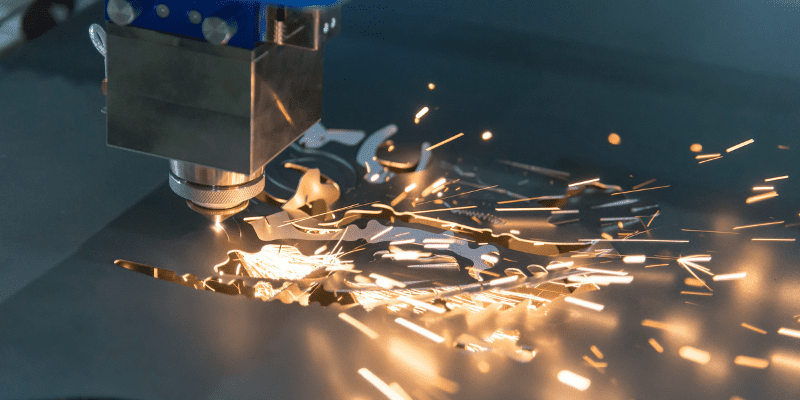
What is a Fiber Laser?- A brief overview
A “laser” can be generated via various active mediums like solids, glasses, gases, semiconductors, and even liquids. But the laser light that is generated through solid element like a “Ruby” crystal, also known as “Neodymium Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet, (Y3Al5O12) -YAG” is called “Fiber Lasers” or “Solid-State Lasers.”

What’s so special about fiber lasers is that they can perform various functions that are key to industrial manufacturing with high precision and accuracy. The most important one is “Laser Cutting,” one of the fundamentals.
The continuous wave (CW) Yb3+ doped fiber lasers are the most common in laser cutting machines as they are extremely powerful. A 01 µm fiber laser cutting machine can cut through high-strength steel easily. Not to mention most of the other metals and alloys.
Unlike traditional cutting machines with some mechanical cutter bound to wear off, these lasers don’t have such consumables. Hence, low maintenance saves energy, cost, and time in cutting processes. This can increase the profit margin for any industry.
Laser cutting is everywhere, from small-scale businesses to the giant automotive and aerospace industry. Fiber lasers are also inherently suitable for micromachining, done on a micro-scale. Thus, truly making it the face of modern manufacturing processes.
How Does the Fiber Laser Cutting Machine Work?
Fiber laser cutters use thermal cutting to cut through various metals and non-metals. It involves the following steps.
First, a high-intensity laser beam is shot from the laser generator to the workpiece. The laser beam usually reaches a high temperature close to 10000-11000 ℃ (19500 ℉), enough to melt or vaporize any material.
The details of the location and shape of the cut are fed through a numeric control system that guides the laser.
As the laser comes in contact with the material, it quickly melts or gasifies it, and pressurized auxiliary gas is blasted to the point of contact, which removes the debris.
The process continues until the desired shape is achieved.
Laser cutting machines come in many shapes and sizes, but the phenomenon behind their principal working is the same. Here are some of the crucial components of a laser cutting machine.
1. Machine Laser Source
The laser source is the heart of any laser-cutting machine. A separate unit usually creates a laser fed to the cutting head. Research shows that ytterbium Yb3+ doped fiber laser produces high-intensity lasers ranging from 900 nm to 1200 nm. Having a wide range of wavelengths means various materials can absorb the laser.
This source is excellent for cutting High Strength, Carbon, Alloy, etc. It can = produce more than 10 KW of power that is intense enough to cut through thin plates (<5 mm) as well as thick plates (5 mm-40mm)
However, thulium Tm3+ and holmium Ho3+ doped fiber laser sources can cut non-metal and transparent materials. The source unit is attached to the main unit through heavy-duty connectors, amplifier plugs, encoder plugs, etc.
2. Electrical components and Numeric Control System
The numeric control and the electronics are what you may call the “brains” of laser cutting machines. The main components are electrical servo motors, switches, operating systems, etc. All the data about the characteristics of the laser beam and details of the soon-to-be machined part are entered here.
A led control panel outside the machine gets data from the operator through computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) files. This control system feeds all the data regarding output power, cutting speed, cutting angles, depth of cut, etc.
After that, it guides the control head and rails during the cutting process. With the advent of computer numeric control (CNC), the precision of laser cutting is increased manifolds, so much so that the only limiting factor of laser cutting is the driving system.
3. Gantry System and Auxiliary Parts
Every industrial-sized fiber laser machine has a gantry system, a mechanized driveway that helps move the laser head in three-dimensional space. The gantry system comprises rails, chains, and motors that help guide the laser head.
