Are you struggling to decide between laser cutting and flame cutting for your next project? Choosing the right cutting method is crucial to ensure precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. But with so many factors to consider, it can be overwhelming.
That’s why we’re here to help! We’ll discuss the importance of selecting the appropriate cutting method based on your project requirements and delve into key factors that should influence your decision-making process. Get ready to make an informed choice that aligns perfectly with your needs.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a technology that uses high-powered laser beams to cut precise patterns, shapes, and designs in various materials. Laser systems are known for their accuracy, speed, and efficiency in manufacturing and creative industries.
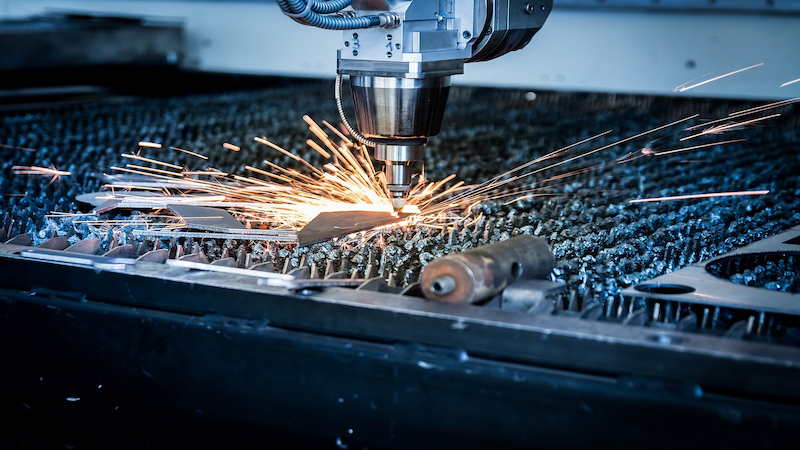

How Does Laser Cutting Work?
- Creation of the Design: The first step in laser cutting is designing the end product. This design is typically created using specialized software, usually CAD (Computer-Aided Design). The digital blueprint serves as the guide for the laser, ensuring precision and accuracy.
- Transmission of the Design: Once the design is ready, it’s sent to the computer system of laser cutting machines. The operator sets up the machine, configuring the parameters like power, speed, and frequency of the laser for the specific material used.
- Laser Cutting Process: The laser cutting machine works by directing a high-power laser beam at the material intended for cutting. The beam melts, burns, or vaporizes the material, resulting in a sharp, precise edge with high-quality finish. The laser’s path is controlled by the computer, following the previously configured design.
- Ejection of Cut Pieces: After the cutting process, the machine disposes of any excess material (often through a vacuum system), leaving behind the finished pieces. These pieces are then cleaned and inspected for quality before proceeding to the next steps in the production process.
At the core of how laser cutting works is the concentration of high energy into a beam, capable of cutting through materials like steel, plastic, fabric, and wood with incredible precision. This technology is favored for its accuracy, efficiency, and the minimal waste it produces, making it a sustainable choice for various industries.
Types of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a versatile and precise method used in various industries. There are different types of lasers used for cutting, each with its own advantages and suitable applications.
1. CO2 Lasers
CO2 lasers are widely used for general-purpose cutting. They work by emitting a high-powered beam of infrared light that is absorbed by the material being cut. This absorption causes the material to heat up and vaporize, resulting in a clean and precise cut. CO2 laser cutters are known for their versatility and can effectively cut materials such as wood, acrylic, paper, fabric, and more.
2. Fiber Lasers
Fiber laser offers high-speed cutting capabilities with excellent energy efficiency. These lasers use optical fibers to deliver the laser beam directly to the cutting head. Fiber lasers are particularly effective at cutting thin metals like stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. They provide faster cutting speeds compared to other types of lasers while maintaining high precision.
Maybe you want to know how fiber laser and CO2 laser technology compare.
