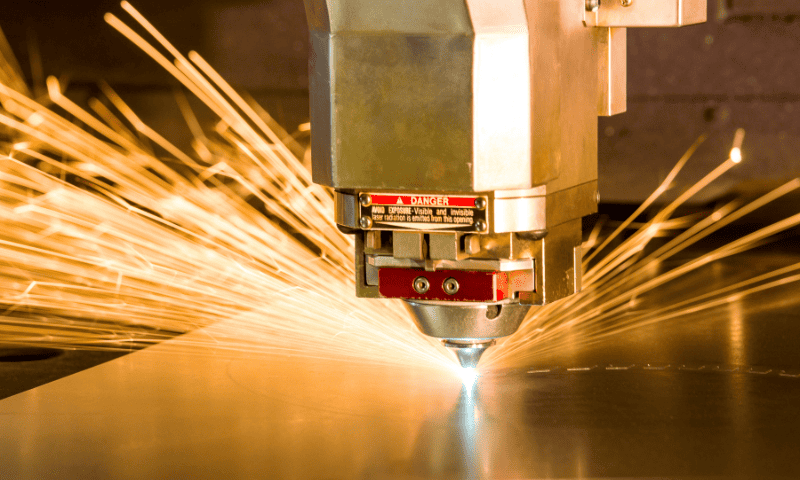
Basic Principles Behind Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technologies utilize lasers to cut through workpieces by harnessing the power of photons. This process showcases the remarkable convergence of optics and thermodynamics. Here are the basic principles that underpin this sophisticated process:
- Coherent Light Source: At the heart of laser cutting is the laser itself, a device that produces a beam of light where all the photons have the same wavelength and are in phase. This coherence allows for a highly concentrated beam of light from the laser head.
- Material Absorption: Different materials have unique absorption rates for laser light. Laser cutting leverages this principle by using the laser’s energy to raise the material’s temperature to its melting, burning, or vaporization point.
- Heat Concentration: The lasers focus their power by emitting concentrated light, which consists of photons, onto a very small area, resulting in rapid heating. This localized concentration is what allows for precision cuts without significantly affecting the surrounding material.
- Optical Systems: Lenses and mirrors in the laser cutter focus the laser beam, ensuring that it’s sharp and precise. Just as a magnifying glass can focus sunlight to burn a leaf, the laser cutter’s optics focus the laser to cut materials.
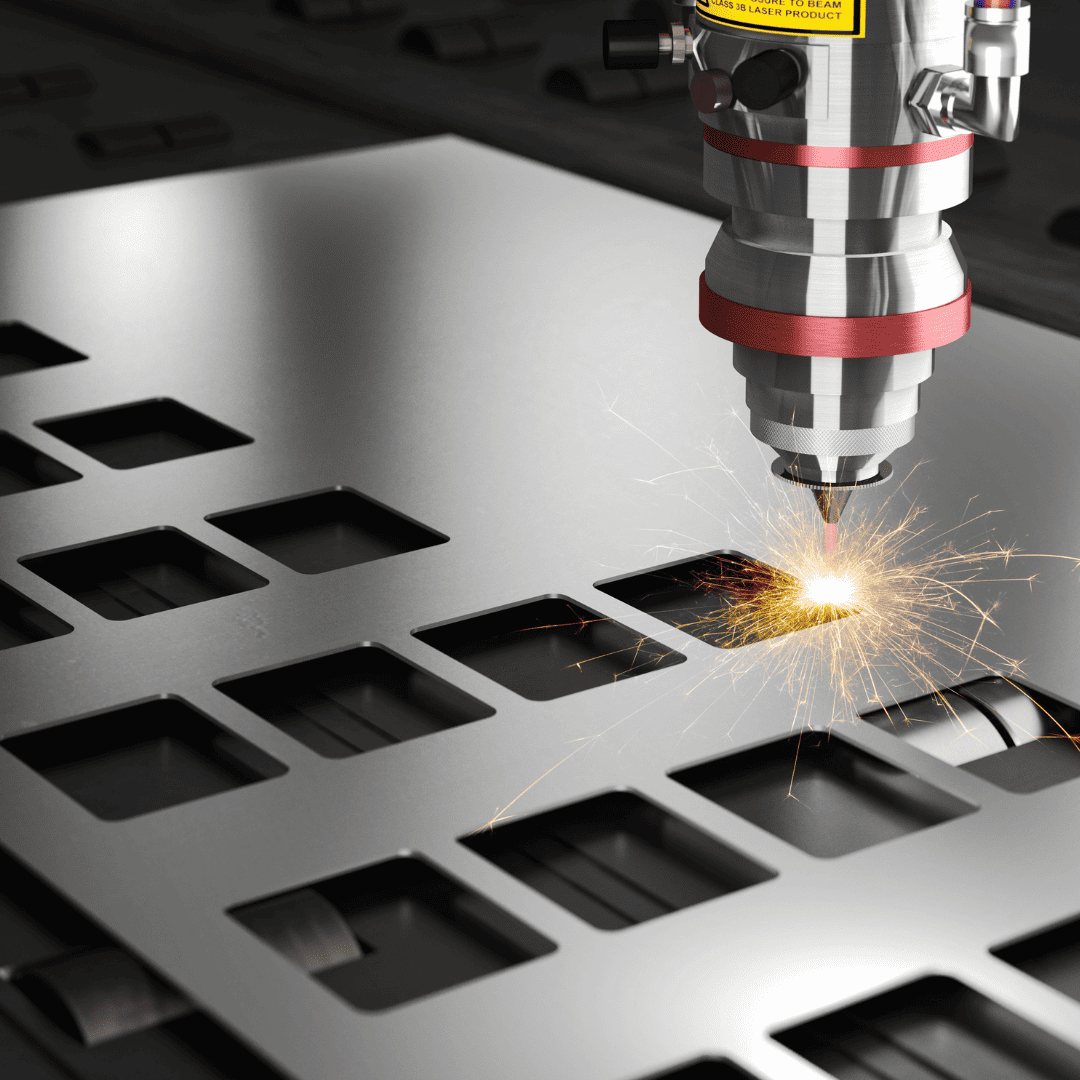