Constant research has been going on to improve the gantry system for fiber laser to reduce the machine time and improve efficiency.
Other parts include the working table(work tables) that holds the workpiece together. Some fiber laser cutting machines have large tables that could compensate 12 meters long metal sheets and carry up to 9 tons of weight. Many laser cutting machines also have an exhaust system that removes toxic gasses from the enclosure.
4. Fiber Laser Cutting Head
The fiber laser cutting head is a device that shoots a laser onto the workpiece. It has a complex system of mirrors (traditional laser machines) or optical fibers that guide the laser beam through the nozzle.
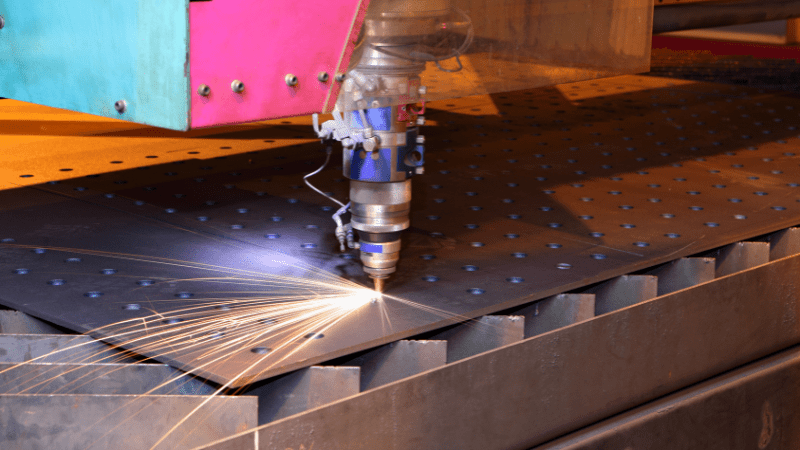
Nozzles are an important component of the laser head controlling the light beam. Not only does it directs the laser, but it also gives direction to discharge gas that blows off the molten material.
Nozzles can be adjusted manually and have a lot of influence on the cutting quality. It’s carefully calibrated before to prevent lack of penetration which can result in material melting. Different diameter nozzles are used to cut various thicknesses.
The laser head is a moving part guided by a gantry system. Typical, the laser head can move in three-dimensional space. But in special cases, laser heads are designed to move at a 45-degree angle, which helps create bevel shape cuts. These metal plates are meant to be welded later on. It saves much money, labor, and time otherwise spent on creating bevels.
Other characteristics regulated by the laser head are beam intensity, beam focus position, cutting speed, cutting feed, gas pressure, etc.
The right cutting power, speed, and feed can make or break your manufacturing processes. Just like a traditional mechanical machine, a laser cutting machine comes with a detailed chart that defines the characteristics of a laser suitable to a particular material.
The whole working station is shielded by a metallic cover that gives the laser cutting machine an enclosed environment. This protects the laser beam and workpiece from external factors like air and dust. It also protects the human eyes as the invisible rays are hazardous.
Difference Between CO2 Laser and Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
When it comes to laser cutting, two technologies stand out. Fiber and CO2 lasers. Both serve the same purpose but have different cutting capabilities. Let’s discuss their differences briefly to select the best option for your needs.
The critical difference between the two is the source of laser production. A CO2 laser has a glass chamber full of carbon dioxide gas exposed to a high electric current. This process excites the gas and results in the release of infrared rays. With the help of mirrors, these infrareds get amplified enough to cut through objects.
In a fiber laser, a crystal (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet- YAG) is wrapped by a flash tube that feeds light energy to the crystal. This excites the atoms in the crystal, which release high-energy photons. These high-energy photons are directed through optical fiber, creating a powerful laser.
Both laser types have their significance. CO2 lasers are relatively older but still used due to their exceptional metal-cutting capabilities.
| Manufacturing Process | CO2 Laser | Fiber Laser |
| Cutting Speed Thickness <8mm | Slow | Fast |
| Cutting Speed Overall | Fast | Fast |
| Cutting Sharp Edges | Lower efficiency | Higher efficiency |
| Cutting Sheet Metal | Lower Compatibility | Higher Compatibility |
| Cutting Organic Materials | Higher Compatibility | Lower Compatibility |
| Engraving Metal | No | Yes |
| Engraving other materials | Yes | Yes |
| Driving system | Gantry | Galvo and Gantry |
| Maintenance Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Operational Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Purchasing Cost | Lower | Higher |
A fiber laser cutting machine is better at cutting metals, especially ones with shiny surfaces. High reflection tends to pose a problem for older laser machines because most of the beam gets reflected. But fiber laser cutter has a sharp beam focus that helps penetrates most metals and alloys. The CO2 laser has better material compatibility with some metal and organic materials.
