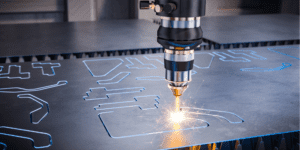
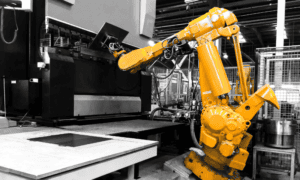
It’s an excellent option in the construction and repair industry where you need mobility or work in tight, difficult-to-reach spaces. It offers the flexibility to weld in different positions where traditional welding methods may need to be more practical. However, handheld welding requires a steady hand and precise movements.
In this article, we will discuss handheld welding and how it is performed. We will discuss different types of handheld welding with their merits and demerits. So stick along, as this article is a complete guide for any new welder who wants to understand the handheld welding process. Before we get into specifications, let’s understand what welding is.
What is Welding?
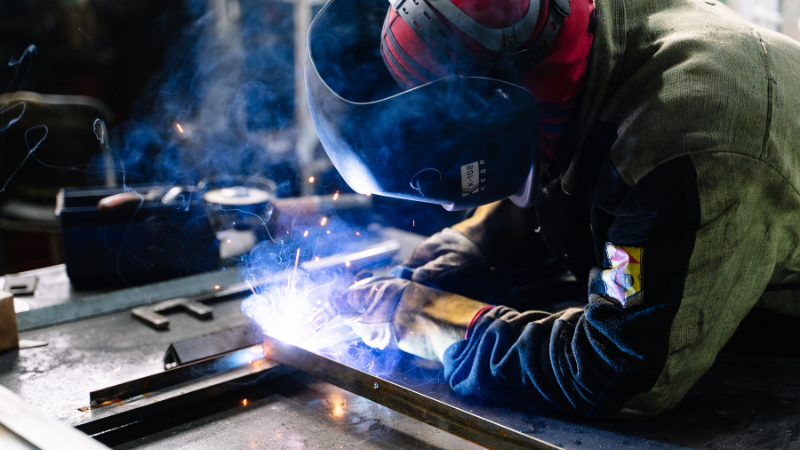

Joining two metal pieces by mealing is welding. You may need to fill the weld with another metal to make the bond more durable. Almost all types of metal goods, small or big, need welding. The metal pieces are heated with an electric gun or arc. Once the metal is melted, two pieces are joined and solidified on cooling.
The process requires heat that is applied to materials. It can be an electric arc, gas flame, or laser; the heat melts the material, and using some pressure, materials are joined together. In some cases, a filler is required to help the joining. The welding process involves heat and fuming of gases, and it requires shielding gas or flux to protect the welding from unwanted fumes as well. Welding can be dangerous, especially if you are not trained to use the welding machines.
What are the Properties of Handheld Welding?

Precision
Handheld welding requires a high level of skill and precision from the welder to ensure the joint is strong and durable. A skilled welder can control the welding tool’s heat, speed, and angle to produce a high-quality weld.
Portability
Handheld welding equipment is portable and can be used in remote locations, making it ideal for repairs or construction work in the field.
Versatility
Handheld welding can be used with various welding processes such as TIG, MIG, and stick welding. Each process has its own advantages and limitations, and the welder must choose the appropriate process for the job.
Flexibility
Handheld welding allows for flexibility in the size and shape of the welded objects. It is possible to weld objects of various sizes and shapes, as long as the welding tool can reach the joint.
Different Handheld Welding Techniques
There are several handheld welding processes, each with unique characteristics and uses. Let’s take a look at different welding techniques.