Understanding the Laser Cutting Process
The laser cutting process involves three main steps: beam generation, focusing the beam on the material, and moving the beam along the desired path. Different types of lasers are used for different materials and applications. The intensity and speed of the laser beam determine the depth and quality of the cut.
Delving deeper into the process of laser cutting, let’s break down the steps and components that make lasers and fiber optic cables the marvels they are.
- Design Input: Before any cutting occurs, a design must be conceptualized and digitized. This design is fed into the laser cutter’s motion control system, often via computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Laser Generation: The machine’s laser source generates the coherent light, ready to be focused onto the target material.
- Beam Guidance: Through a series of mirrors and lenses, the laser beam from the cutting head is directed toward the material. This laser cutting system ensures that the laser cutters maintain a steady and precise beam of light during the laser drilling process.
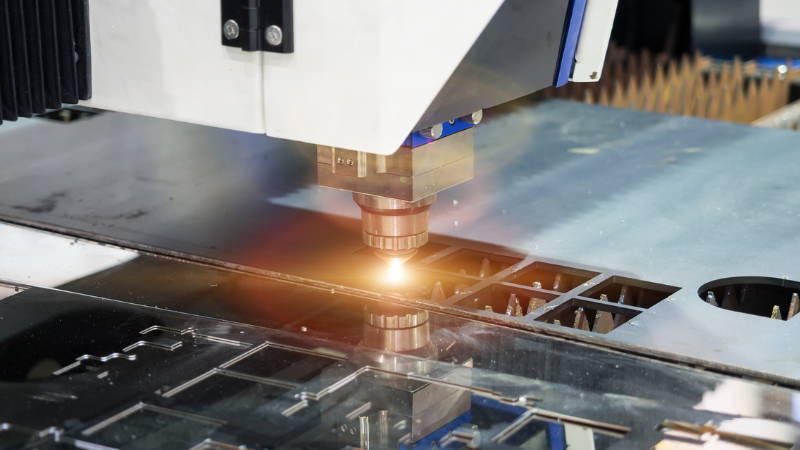

- Material Interaction: As the laser light makes contact with the material, it rapidly heats and either cuts, melts, burns, or vaporizes a very fine layer. Laser cutters use light to create a cut or an engrave, depending on the desired outcome and the settings used.
