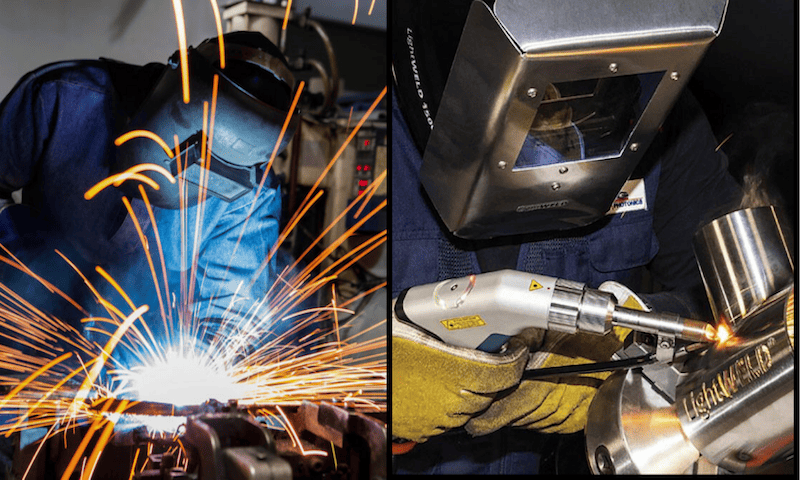
What is Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)?
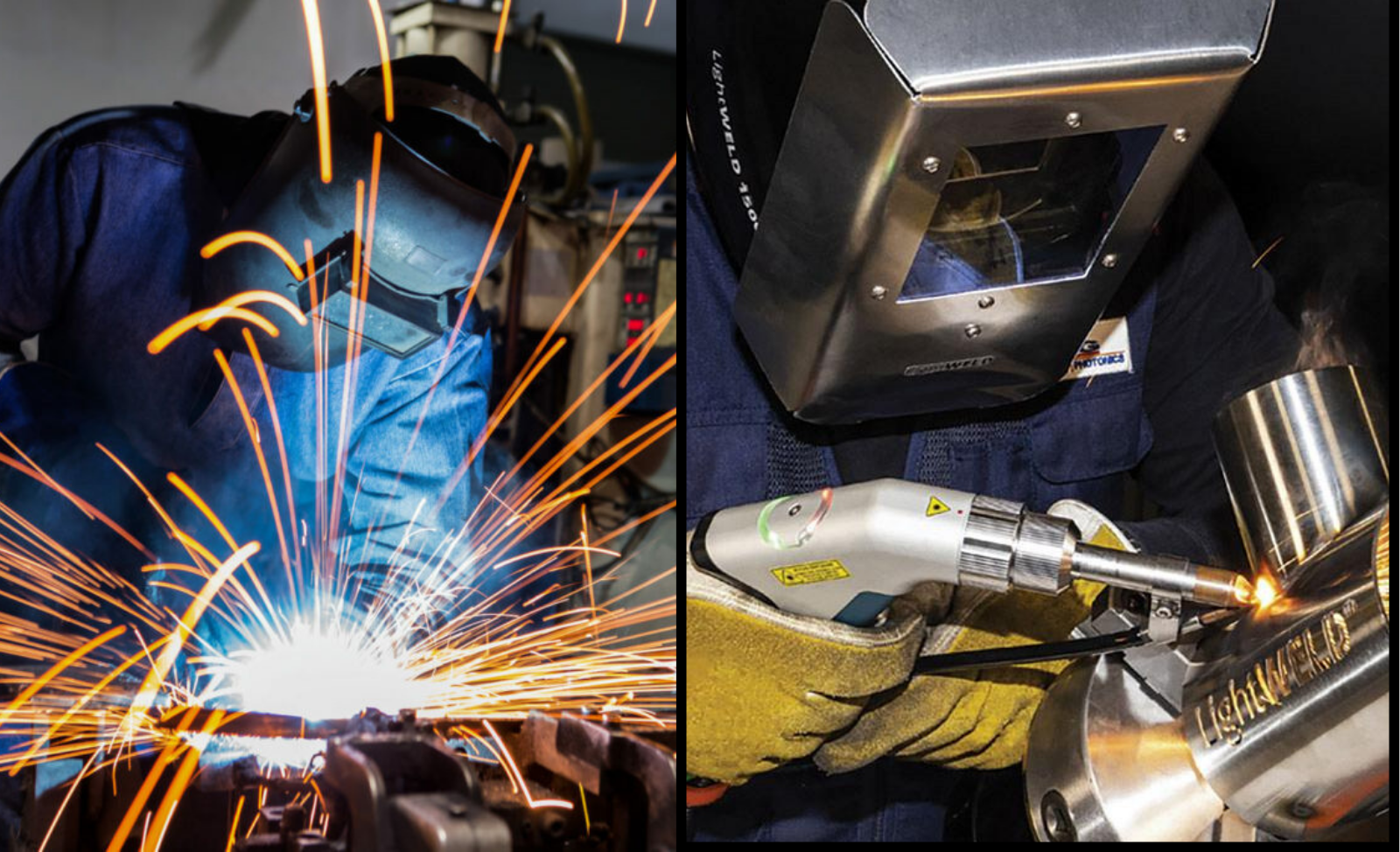
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) which is mostly referred to as stick welding is one of the most important methods of welding. The Welding Process Handbook by K Weman (2011) describes the evolution of Arc Welding from complex processes into simpler methods like SMAW. Due to its simplicity but incredible effectiveness, it has served as a core method in numerous structures and assemblies worldwide. It is one of the traditional welding processes.
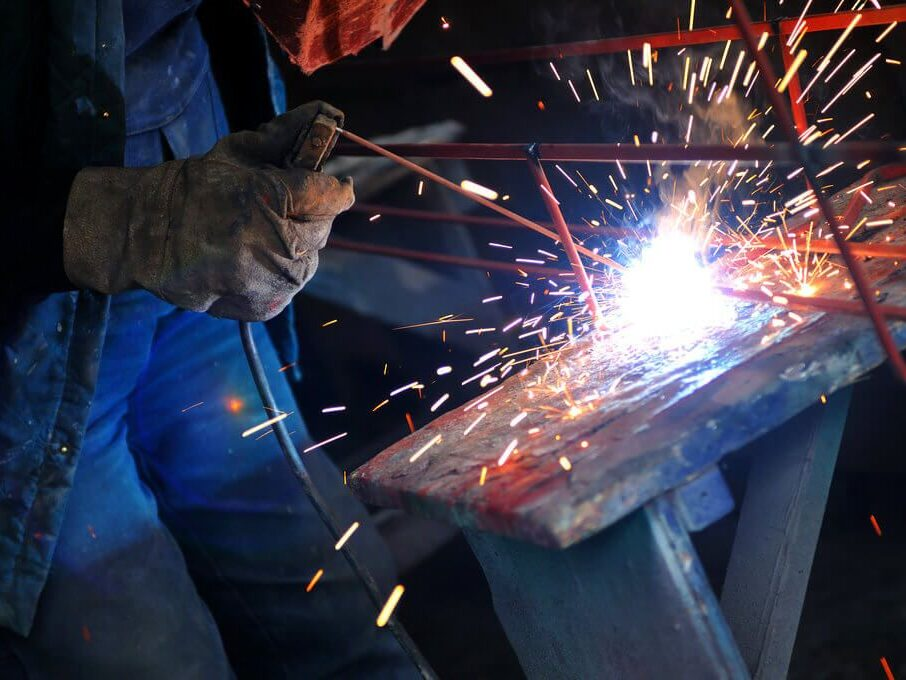

Welding Process
The core of the SMAW process is the electrode. SMAW merges the electrode and filler metal into a singular entity, the consumable electrode coated in flux. In this way, SMAW differs from other techniques such as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) which have the electrode and filler metal separate. You may want to know about the SMAW compared to GMAW.
The SMAW method creates an electrical arc when the electrode strikes the workpiece. This arc has temperatures reaching thousands of degrees which makes it strong enough to melt both the workpiece and electrode.
The melting electrode creates filler metal for the joint. At the same time, the flux that was coating the electrode disintegrates therefore releasing gases to shield the molten wield pool from contamination from the atmosphere. The duality of this action creates not just a clean weld but also a layer that further shields the cooling weld from external contaminants known as slag.
What is Laser Welding?
Laser Welding is the fusion of age-old methods of metal works with cutting-edge science and technology of light. Laser emerged as the world pursued more precise ways of doing just about everything and with the presence of technology, welding also advanced.