Shielded Metal Arc Welding
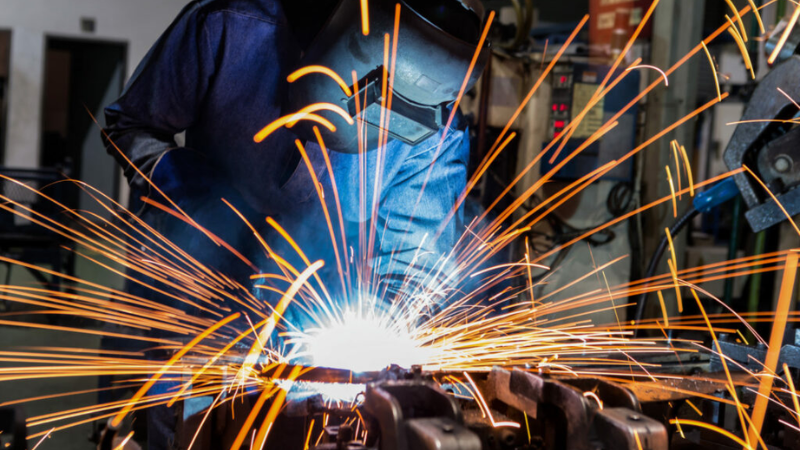

It’s the traditional technique of stick welding or manual arc welding. It’s the most common welding type used in workshops where the welders can’t afford expensive welding machines. In this process, the welder joins two metal pieces using an electrode. Electrodes are also called rods which are coated with flux.
The electrode is typically made of a consumable metal, such as steel or stainless steel, that melts and becomes the filler material for the joint.
Stick welding is a versatile process where consumables are chosen depending o the metal or its thickness. Here is how the stick welding work:
The electric current creates an arc between the electrode and the base material. As the current can’t flow throw the material, it burns the arch that results in producing fusion heat. It also melts the base metal and electrode that works as a filler material. The flux coating on electrodes protects the atmosphere from oxidation and contamination.
Stick welding requires a low electric arc and high amperage. It is easy to learn, produce low noise, and protects the seam with weld slag. It can weld all types of metal and is not sensitive to rust or other contaminations on metal surfaces.
Gas Metal Arc Welding (MIG Welding)
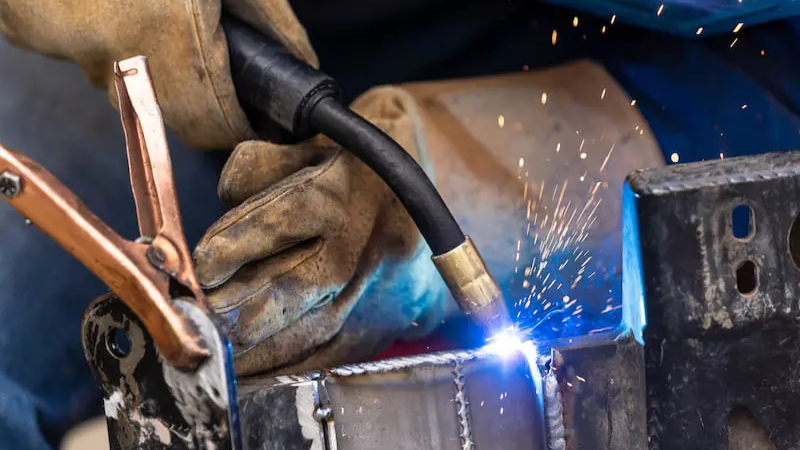

MIG and laser welding are two common types of welding. In general terms, it is also called wire welding.
In MIG welding process, a welding gun feeds wire electrodes into the workpiece. The gun also releases shielding gases to protect the weld pool from contamination. An inert gas, usually argon or a mixture of argon and CO2, shields the weld from oxidation. This process is ideal for welding thin materials and can be used on various metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, and carbon steel. It works well for the 24 gauge or 1/2″ thick material.
MIG welding is a versatile process useful for welding various metals, including steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys. It is also a relatively easy process to learn and can be used in various welding applications, from automotive repair to the fabrication of large structures.