- Assist Gases: For many materials, especially metals, an “assist gas” is introduced at the point of cutting. This gas helps clear out molten material, ensuring a cleaner cut and reducing the chance of imperfections.
- Cooling Systems: Lasers generate a lot of heat. To maintain the efficiency and longevity of laser cutters, integrated cooling systems dissipate excess heat and keep the components at optimal temperatures. For more information on cooling machines, click here.
- End Result: Once the laser has traced the entire design, the material emerges with the desired cuts or engravings. Post-processing steps might include cleaning, polishing, or further assembly.
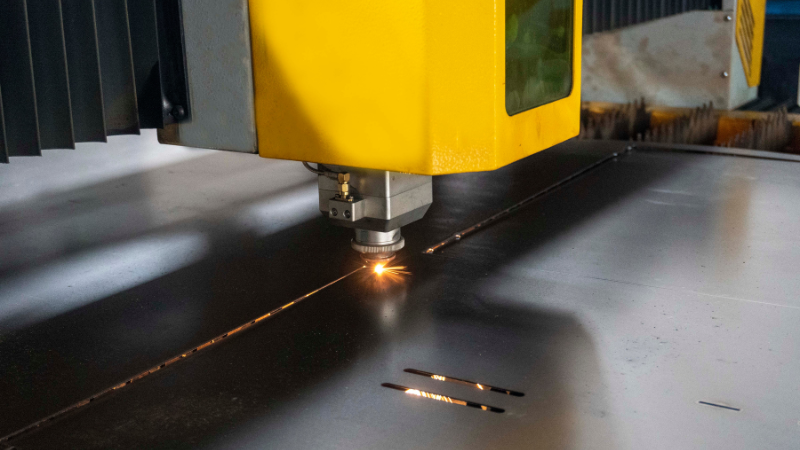

Types of Laser Cutting Techniques
Laser cutting is a versatile and precise method used in various industries to cut materials with the help of a laser beam. Different types of laser cutting techniques are employed based on the material being cut and the desired outcome. Let’s explore some of the main types:
1 – CO2 Lasers
- Origin: These lasers are generated from a gas mixture predominantly containing carbon dioxide. CO2 laser cutters operate by emitting a high-energy beam that vaporizes or burns through the material. The focused laser beam allows for intricate and detailed cuts.
- Applications: CO2 lasers are commonly used for cutting organic materials such as wood, acrylic, fabric, and more.
- Strengths: Laser cutters offer a balance between power and precision, making them popular in many industrial settings. They are highly sought after for their ability to efficiently and accurately cut through a wide range of materials. Additionally, their relatively longer wavelength makes them suitable for cutting thicker materials.
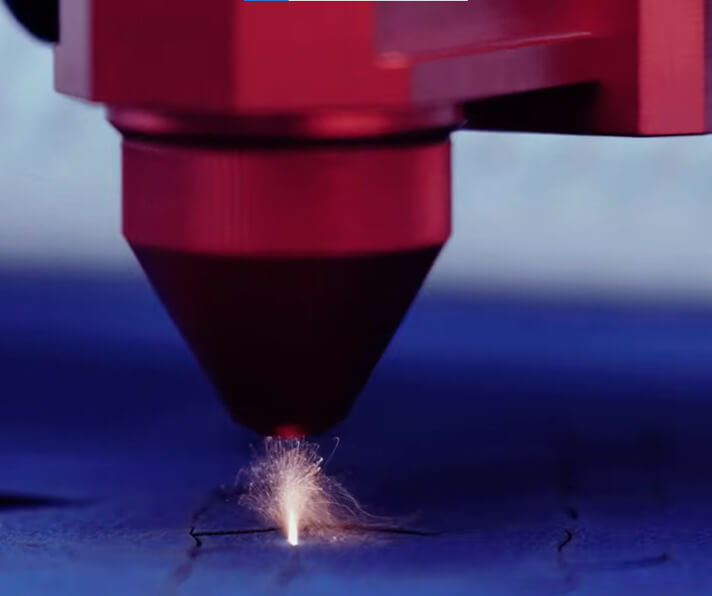

2 – Fiber Lasers
- Origin: Fiber lasers use an optical fiber doped with rare-earth elements, like erbium or ytterbium, as the gain medium.
