With the advancement of laser technology, a new era of ceramic creation has opened for artists and innovators alike.
Whether you are a seasoned ceramicist seeking to expand your toolbox or a curious explorer venturing into the realm of light-powered fabrication, this article will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to transform humble clay into breathtaking masterpieces.
Overview Laser Cutting Technology
Laser cutting is a powerful and versatile technology that utilizes focused laser beams of light to cut materials. Laser-cutting machines use concentrated energy to melt, vaporize, or burn through a wide range of materials. This allows for incredibly precise cuts with minimal heat-affected zones, which makes it ideal for unique designs and delicate projects.

From wood and acrylic to metal and leather, the laser cutting process can handle them all. This process has impressive material compatibility. This makes it a valuable tool for various industries, from prototyping and manufacturing to crafting and design. Whether you’re creating jewelry, detailed architectural models, or industrial components, laser cutting offers a clean, efficient, and precise solution.
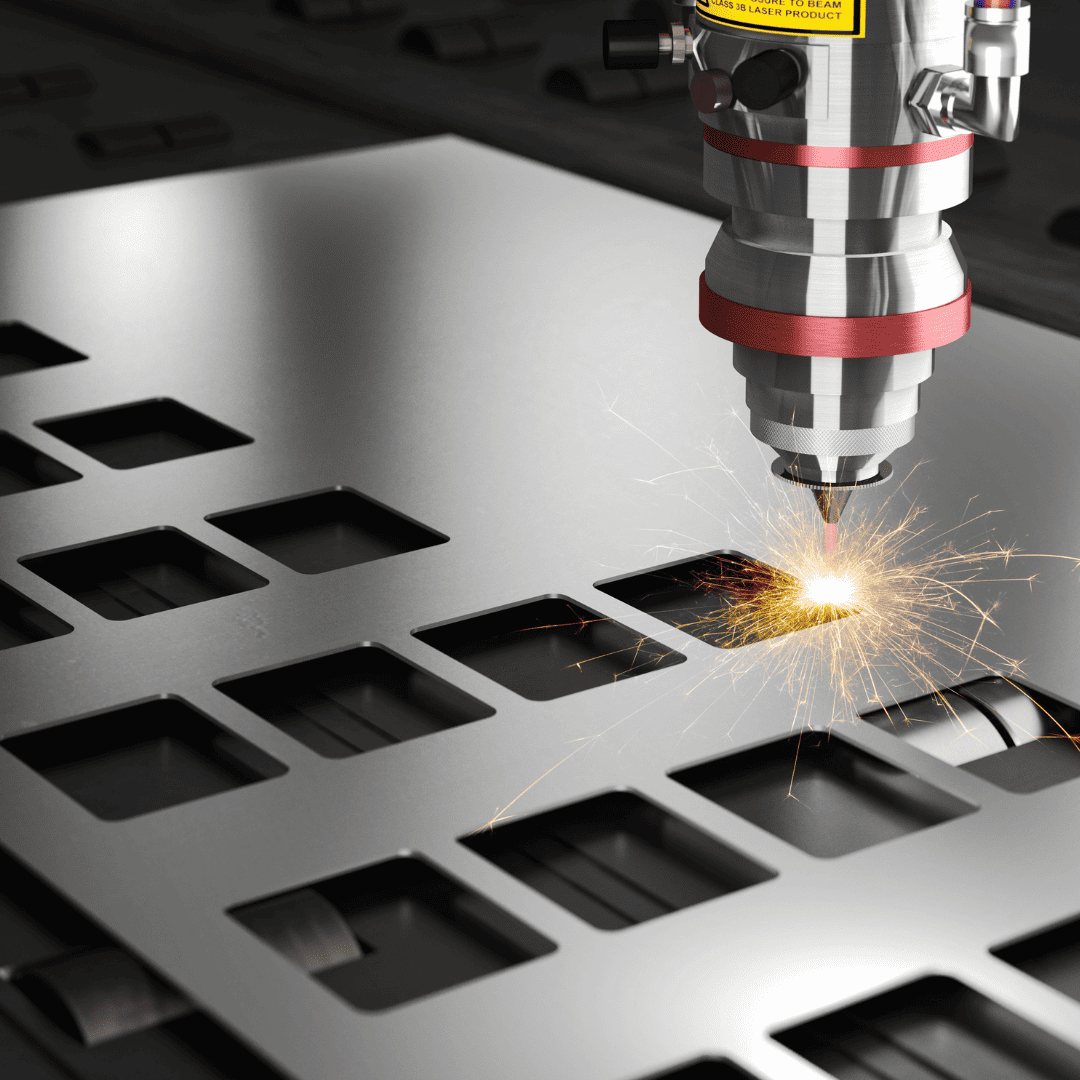
5 Benefits of Laser Cutting Ceramics
Laser cutting has emerged as a revolutionary technique for shaping ceramics, offering a unique blend of precision, flexibility, and efficiency. Compared to traditional methods, laser cutting unlocks various advantages, making it the go-to choice for various applications.
1. Unmatched Precision
You can easily carve delicate snowflakes or geometric patterns on a ceramic tile with laser cutting. The focused laser beam carves with unparalleled accuracy, leaving behind minimal kerf. This finesse opens doors to crafting complex designs and shapes that would be almost impossible with other methods.
2. Ceramic Possibilities
Laser cutting can handle a diverse range of materials, from the delicate elegance of porcelain to the rugged resilience of zirconia. This makes it an all-round process, serving countless industries like medical, dental, electronics, and even jewelry making.
3. Fast Speed
Compared to its traditional counterparts, laser cutting operates at warp speed, significantly reducing production times and boosting throughput. This leads to increased efficiency, cost savings, and a better production line.
4. Minimal Heat Production
The minimal heat-affected zone (HAZ) of a laser cutter ensures the material’s integrity and properties remain intact, which ultimately prevents thermal damage or any kind of warping.
5. Eco-friendly Designs
The laser-cutting process reduces the need for coolants and lubricants and minimizes resource consumption, contributing to a greener planet. With minimal waste generation, it leaves a successful footprint for a brighter future.
Types of Laser-Compatible Ceramics
Some of the major types of laser-compatible ceramics options are given below:
1. Engineering Ceramics
- Alumina (Al₂O₃): It is widely used for laser cutting designs in electronic components, cutting tools, and wear-resistant parts.

