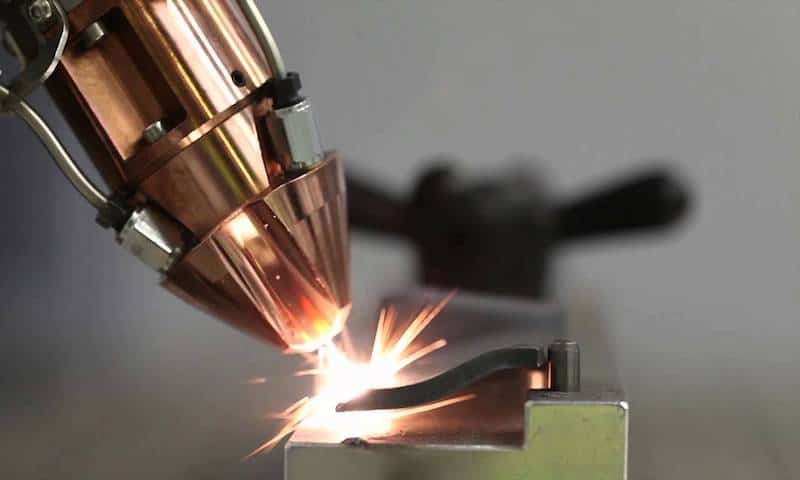
Copper has unmatched electrical conductivity and resistance to corrosion. Yet, when it comes to welding, this wonder metal can be a difficult thing to handle. Its high thermal conductivity and reflectivity make it more tricky to join using traditional methods. Laser welding presents a powerful solution to these issues, unlocking the potential of copper with its precise heat control and focused energy.
In this article, we will go through the challenges posed by this unique metal, explore the most effective laser welding methods, and equip you with the knowledge to achieve high-quality, reliable welds. So, grab your safety glasses and laser pointer; it’s time to conquer the red metal!
The Challenges of Copper Welding
Copper comes with excellent laser energy for electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Because of these qualities, copper finds itself in various applications across industries. However, when it comes to laser welding, this versatile metal throws its own set of challenges due to its unique physical and chemical properties.
1. Thermal Conductivity
Copper has the highest thermal conductivity among other engineering metals. Heat applied for welding evaporates rapidly throughout the material which makes it difficult to localize the heat required to form a strong weld pool. This can lead to incomplete fusion, weak welds, and increased susceptibility to cracking.
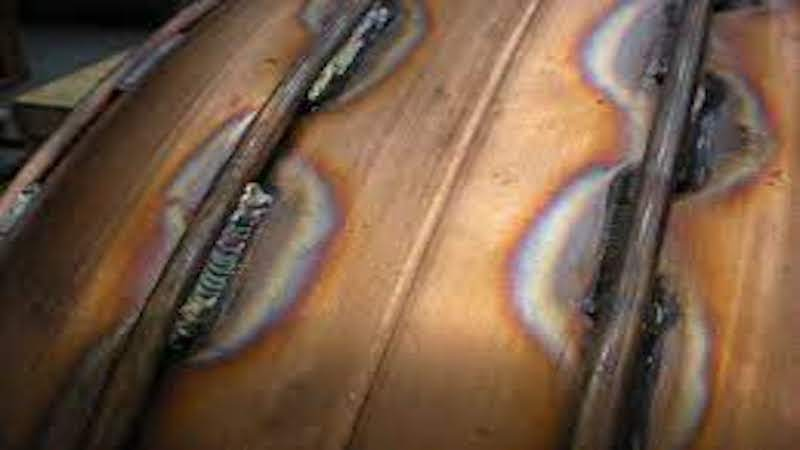

2. Reflectivity
Copper also has high reflectivity and high-quality weld seams, which can lead to another layer of complexity while using it. The laser beam bounces off the surface and reduces the amount of energy absorbed by the metal. This necessitates higher laser power, which can further exacerbate the heat evaporation issue and lead to weld copper defects like porosity and spatter.