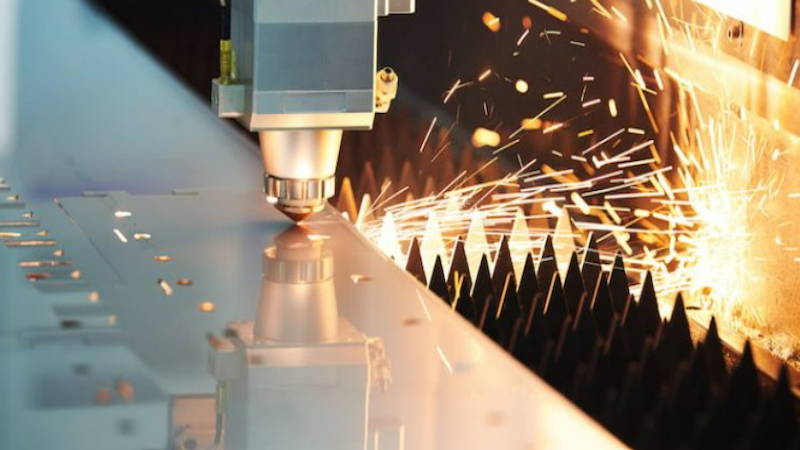

3. Nd: YAG Lasers
Nd: YAG lasers (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet lasers) are commonly used for precision cutting of thin materials or intricate designs. These solid-state lasers produce a concentrated beam of light that can be focused on small areas with great accuracy for cutting purposes. Nd: YAG lasers are often utilized in industries such as jewelry making, electronics manufacturing, and medical device production.
For the choice of YAG laser and fiber laser read this article.
Each type of laser has its own strengths and limitations. For example:
- CO2 laser cutters excel at cutting thicker materials but may struggle with highly reflective materials.
- Fiber laser cutting machine offers exceptional speed but may not be ideal for thick metals.
- Nd: YAG lasers provide precise cuts but may have limited power output compared to other types.
The thickness of the material affected by different lasers is different, which you can learn more about from this article.
What is Flame Cutting?
Flame cutting, also known as fuel cutting or torch cutting, is a process that involves the use of a combination of fuel gas and oxygen to create a controlled flame. This flame is then directed onto the material to be cut, melting away the metal in its path.
The flame cutting process is primarily used for heavy-duty industrial applications that require cuts on thick metal plates. It can handle various types of metals, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloys.
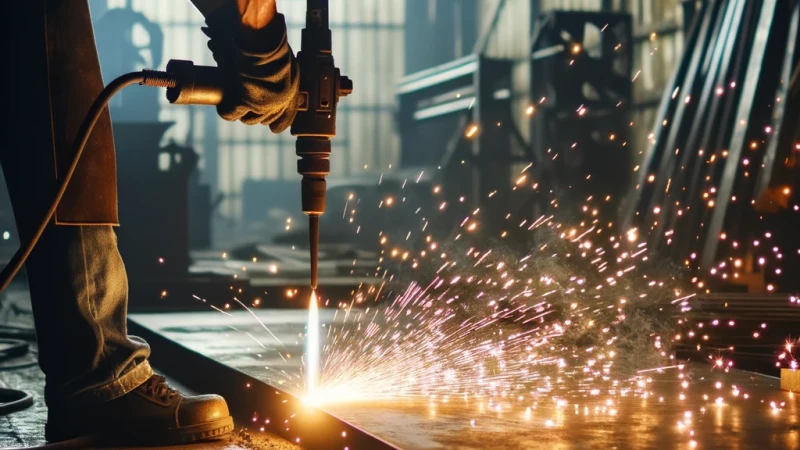

How Does Flame Cutting Work?
The flame cutting process begins with the heating of the material to its ignition temperature using a fuel-gas flame (common gases include acetylene, propane, or natural gas). This is the preliminary step that prepares the metal for the actual cutting process.
- Preheating the metal: Initially, a flame is used to heat a specific area of the metal to its kindling point, the temperature at which the metal will readily react with oxygen in a self-sustaining chemical reaction.
- Oxygen jet: Once the appropriate temperature is reached, a concentrated stream of pure oxygen is directed at the heated area. The oxygen reacts with the metal, forming iron oxide and producing more heat, which further intensifies the reaction. This exothermic reaction between the oxygen and metal continues until the way through the material is completed, or the oxygen stream is stopped.