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding
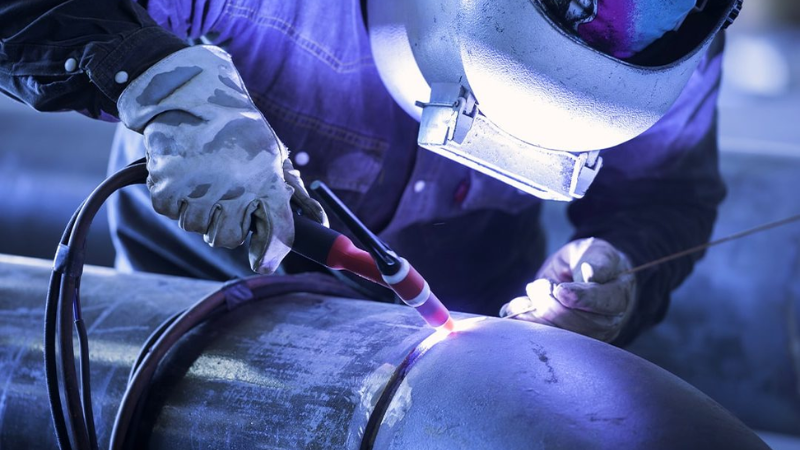

TIG or GTAW, is another handheld welding procedure. It uses a tungsten electrode to send the arc to the base material. Tungsten does not melt with heat and delivers an arc of electricity to the workpiece. The electrode is held in a torch, and an inert gas, usually argon, shields the welding area from the atmosphere. TIG welding can be operated with or without a filler rod.
The TIG process is often used for thin metal components like stainless steel, aluminum, and other non-ferrous metals. It gives precise and high-quality welding, making it a popular choice for applications where you must weld thin metal pieces while looking presentable. This process produces a high-quality, precise weld for welding thin materials, stainless steel, and aluminum. To find out the difference between TIG and laser welding, you can see the article we’ve written before: ‘Laser Welding vs. TIG Welding: Which Option is Best for You?‘
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)

FCAW is similar to MIG welding, but instead of using a solid wire, a hollow wire electrode filled with flux is used. This process is typically used for welding thicker materials like structural steel.
Plasma Arc Welding

Plasma arc welding (PAW) is a type of welding that uses a highly concentrated and ionized gas called plasma to create an electric arc for welding. Plasma and laser welding are both types of fusion welding. The plasma arc generates intense heat, which melts and fuses the metal to create a strong and precise weld joint.
The process uses a plasma arc torch which contains a tungsten electrode and a nozzle that directs the flow of gas. Typically argon gas is used that becomes ionized by the high voltage current from the power source and creates the plasma arc. The electric arc heats the metal to its melting point. A filler rod is added to the welding point, which melts and fuses into the base metal, creating a strong and durable weld joint.
PAW is also an expensive device used for welding thin components with precision. It is commonly used in highly demanding industries like aerospace and electronics. Automotive industries.
Handheld Laser Welding Machines
Besides all these traditional welding processes, handheld laser welding machines combine two pieces of metal with high-powered lasers. They work by directing a focused laser beam onto the surface of the metal, which melts the metal and creates a bond between the two pieces.
The welding machine then focuses the laser beam onto the metal surfaces to be joined. A laser diode or fiber laser typically generates the laser beam. It is delivered through an optical fiber to the handheld deviceThe heat generated by the laser beam causes the metal to form a molten pool, which then cools and solidifies to create a strong, permanent bond between the two pieces of metal. It’s a highly-priced welding procedure that does not distort surrounding material and causes minimum damage.
Handheld laser machines often join small and complex metal pieces with high precision. It’s a more accurate ad speedy procedure than any other welding machine. They are also commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
What are the Components of a Handheld Welding Machine?
Here are the components of a handheld welding machine:
Power Source
An electric power source is required to produce the arc for melting metal. A battery, generator, or electric machine can provide the current.
Electrodes
Electrodes are connected to power sources, producing an arch that melts the metal. It is in the hand of the welder.
Nozzle
A copper-made nozzle is usually used. It is attached to the gun and direct shielding gas over the welding base. It cools the metal and helps it solidify and protect the weld from contamination.