| Laser Cutting | Material | Fiber Lasers | CO2 Lasers |
| Metals | High strength steel | Yes | Yes |
| Mild Steel | Yes | Yes | |
| Brass | Yes | No | |
| Copper | Yes | No | |
| Aluminum | Yes | No | |
| Non-Metals | Glass | No | Yes |
| Acrylic | No | Yes | |
| Wood | No | Yes | |
| Rubber | No | Yes | |
| Leather | No | Yes | |
| Composites | Yes | No |
Since most manufacturing industries deal with steel and metals, fiber laser cutting has more market.
When it comes to cost, there is no simple answer. High-power fiber lasers are pricier than average CO2 laser cutting machines. But CO2 lasers have consumable tubes that need replacement typically after 20000 hours of operation. Furthermore, it consumes larger power during a typical run than fiber lasers. So the operational and maintenance cost adds up. For continuous and long-term projects, experts prefer fiber laser cutting machines.
Things to Consider Before Buying Your First Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
1. Material Consideration
What kind of material you manufacture is of utmost importance. Some materials benefit from fiber laser cutting and give great results, while others don’t. Fiber laser cutting machines work best on sheet metal work and materials with high reflection. Learn more about What Materials Can a Fiber Laser Cut?
2. Usage and Production Rate
If your industry requires a high production rate and manufacturing of intricate parts, then fiber laser cutting is suitable. Otherwise, you won’t be able to cover the purchase cost. I would suggest a CO2 laser machine for cutting and a fiber laser for engraving for hobbyists who want a laser machine for their backyard projects.
3. Surface finishing
Regarding the thicker material, fiber lasers may not have the best cuts, which will cost money and time in the post-processing of the project. However, lasers make the state of the art cuts for sheet metal work and thinner plate fiber.
Major Applications of Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
1. Robotics Industry
Laser-cutting machines and robotics have a deep relationship. Many laser cutting, welding, marking, and drilling machines support a robotic arm that automates manufacturing.
It is even helpful in manufacturing small intricate parts used in robots that are impossible to create using traditional cutters. Laser cutting combined with CNC has revolutionized the world.
2. Automotive Industry
The demand for automobiles is ever-growing, and so is the need for efficient manufacturing processes. Due to their high precision and shorter lead times, many automotive industry companies have switched to fiber laser cutting machines to cut hydroformed car parts.
3. Aerospace Industry
The aerospace industry deals with one of the most sophisticated designs that need accuracy. Many traditional machines affect the integrity of the material while cutting. This raises a safety concern. Plasma cutting is one example of this.
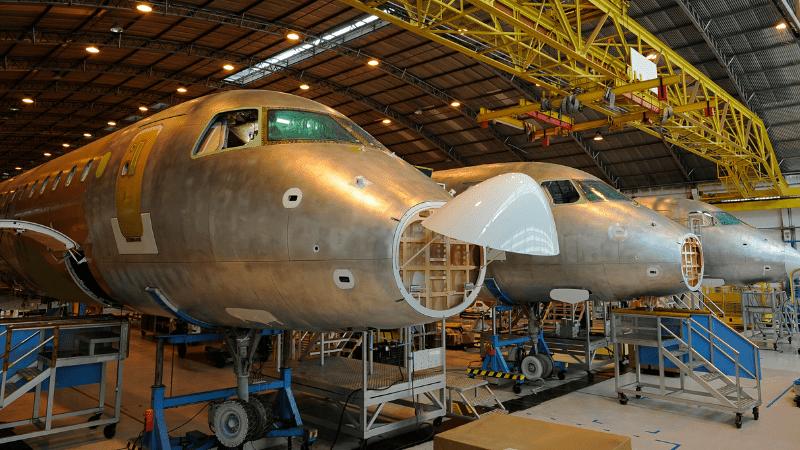
However, fiber laser cutting has solved this issue because it’s naturally good at thermal dissipation, exact cut, and minimum tolerances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Fiber Laser Cutting Machine
1. High Precision and Accuracy
Fiber laser focuses a huge power density at a small point, melting the material and forming a small pore. As the laser moves, the material is cut evenly without deformation or burrs at the edges. Since the wavelength of a fiber laser is only 1 micrometer, compared to the CO2 laser with a wavelength of 10.7 micrometers, any complex shape can be cut with superior accuracy.