3. Oxidation
Copper readily forms oxides at high temperatures, posing a significant challenge during welding. These oxides can contaminate the weld, weaken its mechanical properties, and introduce inclusions that disrupt the weld integrity. If you want to avoid this problem, you may need to be more careful with shielding techniques and flux selection.
Besides these key properties, many other factors contribute to the difficulty of welding copper. Its high coefficient of thermal expansion can lead to warping and distortion during welding. Additionally, the limited availability of suitable filler metals for copper welding can add to the challenges of copper welding.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Overview of Laser Welding Technology
Laser welding technology utilizes a focused beam of light to melt and fuse materials while offering unmatched precision, speed, and versatility. Unlike traditional methods, it generates minimal heat, minimizes distortion, and enables delicate welds on thin materials.
This process welds various metals, plastics, and even some ceramics. From conduction welding for thin sheets to deep penetration welding for thicker components, laser technology is involved in diverse applications across industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. Its automation capabilities and consistent quality make it a game-changer in modern manufacturing.
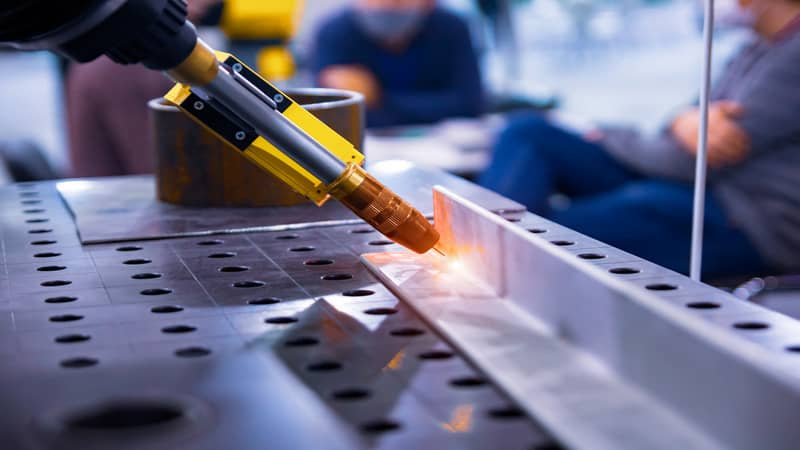

4 Benefits of Laser Welding Copper
Laser welding has emerged as a preferred technique for joining copper components due to its numerous advantages over traditional methods like arc welding or soldering. Some of the major benefits are given below:
1. High-Quality Welds
Precise energy delivery of the welding process creates clean, strong welds with minimal heat distortion.
2. Deep Penetration Welding Process
The focused laser beam of laser welding achieves deeper weld penetration compared to traditional methods. It is also famous for enhancing joint strength and resistance.

3. Heat Conduction Welding Process
Localized heating of copper welding minimizes heat-affected zones, which can reduce warping and cracking.
4. Improved Conductivity
The welding process of copper helps to promote precise control and inert gas shielding. At the same time, it can prevent oxidation and maintain copper’s excellent electrical conductivity in the weld zone.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Which Laser Welding Method is Best for Copper?
Determining the best laser welding method for copper depends heavily on customer preferences and requirements. Some of the methods that are best for copper welding are given below:
1. Continuous Wave (CW) Laser Welding
Among other laser welding processes, continuous wave laser welding works with deep penetration welds in thick copper sections. Unlike other laser techniques with their intermittent bursts, CW lasers deliver a continuous beam of energy and a steady stream of light.