- Cutting through the material: The heightened temperature and chemical reaction between the metal and oxygen create a narrow cutting kerf, removing the oxidized metal by the force of the jet — effectively separating the metal where the reaction is occurring. The quality and precision of the cut depend on several variables, including the speed of cutting, the preheating temperatures, and the oxygen stream’s purity and focus.
If you want to know how to use torch cutting, we also found out operational approach for you.
Flame cutting machines are particularly suitable for high-thickness materials where laser, waterjet cutting machines, or plasma cutting machines might not be feasible or cost-effective. However, it’s generally limited to steel and other ferrous metals, as these materials readily engage in the exothermic reaction necessary for this cutting method.
Types of Flame Cutting
Flame cutting is a widely used method for cutting metals, offering precision and efficiency. There are two main types of flame cutting: oxygen fuel gas flame-cutting and air plasma arc cutting. Each method has its own advantages and is suitable for different material thicknesses and applications.
1. Oxygen Fuel Gas Flame Cutting
Oxygen fuel gas flame-cutting utilizes pure oxygen combined with acetylene or propane as the fuel source to generate the intense heat required for melting through metals effectively. This method is commonly used for cutting thick materials, such as steel plates. The high temperature produced by the oxygen-fuel gas flame in oxy-fuel cutting allows for quick and efficient metal removal.
Pros:
- Ideal for cutting thick materials
- Provides precise cuts with smooth edges
- Suitable for various types of metals, including cutting carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum
Cons:
- Requires additional safety precautions due to the use of flammable gases
- Produces heat-affected zones that may require post-cutting treatments
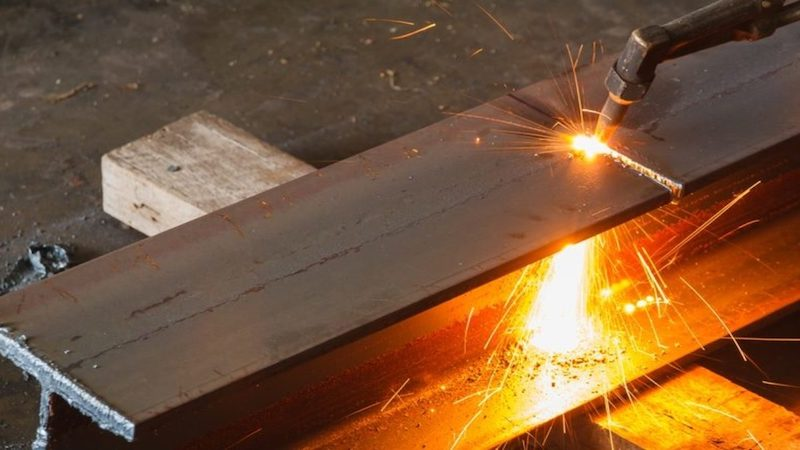

2. Air Plasma Arc-Cutting
Air plasma arc-cutting employs compressed air instead of oxygen from plasma arc cutting, making it a more cost-effective option for cutting thinner materials.
It uses an electrical arc to ionize the air, creating a plasma that reaches extremely high temperatures to melt through metals. This method is commonly used in industries where precision cuts on thinner materials are required.
Pros and Cons of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a popular technique used in various industries due to its precision and versatility. However, it comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- High Precision: Laser cutting offers high precision and accuracy with a narrow kerf, producing clean and detailed cuts. This level of control makes it ideal for intricate designs and patterns.
- Non-Contact Process: The laser cutting tool doesn’t directly touch the material, preventing any contamination or mechanical distortions on the surface.
- Versatility: One of the significant advantages of laser cutting is its ability to work with multiple materials, including various metal materials, plastics, wood, glass, and rubber.
- Automation and Customization: With the use of CAD/CAM systems, operators can automate the cutting processes, allowing for high repeatability and the easy creation of customized products.
- Reduced Material Waste: Due to its precision, laser cutting generates less waste material, making it a more sustainable option compared to traditional cutting methods.
Cons:
- High Energy Consumption: Laser cutting can be energy-intensive, especially for thick or dense materials, leading to high operational costs.
- Limitation on Material Thickness: While laser cutting is versatile, there’s a limit on the thickness of materials that can be effectively cut, especially for harder materials like steel.