Shielding Gas
Shielding gas is a separate component connected to the welding gun.
Wire feeder
A wire feeder is attached to the welding gun if the welding process requires a wire.
Control Panel
The control panel is located on the welding machine. It adjusts welding parameters like e, voltage, current, and wire feed speed through a control panel.
Handle
It’s part of the welding gun that the welder holds while carrying out the welding process.
What are Consumables in Handheld Welding?

Consumables are material that is consumed or worn out during the welding procedure and need to be replaced from time to time. Here are a few consumables:
Electrodes
Welding electrodes, also known as welding rods, are made of steel, aluminum, or titanium. They are the medium for the electric arc to create heat for melting the base metal.
These are also called stick electrodes or welding electrodes. They are specifically important in Stick welding. They can be made of a different material of different materials like steel, titanium, or aluminum. They are used to create an arch between the electrode and base material.
1. Types of Electrodes
Here are some common types of welding electrodes:
- E6010: This cellulose-based electrode can be used on dirty, rusted, or painted materials and is commonly used in pipeline welding. It is not recommended for use on thin materials.
- E6011: It’s similar to E6010 but has a higher deposition rate and can be used on thinner materials.
- E7018: A low-hydrogen electrode, It produces a strong, crack-resistant weld. It is commonly used in structural welding, heavy equipment repair, and fabrication.
- E7024: This electrode has a high deposition rate and is commonly used in heavy fabrication and construction. It can be used on AC or DC welding currents.
- E308L-16: Used for welding stainless steel. It is commonly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing.
2. How to Choose Electrodes?
The electrode choice depends on the welding type and base material. For instance, steel electrodes are suitable for welding steel, while aluminum electrodes are better for welding aluminum.
The thickness of the material being welded should also be considered before choosing the electrodes. Thinner materials require smaller diameter electrodes, while thicker ones require larger ones.
The amperage of the welding machine is also important to consider, as the higher amperage requires larger diameter electrodes.
Lastly, the polarity of the welding machine also matters as DC negative polarity requires a different electrode than DC positive polarity.
Besides, all these coatings on electrodes and welding positions can also affect the choice of electrodes.
Shielding Gases
Shielding gases are an important consumable in handheld welding, it saves the atmosphere and welding from the fumes and gases generated during the welding procedure. Atmospheric contamination as a result of welding can cause weld defects. Inert gases neutralize other elements like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor.
Here are some shielding gases that are used:
Argon: Argon is commonly used for aluminum, copper, and magnesium TIG welding. It provides good arc stability and produces a smooth, consistent weld.
Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide is often used for MIG welding of carbon and low-alloy steel. It provides good penetration and produces a strong, durable weld.
Helium: Helium is also used in TIG welding. It is used to weld thick materials and non-ferrous metals. It provides excellent heat transfer and helps to produce a clean, strong weld.
Oxygen: Oxygen is used in some welding processes to increase the heat of the welding arc and improve penetration. However, too much oxygen can cause oxidation, so it should be used cautiously.
Mixtures of gases: Many welding applications require a mixture of gases to achieve the desired weld characteristics. For example, a mixture of argon and helium can be used to weld thicker materials or to increase travel speed, while a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide can be used to balance penetration and deposition rate.
Filler Materials
Filler materials are added while joining two metal pieces to strengthen and strengthen the bond. The choice of filler material depends on the following:
- Composition of base material
- Desired bond
- Welding process
- The thickness of the material
- Environmental conditions in which welding is performed.
Here are a few materials used as fillers:
Mild steel: A commonly used filler material for handheld welding, especially for welding carbon steel.
Stainless steel: Stainless steel requires a filler material that matches the properties of the base metal.
Aluminum: Like stainless steel, aluminum filler material is required for welding aluminum alloys.
Nickel alloys: These are used for welding high-temperature metals and alloys such as Inconel, Monel, and Hastelloy.
Copper: Copper filler materials are often used for brazing and soldering applications.