Advantages:
- Delivers consistent heat input.
- High welding speed and efficiency.
- Good control over weld depth.
Disadvantages:
- Requires careful control of power to avoid excessive heat input and distortion.
- It may not be suitable for thin sections due to high heat penetration.
2. Green Diode Lasers
Green diode lasers are best for joining thin copper sheets, microwelding, and additive manufacturing. Instead of the broad wavelengths of traditional lasers, they emit concentrated green light, perfectly compatible with copper’s welding technique.
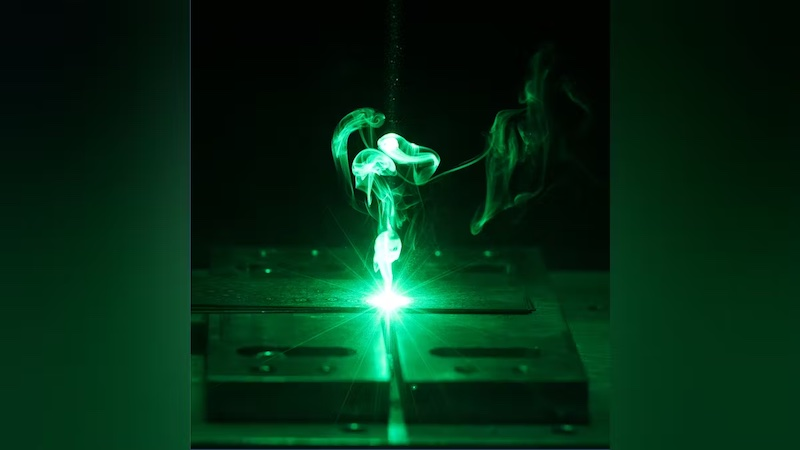

Advantages:
- Excellent absorption by copper due to the shorter wavelength (around 515 nm).
- Reduced heat input compared to traditional infrared lasers, which minimizes distortion and spatter.
- Precise control over weld size and heat-affected zone.
Disadvantages:
- Limited power compared to other laser types.
- Relatively new technology.
- Higher equipment cost.
3. Fiber Lasers
Fiber lasers have emerged as powerful contenders, offering a versatile and efficient solution for welding copper. These lasers work best for versatility across various copper thicknesses and applications.

Advantages:
- High power and beam quality.
- Suitable for both thin and thick sections.
- Flexible wavelength options (915 nm, 1064 nm) can be tailored to specific copper alloys.
- Compact and efficient design.
Disadvantages:
- Shows a lower absorption rate in pure copper.
- Requires careful parameter optimization to avoid heat-related issues.
4. Blue Laser
By using the laser power of a blue laser, you can easily weld copper. Usually, blue lasers are ideal for applications like battery tabs, electronics, and heat exchangers. It is also used in delicate components like medical devices and sensors.

Advantages:
- Blue lasers have lower power requirements and less heat generation because of their wavelengths being between 360 and 480 nanometers and their 65% absorption in copper.
- Blue lasers enable heat conduction welding and focus heat on a small area, ultimately minimizing the heat-affected zone (HAZ).
Disadvantages:
- While blue lasers are rapidly evolving, their power levels are still lower. This may limit their use in thicker copper sections.
- Blue lasers are generally more expensive compared to other lasers.
5. Infrared Laser
Infrared laser is famous for joining delicate components like wires and circuits in smartphones, sensors, and printed circuit boards. They are also used for welding battery tabs, busbars, and heat exchangers for electric vehicles. Besides, the infrared laser can be used for fabricating lightweight and robust structures for aircraft and spacecraft.

Advantages:
- Compared to newer laser technologies, Infrared lasers offer a more budget-friendly option for copper welding.
- Infrared laser welding is a well-established technology with a mature infrastructure and readily available equipment.
- Infrared lasers can be adapted to various welding techniques, including conduction, keyhole, and deep penetration welding.
Disadvantages:
- The high heat input can lead to spatter and porosity in the weld.
- This process requires more cleaning and potentially impacting joint strength.
- The larger HAZ and potential for distortion make Infrared lasers less ideal for high-precision welding of thin copper sheets.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Preparation for Laser Welding Copper
Laser welding offers superior results for copper compared to traditional methods, but proper preparation is important for success. Here is a detailed guide to ensure your copper parts are ready for a strong and clean weld:
I. Cleaning
- You must eliminate all surface contaminants like oils, greases, oxides, and dust. As they can hinder laser absorption and welding quality.
- You must consider abrasive cleaning methods like grit blasting or wire brushing to remove oxides and achieve a slightly roughened surface.
- For sensitive components or post-mechanical cleaning, you may need to use pickling solutions like sulfuric acid or citric acid to remove the remaining oxides.