Fiber laser cutting can reach a dimensional accuracy of ±0.5mm. The heat-affected zone is very small, and the final unit requires minimal to zero machining before directly using it.
2. Cutting Speed
Fiber laser cutting is faster than traditional laser techniques. Regarding thin sheets, no other cutting technique is comparable to fiber lasers. Comparing the cutting speeds of fiber and CO2 lasers, we see that a 2000W fiber laser can cut as fast as a 6000W CO2 laser.
As the fiber laser technology advances, it won’t be long until we see a high fiber laser power machine cutting thick materials at a rate that can be compared to no other technology.
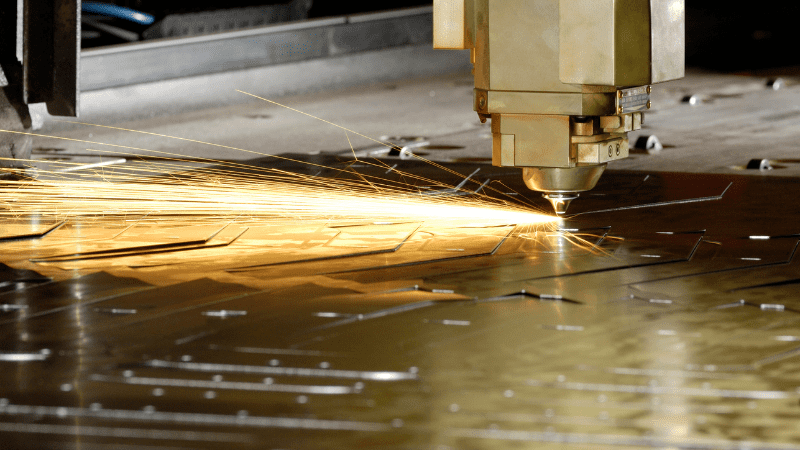

3. Non-Contact Cutting
A non-contact cutting tool means there is no need to replace the cutting tool due to wear and tear. There is no need to consider the hardness of the tool before processing every new material because laser beams can cut through many types of materials.
4. High Adaptability and Flexibility
With CNC control and automation, laser beams can be adjusted and optimized to cut complex designs and intricate edges. The compact beam packing immense power results in a minimal heat-affected zone that does not deform the shape of the final product.
5. Reduced Power Consumption
Fiber laser machines consume 50% less energy than CO2-cutting machines. Compared to CO2 lasers, fiber laser machines do not require high maintenance and costly repairs. The design is more efficient, compact, and has a smaller carbon footprint. CO2 laser machines need at least 10 minutes to warm up before processing material. In contrast, a fiber laser machine can start the process immediately.
The ability to process different materials faster makes fiber lasers suitable for high-volume manufacturers and producers.
6. Variety of Materials
For a long time, reflective materials posed a challenge for laser-cutting machines. Still, fiber lasers can efficiently process highly reflective materials like aluminum, copper, silver, gold, and polished stainless steel. Gone are the days when laser cutting was not suitable for thick plates. Due to a wide range of laser powers, fiber lasers can process thicker plates at a rate comparable to CO2 laser cutting.
Other than metals, fiber lasers can process acrylics, polyoxymethylene, poly (methyl methacrylate), Lucite, and rubber. Check out our article for more information on what materials fiber lasers can or cannot cut.
7. Expensive Investment
The only downside of fiber laser cutting machines is their high investment cost. Fiber laser is 2-3 times more costly than CO2. But considering it’s only a one-time investment offering far more significant benefits than any other laser technology, fiber lasers are cost-effective in the long run.
Fiber laser machines do not require regular maintenance or high operational costs. A 3000W fiber laser consumes an estimated 10kW of electric power. On the other hand, the equivalent 4000W CO2 laser machine will consume energy as high as 250kW. This makes a huge difference in the annual electricity bills between both machines.
In addition, due to its efficient design, a fiber laser machine can last a lifetime.
Why Choose Baison Laser for Fiber Laser Cutting Applications?
Baison Laser is an expert in providing premium and durable fiber laser cutting machines suitable for multiple applications such as sheet metal cutting, shaping, broaching, drilling, etc.
Built with the highest quality of material and advanced laser technology, our machines can handle various industry requirements. Moreover, our prices are market competitive, and after-purchase services are parallel to none.
Our various catalogs include high-tech fiber laser cutting, welding, cleaning, and engraving machines.
Contact our experienced technical team to get the best bang for your buck. Get your quote now and be part of the Baison Laser family.