- Zirconia (ZrO₂): It is known for its exceptional strength and chemical resistance. Its high melting point makes it ideal for laser-cutting complex shapes.
2. Advanced Ceramics
- Macor: This machinable glass ceramic is particularly suitable for laser micromachining and prototyping delicate components for medical devices, sensors, and optical applications.
- LTCC (Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic): This multi-layered ceramic is widely used in electronic packaging and microfluidic devices due to its laser-compatible nature.
3. Traditional Ceramics
- Porcelain: With its fine grain structure and white color, porcelain is perfect for laser engraving and marking decorative items, jewelry, and artistic creations.
- Stoneware: Its laser-compatible nature allows for cutting decorative features, logos, and inscriptions for added aesthetic appeal.

Preparation Before Laser Cutting
Preparing for laser cutting is important for ensuring a smooth, efficient, and successful process. Here are some key steps to take before firing up the laser:
1. Material
- Choose the right material: Ensure your chosen material can withstand the laser’s heat and doesn’t emit harmful fumes when cut.
- Clean and dry the material: Remove any dirt, dust, or moisture from the material’s surface to prevent imperfections or safety hazards during cutting.
2. Design and File
- Prepare your digital file: If you are using a laser cutter with software, create your design using vector graphics software like Adobe Illustrator.
- Check for errors: Double-check your design for any errors or inconsistencies before sending it to the laser cutter.
- Set cutting parameters: Depending on the material and desired outcome, adjust the laser power and speed in the software settings.

3. Machine and Workspace
- Set up the laser cutter: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to properly install and calibrate the laser cutter.
- Prepare the workspace: Clear the area around the laser cutter of any flammable materials or obstructions.
3 Methods to Laser Cut Ceramics
The versatility of ceramics meets the precision of laser technology, paving the way for innovative creations. Some of the popular laser cutting methods for successful ceramic cutting with the help of a laser are given as follows.
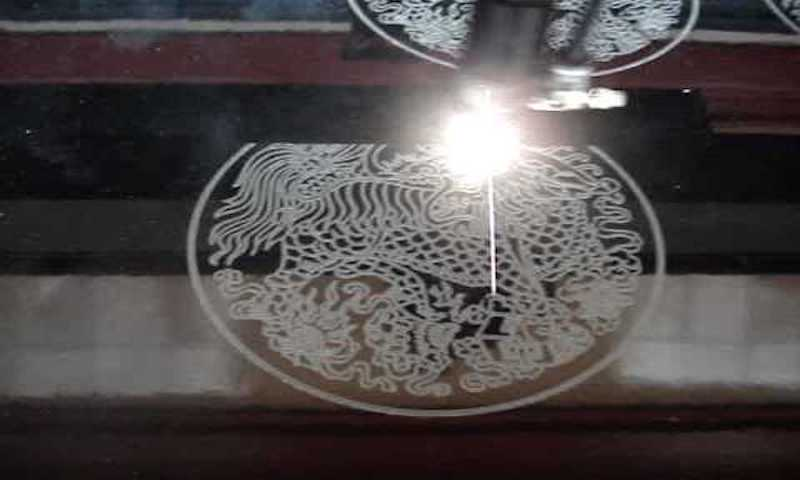
1. Fiber Laser Cutting
This precise and efficient technique of fiber laser cutting utilizes short, high-peak-power pulses to vaporize the ceramic with minimal heat spread compared to other laser cutting methods. Fiber laser cutting of biocompatible ceramics is used in the medical and dental fields. This process is also used for cutting aerospace and automotive ceramics and architectural and decorative ceramics.
While using this technique, we need to consider the fact that different ceramic materials have varying laser absorption and heat dissipation characteristics. So you may need to adjust the laser parameters for optimal results.
The advantages include:
- Reduced Thermal Impact
- Broad Material Compatibility
- High Efficiency