- Safety Concerns: The accurate process involves a high-powered laser light that requires strict safety measures to protect operators from potential burns or eye damage. We have prepared an article to help you understand the laser class and safety guarantees.
- Cost of Equipment: Advanced laser cutting machinery requires a significant initial investment and ongoing maintenance, potentially limiting access to smaller operations.
- Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): The laser cutting process can generate heat that may affect the material’s structural integrity or properties, especially in metal cutting, leading to potential warping or deforming.
While laser cutting is a valuable technique for many applications due to its precision, efficiency, and versatility, these factors must be weighed against its high energy use, safety requirements, and potential impact on materials.
Pros and Cons of Flame Cutting
Flame cutting, while an excellent resource for specific applications, does have its limitations. Here’s a balanced overview of its pros and cons:
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: Compared to laser or plasma cutting machine, flame cutting machine is relatively inexpensive. Operating costs are also lower because it doesn’t require electricity or high-cost gases.
- Excellent for Thick Materials: Flame cutting is ideal for cutting thick sections of steel (from 1 inch up to several feet), where other cutting methods might struggle or be prohibitively expensive.
- Portability: The equipment is portable and can be used in different settings without the need for a power source. This aspect is particularly beneficial for sites without access to electricity.
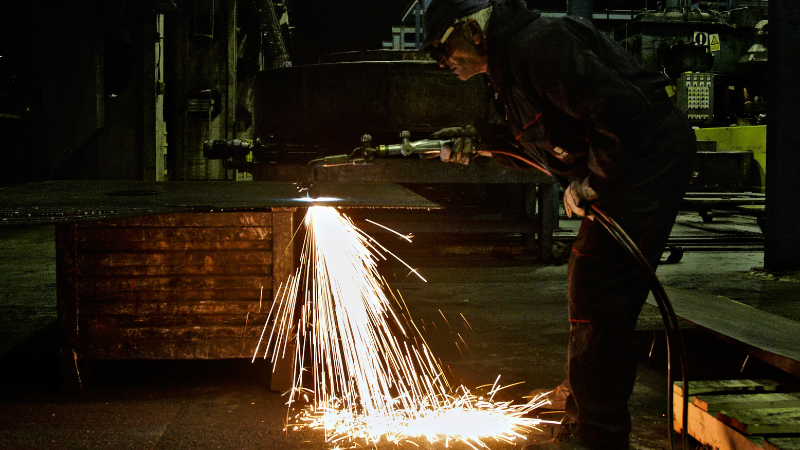

Cons:
- Limited Material Compatibility: According to Metal Supermarkets, flame cutting is mostly limited to carbon steel and some low-alloy steel. It’s not applicable to materials like aluminum or stainless steel due to the absence of a rapid exothermic oxidation reaction in such metals.
- Lower Precision: Compared to laser or fine plasma cutting, flame cutting is generally less precise, with broader kerf widths and more significant heat-affected zones, which can alter the material’s properties around the cut.
- Slow Cutting Speed: The process is slower compared to other thermal cutting methods, particularly for thinner materials.
- Larger HAZ: The intense heat generated during flame cutting can lead to a larger Heat Affected Zone (HAZ) compared to laser cutting. This means that the surrounding area of the cut may experience changes in material properties due to the excessive heat exposure.
While flame cutting is a valuable technique for cutting thick sections of steel, particularly in settings without ready access to power, its limitations in speed, precision, and material compatibility need to be considered for various applications.
Laser Cutting and Flame Cutting – Comparison Highlights
We have prepared a comparison table on laser cutting and flame cutting to help you quickly understand.
| Laser Cutting | Flame Cutting | |
| Process | Utilizes a focused high-intensity laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize the material. | Uses an oxygen and fuel gas flame to heat and oxidize the material, causing it to burn and create a cut. |
| Precision | Offers high precision for complex and detailed designs. | Less precise than laser cutting with a broader kerf. |
| Cut Quality | Clean cuts with minimal kerf and heat-affected zone. | Rougher edge finish, requires post-processing in most cases. |
| Applicable Materials | Versatile; works with metal, plastic, wood, and others. | Primarily used for iron and steel. |
| Cutting Thickness | Best suited for thin to medium-thick materials. | Effective for thicker metal sections, often used for materials over 3 inches thick. |
| Speed | High cutting speed, especially for thin materials. | Slower compared to laser, dependent on material thickness and type. |
Here are some specific explanations of the table.