Flux
Flux is a material that is used to protect the weld from contamination. It is also used for better adhesion. Flux can be a powder or a paste, which is applied to the welding rod or electrode.
In handheld welding, flux can be used in two different ways: as a coating on the welding electrode (known as flux-coated electrodes) or as a separate material added to the weld pool during the welding process (known as flux-cored welding).
Different types of flux are designed for different applications, such as low hydrogen flux for welding high-strength steels, basic flux for welding stainless steel, and rutile flux for general-purpose welding. It is essential to select the appropriate flux for the particular application to ensure the quality and integrity of the final weld.
The flux can be chosen depending on
- Base material
- Welding position
- Welding technique
- Required properties in the final weld
Besides these major consumables, some minor consumables are:
Contact tips: These are used in MIG welding to transfer the welding current from the welding gun to the wire. They are made of copper and must be replaced periodically as they can become worn or damaged.
Nozzles: Nozzles are used in MIG welding to direct shield gas flow around the welding area. They can become clogged with spatter and must be cleaned or replaced regularly.
What are Some Factors to Consider Before Choosing Consumables?
The following factors should be considered while choosing the consumables:
Welding process
Welding consumables depend on the type of welding. For example, MIG welding requires a wire, while TIG welding uses tungsten electrodes.
Material to be welded
The choice of consumables also depends on the material you need to weld. For example, electrodes for each type of material are different.
Thickness of Material
The metal thickness affects the choice of consumables. Thicker materials require higher amperage and larger consumables.
Welding Position
You need to consider the welding position while selecting consumables. Different welding positions require different electrodes. For example, electrodes for vertical and overhead positions are designed to have a lower melting rate, a more stable arc, and greater penetration capability than electrodes used in flat or horizontal positions.
Amperage
The amperage of the welding machine also plays a crucial role in selecting the consumables. The higher the amperage, the larger the consumables required.
Manufacturer’s recommendations
Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for consumables. The manufacturer will have tested the consumables to ensure they work with their welding machines and provide the best results.
Why is it Important to Choose the Right Consumables for Handheld Welding?
Quality of Weld: The choice of consumable can significantly affect the quality of the weld. The type of consumable should be compatible with the base metal being welded and the welding process being used. If the wrong consumable is chosen, the weld may not hold up to the intended use, leading to potential failures or defects.
Appropriate consumables can also improve productivity. It can save the welder from the extra hassle. Consumables with a longer life and less need for replacement can help save time and money. A high-quality consumable can also reduce the need for rework or touch-up, which can be time-consuming.
The right consumable can also contribute to worker safety. Some consumables produce fumes or other hazardous byproducts during welding. Choosing the right consumable with lower levels of hazardous byproducts can help reduce worker exposure to these substances.
How to Improve Results of Handheld Welding?
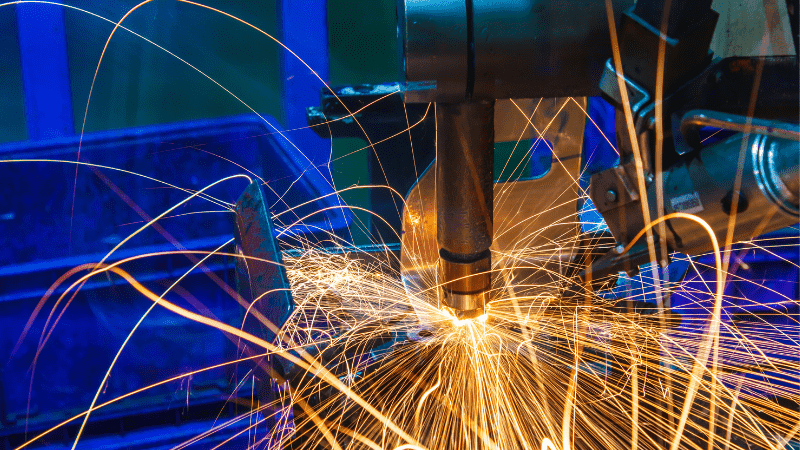
Here are a few tips to improve handheld welding results.