2. Nd: YAG Laser Cutting
This technique employs a continuous wave laser beam emitted by a neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd: YAG) crystal. The YAG laser melts the ceramic along the cutting path. Nd: YAG lasers produce narrow kerfs with minimal heat-affected zones, leading to highly accurate and clean cuts. They can cut a wide range of ceramic materials, including brittle and delicate ones, with minimal risk of chipping or cracking.
The main advantages include:
- Clean Edge Quality
- Faster Cutting for Thicker Materials
- Material Versatility
Perhaps you are interested in learning about fiber laser vs. YAG laser?
3. CO2 Laser Cutting
A classic workhorse, the CO2 laser emits infrared radiation readily absorbed by many ceramics. Compared to Nd: YAG lasers, CO2 lasers often offer faster cutting speeds, particularly for thicker materials. These laser systems are generally less expensive than Nd: YAG lasers, making them more accessible for various applications.
CO2 lasers can be used for underwater cutting of thin ceramic sheets, which eliminates thermal stress cracking risks and improves edge quality.
The benefits are:
- Cost-effectiveness
- High Cutting Speed
- Material Specificity

Setup and Tips for Laser Cutting Ceramics
Before you start working with the laser cutters for ceramic cutting, here are some important setup steps and pro tips to guide you toward creative ceramic creations:
1. Preparation is Key
- Material Matters: You need to research the specific properties to choose laser-compatible options like alumina, zirconia, or porcelain for optimal results
- Safety First: You will need to wear protective eyewear, gloves, and closed-toe shoes throughout the process.
2. Tips for a Flawless Finish
- Test Run: You have to run a test cut to fine-tune the settings and avoid costly mistakes. Troubleshooting laser-cutting flaws has also been found to be beneficial.
- Support System: For delicate or thin ceramics, consider supporting them with a honeycomb bed or sacrificial layer underneath to prevent warping.
Post-processing and Finishing
Post-processing and finishing play a crucial role in taking your laser-cut ceramic creations from good to truly exceptional. Here are some crucial steps and techniques to consider:
- Start by gently removing any dust, soot, or residue left after laser cutting. Use a soft brush or compressed air.
- For intricate cuts or hard-to-reach areas, consider ultrasonic cleaning.

- Choose an appropriate etching solution and mask any areas you want to protect.
- Apply metallic paints or foils to highlight specific elements on your piece. This adds a unique and eye-catching dimension.
- If your project involves multiple pieces, use an appropriate adhesive specifically designed for ceramics.
Future Trends in Laser-cut Ceramics
The future of laser-cut ceramic pieces is very prominent because of continuous innovation.
Expect micro-precision cutting through femtosecond laser technology, creating delicate details. 3D laser printing will rise, crafting complex ceramic structures impossible with traditional methods. Sustainability takes center stage with green lasers minimizing energy consumption and waste.
Get ready for AI-powered optimization, suggesting ideal laser parameters for flawless cuts on any ceramic type. It can be said that the future of laser-cut ceramics is a breathtaking journey waiting to be carved.
FAQs
1. Can Ceramic be Lasered?
The answer is yes, ceramic can be lasered. Laser-cutting ceramic materials is frequently a safe choice because ceramic is easily broken, with one crack swiftly destroying the entire substance.
2. Can You Laser-Cut Alumina Ceramic?
An accurate method used in the production of alumina ceramic plates is laser cutting. Because of its hardness and heat endurance, alumina poses difficulties for conventional cutting techniques. That’s why laser cutting is more suitable for alumina ceramic.
3. How does the cost of laser cutting ceramics compare to traditional cutting methods?
Laser cutting can be more expensive than traditional methods, but its precision and efficiency may offset the cost, especially for complex or large-scale projects.
4. Can the laser cutting process be used for both prototyping and mass production?
Suitable for both prototyping and mass production, laser cutting offers quick, precise designs for prototypes and efficient, consistent production for large volumes.

Conclusion
Whether you are an established ceramicist seeking to expand your toolkit or a curious DIYer embarking on a laser-fueled adventure, making aesthetic and functional elements, remember that the best learning takes place hand-in-hand with practice. Experiment, tweak, and most importantly. Laser cutting ceramics opens doors to a universe of possibilities – intricate jewelry, custom tiles, innovative prototypes, and beyond
Unlock the Secrets of Laser-Cutting Ceramic with Baison!
Ready to fire up your creativity with laser-cut ceramics? Don’t get bogged down by technical jargon – let Baison Laser be your kiln-side companion!
Whether you’re a ceramic newbie or a seasoned pro sculpting with lasers, we’ll guide you through the fiery furnace of laser cutting, from choosing the perfect material to mastering those intricate cuts. Feel free to Contact Baison Laser today if you have any queries.