1 – Precision and Processing Quality
Laser cutting is known for its precise, clean cuts with minimal Heat Affected Zone (HAZ). It is the go-to method for intricate designs or thin materials. On the other hand, flame cutting may not offer the same level of precision as laser cutting. It can result in a larger HAZ and less cutting accuracy due to the nature of the torch jet.
2 – Applicable Materials
Laser cutting has a broader range. It can effectively work with various metals, including stainless steel, low alloy steels, carbon steel, nickel alloys, and more. Flame cutting, on the other hand, is particularly cost-effective for thicker materials like steel.
3 – Cut Quality
Laser cutting excels in providing intricate details and smooth edges while minimizing distortion. Meanwhile, flame cutting offers cost-effectiveness for thicker materials but may sacrifice precision and result in rougher cut edge quality.
Laser or Flame Cutting: Which One to Choose?
Selecting between laser cutting and flame cutting involves a direct comparison of their attributes and how each performs in various operational aspects. Here’s a consolidated view, considering the key facets:
1. Cost-Effectiveness
- While laser cutting offers minimal waste due to its precision, the initial investment and maintenance costs are significantly higher. It, however, can lead to savings for high-volume production and complex parts that require detailed work or fine cutting.
- Flame cutting, on the other hand, involves lower operational and setup costs. It’s a more economical option for cutting thicker sections of steel where high precision is not a requirement, keeping overall project costs down.
2. Automation and Production Speed
- Laser cutting integrates seamlessly with automated systems, allowing for faster, high-volume production and consistent, repeatable cuts. This speed and ease of automation make it suitable for projects requiring rapid, large-scale production.
- Flame cutting is generally slower and less suited to automation, making it more time-consuming, especially for intricate designs. However, it remains a viable option for simpler cuts and lower volumes.
This article can help you maximize the value of laser cutting automation in different ways. For example, through automatic loading and unloading, the beam-on time can be reduced by more than 80%.
3. Energy Consumption and Environmental Impact
- Laser cutting, though precise, requires substantial energy, particularly for thick materials, and its operation may necessitate specific safety and waste disposal measures due to potential fumes.
- Flame cutting uses less energy per job and can be more environmentally friendly, though it exposes operators to fumes and requires proper ventilation.
Take a moment to evaluate your priorities before making a decision. Whether you opt for the precise finesse of laser cutting or the affordability of flame cutting, remember that professional advice from experts in the field can help guide you toward the best choice for your specific needs.
FAQs
FAQ 1: Is a laser cut better than a flame cut?
Whether laser cutting is better than flame cutting depends on your specific requirements. Laser cutting offers greater precision and cleaner cuts, ideal for detailed designs and thinner materials. However, flame cutting is more cost-effective for thicker materials, providing a rougher finish but operating at lower costs.
FAQ 2: Can I achieve intricate designs with flame cutting?
Flame cutting is generally better suited for simpler, less intricate designs due to its inherent limitations. The nature of the process can result in rougher edges and less precise cuts compared to laser cutting, making it more challenging to achieve intricate details.
FAQ 3: Are there any environmental considerations when choosing cutting methods?
Laser cutting tends to be more environmentally friendly as it produces less waste, emits fewer harmful fumes, and consumes less energy compared to flame cutting. However, it’s important to properly dispose of any materials used in laser cutting that may be hazardous or require special handling.
Conclusion
Now we have a full understanding of what laser cutting and flame cutting are and their differences. How you choose between the two will determine the progress of your project. By weighing the specific needs of your operation against the strengths of each method, you can confidently select the technique that promises efficiency, quality, and economic sense for your production environment.
Baison Illuminate Your Path to the Right Cutting Solutions!
Baison has the most advanced laser machines and a number of European CE certifications. With our expertise in laser technology, we’ll help you assess your project needs, ensuring you make an informed decision that maximizes efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Contact Baison today to explore the cutting-edge solutions we can provide for your business. Let’s shape the future of your projects together!