- Applications: Predominantly used for metal cutting and engraving like steel or aluminum due to their excellent beam quality.
- Strengths: Fiber lasers are known for their efficiency, precision, and speed. Laser cutters have beam quality that allows for a tight focus, enabling the cutting of intricate patterns and fine details.
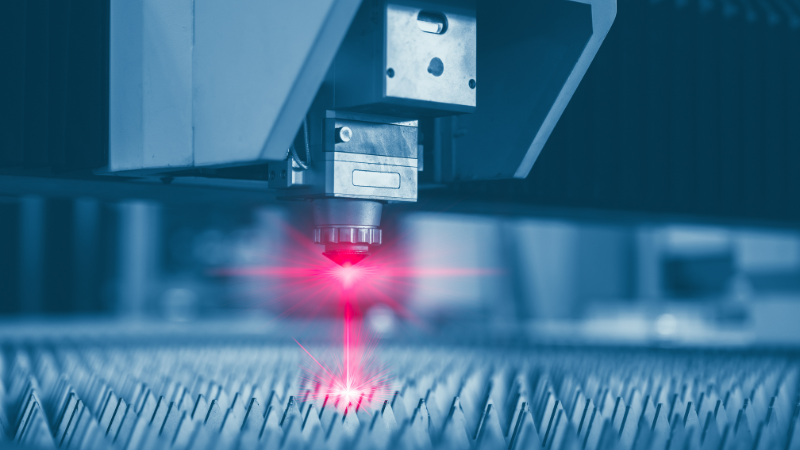

You may want to know the CO2 lasers compared to fiber lasers.
3 – Fusion Cutting
- Origin: Fusion cutting is rooted in the principle of melting the material using the concentrated energy of a laser beam. After the material reaches its melting point, a high-pressure assist gas is introduced to eject the molten material from the kerf.
- Applications: Predominantly used for metals that have low reflectivity or thermal conductivity, especially stainless steel and aluminum. Fusion cutting with laser cutters finds utility in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics manufacturing, where clean cuts with minimal residue are crucial.
- Strengths: The process ensures smooth and clean cuts, with reduced thermal distortion. The use of inert gases like nitrogen ensures minimal oxidation, preserving the material’s surface quality.
4 – Flame Cutting (Reactive Laser Cutting)
- Origin: Material is heated by a laser to ignition, followed by an oxygen-assisted exothermic reaction to facilitate cutting.
- Applications: Preferred for carbon steel and low-alloy steel in construction and shipbuilding.
- Strengths: Efficient for thicker materials, aided by the energy from the burning process.
5 – Sublimation Cutting
- Origin: Intense laser energy directly converts a material from solid to gas, bypassing the liquid phase.
- Applications: Suitable for specific polymers, woods, and composites in arts and crafts.
- Strengths: Achieves precise cuts with minimal thermal impact and clean edges.

Materials Suitable for Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a versatile process that can be used on a wide range of materials, making it a popular choice in various industries. Let’s explore the different materials suitable for laser cutting and some important considerations to keep in mind.
Metals
Laser cutting is commonly used on metals like aluminum, steel, and stainless steel. The high-energy laser beam melts or vaporizes the material, creating precise cuts. It is ideal for thin to medium thicknesses of metal sheets.