Welding Type
Choose the right welding technique: Welding techniques can affect the final weld. Each technique has its own merits and suits specific needs and materials. Different welding techniques are better suited for different materials and applications, and the choice of technique can significantly impact the weld’s strength, durability, and appearance. For example, some welding techniques are better suited for thin, delicate materials, while others are better for thicker, heavier materials.
Prepare the surface
Cleaning the metal is essential for good weld quality. Prepare the surface before welding and make sure there is no dust, debris, or paint on it. It helps to ensure solid and durable welds.
Correct welding Settings
Welding settings are important for good results. Ensure you know the metal you are welding and everything about the shield gases, the amount of amper required, and what electrode to use.
Maintaining Consumables
Maintaining electrodes or other consumables is essential for good welding results. Keep them in a cool, dry place, preventing containments from affecting their efficacy.
Use the Proper Welding Technique
Proper welding techniques can reduce the time needed to complete the weld. This includes maintaining a consistent arc length and travel speed. It may require some practice and proper training. The more experience a welder has, the faster they can complete a weld without sacrificing quality.
What are Some Safety Tips to Follow for Handheld Welding?

Here are some safety recommendations for handheld welding:
- Welding involves high heat, electric components, current use of high heat, and potentially hazardous equipment so that the improper technique can result in serious injury, damage to property, or even death.
- The welder must know all about the welding technique and safety precautions. An inexperienced welder and an unsteady hand can lead to structural weakness, corrosion, and other defects that can compromise the integrity of the welded object.
- Enrol in a formal welding training program or seek instruction from an experienced welder to learn proper welding techniques.
- Wear protective clothing: Welders should wear protective clothing such as a welding helmet, gloves, long-sleeved shirt, and pants to protect their skin from the intense heat and UV radiation.
- Welding produces hazardous fumes and gases that can be harmful if inhaled. Always ensure the area where you are welding is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling these gases.
- Welding produces intense light that can damage your eyes. Wear appropriate eye protection, such as a welding helmet with a shaded lens, to protect your eyes from this harmful light.
- Secure the workpiece before beginning to weld to avoid any accidental movement or displacement that could cause injury.
- Welding can produce sparks and ignite flammable materials. Keep a fire extinguisher nearby and know how to use it in an emergency.
- Always use the appropriate welding technique for the job at hand. Improper welding techniques can cause accidents, damage the workpiece, or poor-quality welds.
- A clutter-free workplace helps to prevent accidents, injuries, and fires. Ensure the welding area is free from clutter or debris that could cause accidents.
Final Words
Handheld welding provides a versatile and convenient option for various welding applications. It allows the welder to reach tight spaces and perform welding in different positions. Handheld welding techniques differ, and each has its merits and demerits.
Laser handheld welding devices are the most efficient, reliable, and user-friendly. These handheld devices may cost more than traditional welding machines, but they help businesses save money by reducing manual labor and enhancing the quality of end products. Traditional handheld welding devices suit smaller welding jobs, repairs, and maintenance tasks.
Baison’s Handheld Laser Welding Machines
Baison provides top-of-the-line laser machines suitable for small and large industries alike. Our state-of-the-art laser machines are capable of cutting, welding, and marking with exceptional precision.
Baison’s handheld laser welding machines have transformed the welding process, making it more efficient and accurate for industrial purposes. Our handheld welding machines are equipped with all the necessary safety features and are effortless to operate.
Upgrade Your Welding Game with Baison’s Handheld Fiber laser Welding Machine.
Are you tired of slow and unreliable welding machines? Upgrade to the latest laser handheld welding technology and revolutionize your welding experience! With our cutting-edge machines, you can perform fast and precise welding, saving you time and money on every project. Visit our website to learn all about laser welding machines. Contact our team of experts for a free evaluation of the application to help you choose the handheld laser welding machine your business needs.