results in the melting of the desired material. It also limits the melting of wire at the initial exposure point. It ensures effective deposition of the filler wire in the air gap.
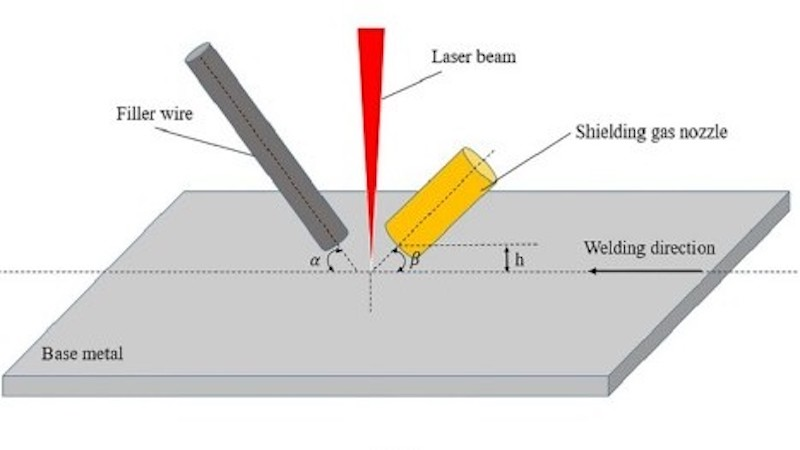
However, if a long wire is exposed to the laser beam, the extended end is excessively melted, leading to inconsistent weld bead formation. In extreme scenarios, exposure to long wires can disturb the shielding gas.
3. Delivery Angle
For accurate wire feeding during laser welding, angles between 30 and 60 degrees from the perpendicular are most suitable. An angle of 45 degrees is the best for simplifying the setting. However, angles greater than 60 degrees and lesser than 30 degrees make the setting complicated.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
3 Types of Wire Feeders for Laser Welding
The following three types of wire feeders are commonly used for laser welding:
1. Basic Wire Feeders
These feeders have a main control for managing the wire feeding rate. Basic feeders employ a two-roll drive system, which is designed to work with 2 to 3-meter-long welding guns.
Some basic feeders also have a four-roll drive system for working with welding guns that are longer than 3 meters. Their motor is not powerful enough and is suited for feeding short wires with small diameters.
2. Intermediate Wire Feeders
Intermediate wire feeders come with four-roll drive systems, offering better grip and work with larger wires than a simple two-roll drive system. They are employed for longer welding guns. You can work with up to 6 long guns with this feeder.
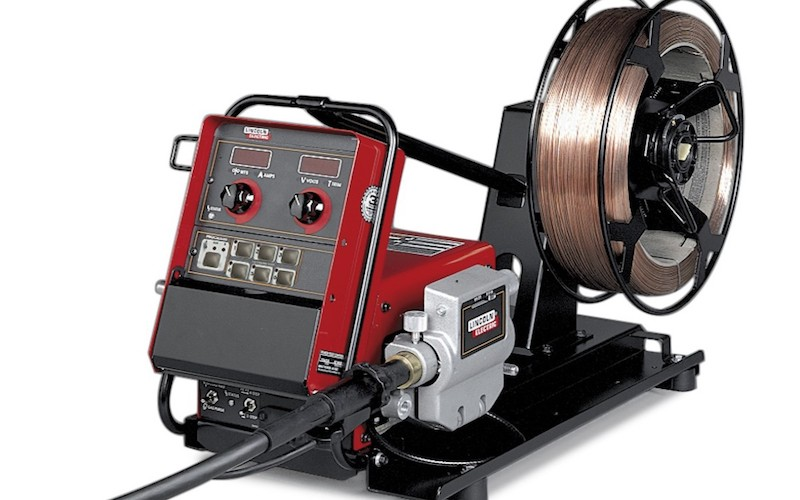

3. Advanced Wire Feeders
Advanced wire feeders are designed to give you maximum control over the wire feeding process. They have enhanced displays that enable you to view and adjust various settings. They can handle complex manufacturing tasks and multiple materials at once.
Common Problems and Solutions
The following are some common issues with wire feeding and their solutions:
- Wire feeders are crucial for smoothly feeding wire. However, a malfunctioned wire feeder can lead to poor wire feeding. To prevent issues with wire feeders, you need to clean and lubricate them regularly.

- Inaccurate size of drive rollers also results in uneven wire feeding. Use the right size and style of drive rollers to feed the wire effectively.
- Contact tips wear down over time. Debris and dirt on contact tips also lead to several issues during wire feeding. Regular maintenance of the contact tip can facilitate the wire-feeding process.
FAQs
1. What is a wire feeder in welding?
Wire feeders are specially designed instruments for adding filler material to fill the air gap between the workpieces.
2. How is the welding wire fed to the welding gun?
The welding wire is fed to the welding gun via a wire feeder. The wire feeder pulls the filler wire from the spool through a cable into the welding gun.
3. What happens to the welding current if you increase the wire feed speed on the welding controller?
As you increase the wire feed speed on the welding controller, the power source will deliver more welding current.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Conclusion
Wire feeding is a crucial aspect for precisely welding various types of workpieces. However, this process requires various considerations for desired weld characteristics. Choose the right material and diameter of the wire to fill the air gap accurately and have a robust weld.
Moreover, having a reliable laser welding machine is also necessary. Baison Laser offers you a durable laser welding machine and other laser solutions, including laser cutting, marking, and cleansing machines.
Start Wire Feeding in Laser Welding with Baison Laser!
With the increasing usage of laser welding technology, various laser welding machines are available today. Choosing the right laser welding machine impacts your projects. Baison Laser offers you the best laser welding machines. Contact us today to learn about our latest laser solutions. Our team will help you get the right laser welding machine for your needs.