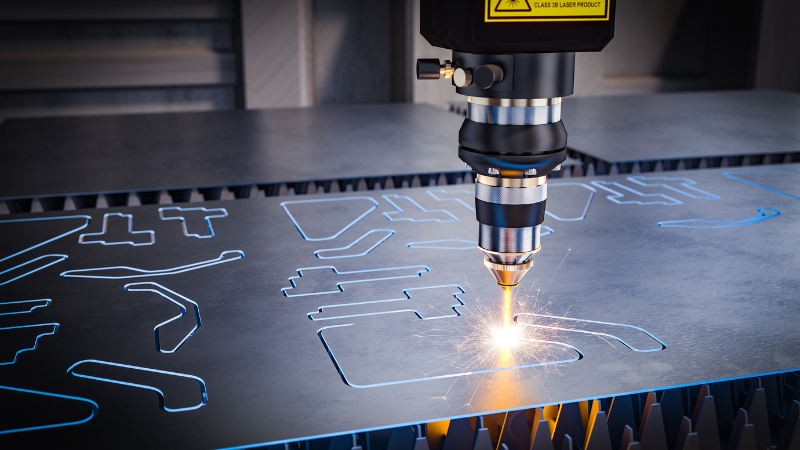

Plastics
Plastics such as acrylics and polycarbonate are also compatible with laser cutting. The laser beam heats the material, causing it to melt or vaporize along the desired path. This method provides clean and accurate cuts without chipping or cracking.
Wood
Wood is another material that can be effectively cut using lasers. Different types of wood, including plywood and MDF (medium-density fiberboard), respond well to laser cutting due to their composition. The laser beam burns away the wood, leaving behind precise cuts with minimal scorching.
Paper and Fabric
Laser cutting offers intricate designs on paper like cardboard and fabric with great precision. The concentrated heat from the laser beam causes these materials to burn or vaporize along the designated lines, resulting in clean edges.

Other Materials
In addition to metals, plastics, wood, paper, and fabric, lasers can also cut materials like leather and glass. However, certain precautions must be taken when working with specific materials. For example, PVC should not be cut due to potentially hazardous fumes released during the process.
Reflective surfaces may require additional coatings or methods to ensure proper absorption of laser energy during cutting. Thick materials may need multiple passes or adjustments in power settings to achieve desired results without excessive melting or burning.
By understanding which materials are suitable for laser cutting and considering their unique properties and requirements during the process, you can harness the full potential of laser technology in your projects.
Applications and Benefits of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a versatile technology that finds applications in various industries, ranging from signage making to jewelry design and production, automotive manufacturing, electronics, and medical devices. Compared to other cutting methods like plasma cutting or vector cutting, laser cutting offers numerous advantages.
One of the key benefits of laser cutting is its ability to achieve high precision and intricate detailing. The laser beam can cut through materials with extreme accuracy, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and designs. This level of precision is particularly valuable in industries like jewelry making, where intricate patterns are often required.
Another advantage of laser cutting is its efficiency in material usage. Due to the narrow kerf width of the laser beam, there is minimal material waste during the cutting process.
This not only helps reduce costs but also promotes sustainability by minimizing environmental impact. Laser cutting enables efficient nesting of parts, maximizing the utilization of materials and optimizing production processes.
The non-contact nature of laser cutting is another significant benefit. Unlike traditional methods that involve physical contact with the material being cut, laser cutting operates without direct contact. This reduces the risk of damage or contamination to delicate materials such as electronic components or medical devices.
Exploring Different Laser Cutting Machines
Now we have understood the basic content of laser cutting. If you want to apply laser cutting to production, you need a laser cutting machine. Let’s take a look at the types of laser cutting machines.
1. CO2 Laser Machines: Versatile but Limited for Metals
CO2 laser machines are widely used in various industries due to their versatility. They can cut through materials like wood, acrylic, fabric, and plastic with precision. However, CO2 lasers have limitations.
The wavelength of the CO2 laser beam is not well-absorbed by metal surfaces, making it less efficient and slower compared to other laser cutting methods.