II.Fit-up and Jigging
- You will have to ensure tight joint fit-up with minimal gaps (ideally < 0.1mm) to optimize laser penetration.
- You must employ robust jigs and fixtures to hold parts firmly in place. It can prevent movement and distortion during welding.
III.Joint Design
- You will have to aim for a V-groove angle between 45° and 60°. Wider angles require less filler metal but offer shallower penetration.
- For thicker sections, consider double-V grooves or J grooves for deeper penetration.
- Maintain a consistent and minimal gap (0.1-0.3mm) along the joint to ensure proper molten metal flow and avoid excessive spatter.
Tips for Successful Laser Welding of Copper
Copper poses unique challenges due to its high reflectivity and thermal conductivity. However, with the right techniques and parameter choices, successful laser welding is achievable. Here are some key tips:
- You must ensure the welding surfaces are free of oxides, oil, and other contaminants. This improves laser absorption and weld quality.
- Preheating the material slightly can reduce initial reflectivity and improve energy absorption.
- You must select a laser wavelength with high absorption by copper. Green lasers (532 nm) are commonly used, but diode lasers (808 nm, 940 nm) can also be effective with specific techniques.
- You will have to use relatively high peak power and short pulses to minimize heat-affected zone (HAZ) and improve weld depth.
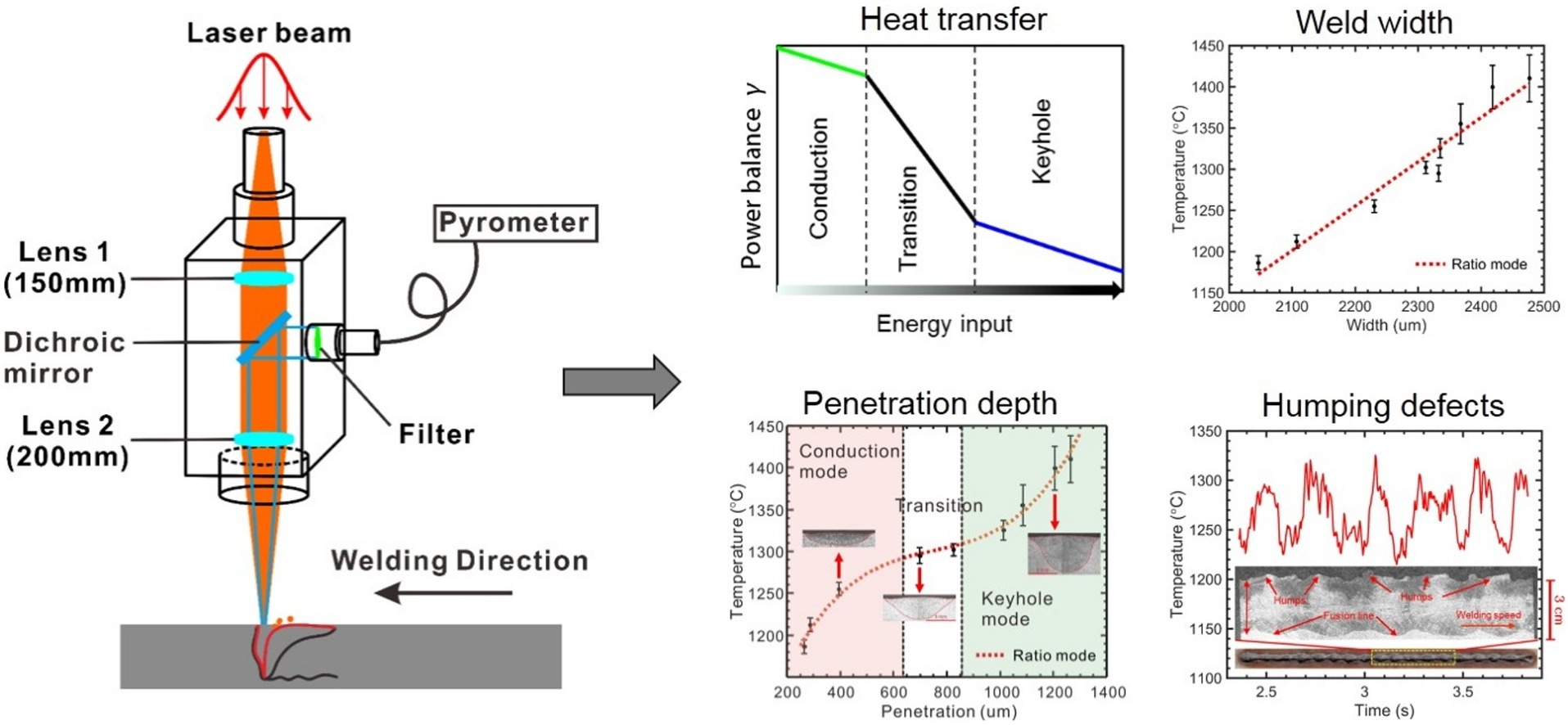
- You must use inert gas like argon or helium to minimize oxidation and plasma formation, further reducing reflectivity.
- You must use a backing material to absorb heat and prevent melt-through.
- Try to optimize travel speed to balance weld penetration with solidification rate and prevent defects like porosity.
- It would be better if you could consult with experienced laser welding professionals for specific material, application, and equipment guidance.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Common Issues and Solutions in Copper Laser Welding
Copper’s unique properties present specific challenges during laser welding. Here are some common issues and potential solutions:
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|
Application of Laser Welding of Copper