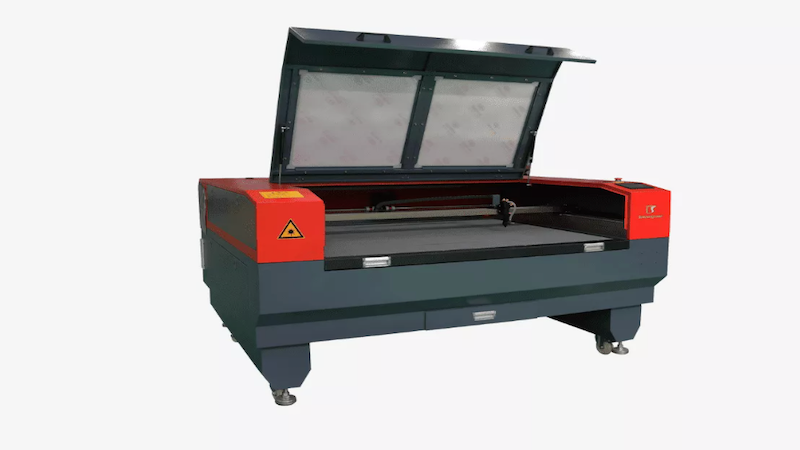

2. Fiber Laser Machine: Efficient for Metal Cutting
Fiber lasers are highly efficient. They utilize a focused laser beam that delivers high power density, allowing them to cut through even thick metal sheets with speed and accuracy. The wavelength of fiber laser is better absorbed by metal surfaces, resulting in improved efficiency and faster cutting speeds compared to CO2 lasers.
3. CNC Integration: Precise Control over Cutting Process
Many laser cutting machines incorporate CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems. These systems use computer programs to control the movement of the laser cutter’s gantry and the positioning of the workpiece. This integration allows for precise control over the entire cutting process, ensuring accurate cuts and minimizing errors.
4. Advanced Features: Rotary Attachments and 3D Engraving
Some advanced laser cutting machines offer additional features that enhance their capabilities. For example, rotary attachments can be added to enable the cutting of cylindrical objects like pipes or tubes. This feature expands the range of applications for laser cutters.
Certain machines have 3D cutting and engraving capabilities that allow for intricate designs on three-dimensional surfaces.
How to Choose a Laser Cutter?
It’s time to explore how to choose the right laser cutter for your needs. With so many options available in the market, finding the perfect fit can be overwhelming. But fear not! We’re here to guide you through the process.
Firstly, consider your specific requirements. What materials will you be working with? What thicknesses do you need to cut or engrave? Assessing these factors will help you determine the power and capabilities required from your laser cutter.
Next, think about your budget and workspace limitations. Laser cutters come in various sizes and price ranges, so it’s essential to find one that fits both your financial constraints and available space.
Lastly, don’t forget about customer reviews and ratings – they provide valuable insights into the reliability and performance of different models.
In conclusion, choosing a laser cutter is an important decision that requires careful consideration of your needs, budget, space limitations, and customer reviews. By following these guidelines and taking into account all relevant factors, you’ll be well-equipped to make an informed choice that suits your specific requirements.

FAQs
Can I use any material with a laser cutter?
Laser cutters are versatile tools that can work with a wide range of materials including wood, acrylic, fabric, leather, paper, cardboard, glass, and more. However, it’s crucial to check if the material you intend to use is compatible with the specific laser cutter model you are considering.
How much power do I need in a laser cutter?
The required power for a laser cutter depends on the type and thickness of materials you plan to work with. Thicker or denser materials usually require higher wattage lasers for efficient cutting or engraving.
Are all laser cutters capable of engraving?
Not all laser cutters are designed for engraving. Some models are primarily focused on cutting, while others offer both cutting and engraving capabilities. Make sure to check the specifications of the laser cutter you are interested in to ensure it meets your specific needs.
Conclusion
Laser cutting, with its blend of precision and versatility, has revolutionized industries and artistry alike. As we grasp its principles and applications, we unlock a world of design and manufacturing potential. As laser cutting technology evolves, it promises to continually redefine the boundaries of what’s possible.
Discover the Future of Laser Cutting with Baison Laser!
At Baison Laser, we’re passionate about providing you with cutting-edge solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you’re taking your first step into the world of laser cutting or seeking to elevate your current operations, our team is here to guide, support, and inspire. Don’t settle for the ordinary. Dive deeper, reach higher, and redefine your boundaries.