The potential applications of welding copper are constantly expanding. Some of the major applications are given below:
| Industry | Application | Benefits |
|---|
FAQs
1. What Is Required for Laser Welding?
The laser welding process makes laser light which is then directed toward an optical head. Afterward, it results in a limited melt pool and intensely confined heat buildup.
Usually, a solid-state, fiber, or CO2 laser generates the laser welding beam. The metal melts at the focus point of the beam and forms a confined pool.
2. How Much Heat Does Laser Welding Produce?
Deeply piercing the material, the laser beam warms the surface to the point of vaporization. This produces a keyhole in a state similar to plasma. The mercury crosses the 10,000K mark. This kind of welding uses a high-power laser that produces more than 105W/mm2.
3. Can Laser Cut Through Copper?
CO2 technology made it challenging to laser cut delicate materials like copper and brass because of their reflecting qualities. With the advancement of fiber laser cutting technology, we can now laser cut copper up to 12 mm and brass up to 15 mm without burrs or flaws.
Do You Have Any Questions?
Let Us Solve Your Problem
Conclusion
While copper has impressive properties, its unique nature throws down some complications. By understanding the hurdles posed by its thermal conductivity, reflectivity, and oxidation susceptibility, you can easily utilize the power of laser technology to achieve robust and reliable copper welds.
You will need to consider meticulous joint preparation, proper shielding gas selection, and optimized parameters, which will be some important allies in your welding journey. By mastering these elements, you can transform the challenges of copper welding into opportunities to create high-quality, lasting connections.
Find the Perfect Laser Welding Machine for Deeper Penetration and Cleaner Welds!
If you want to experience a smooth and comfortable laser welding experience, you will need to get the best laser welding machine. In Baison, we offer the best quality laser welding machines for copper at the most affordable prices.
You can choose the laser welding machine according to your preference with the help of our expert insights and practical tips. Feel free to send us a message and you can get a quote!