Laser Welding differs from traditional welding methods since it does not rely on direct flame or electric arc but rather uses a laser beam that produces heat. You can check out our blog to see how laser welding and other methods compare.
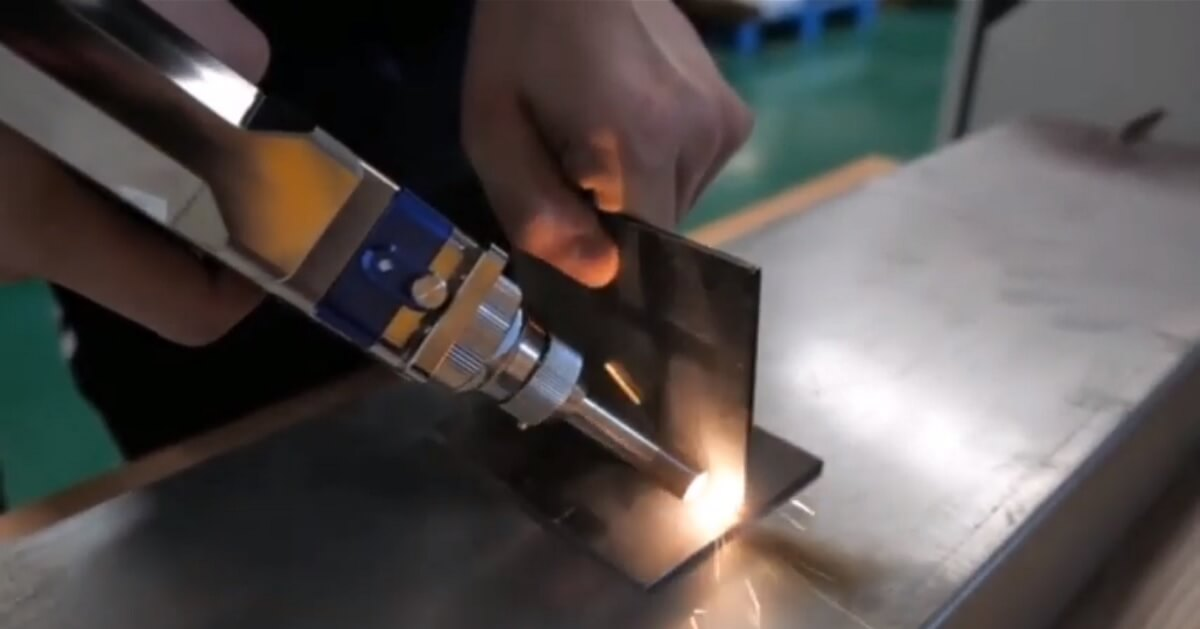

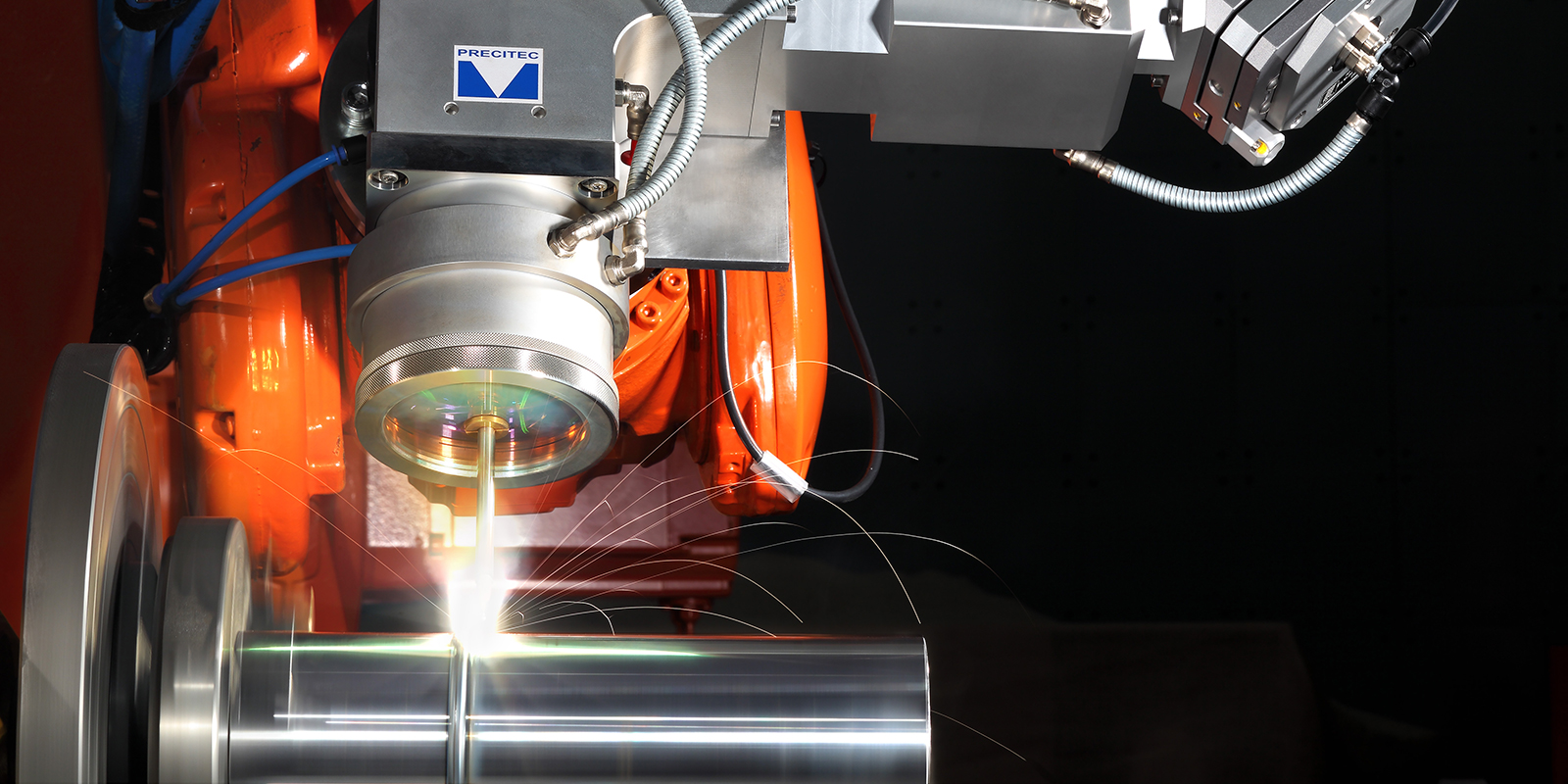
Welding Process: Focused Laser Beam
Laser is an acronym for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Cheng et al., (2021), describe Laser Welding as a process that melts and joins metals by heating them with a laser beam. This amplified light is focused on a small spot on the workpiece. An intense heat of over several thousand degrees Celsius is generated at the focal point. This heat melts the material and fuses materials together as the focal point is moved over the desired path.
Precision is the defining characteristic of Laser Welding. It is able to utilize localized heating which ensures that the heat energy is only focused on the small portion of the material at any given time. This leaves the surrounding areas unaffected thereby resulting in minimal distortion, cleaner welds, and less post-weld processing.
What Materials Can SMAW and Laser Weld?
There are several factors that decide the welding technique to be used including desired outcome and the nature of the materials being used.
SMAW Welding
- Steel: As the most common structural material, all the various grades of steelwork really well with SMAW.
- Stainless Steel: It’s mainly known for its anti-corrosive properties and is used in kitchenware and infrastructure. Stainless steel is often welded using the SMAW technique.

- Cast Iron: Welding cast iron can be challenging due to it’s carbon content however, SMAW has proven a great solution especially when it comes to repair tasks.
- Alloys: SMAW works on various metal alloys whether it’s copper-based or nickel-based.
SMAW’s resilience makes it compatible with thicker materials making it the best choice for heavy-duty and robust applications. This resilience also makes SMAW able to weld on painted, rusted, or even slightly contaminated surfaces. A feature that’s not found in other delicate welding techniques.
Laser Welding
Laser as a welding process is defined by precision and delivery of a focused laser beam which makes it compatible with a unique set of materials.
- Aluminum: Mainly used in aerospace and automotive industries due to it’s strong and lightweight properties which are well preserved under Laser Welding.
- Titanium: It’s popular in high-performance aerospace and medical implant applications and requires the high precision of the laser beam.
- Stainless Steel: Laser welding also works with stainless steel just like SMAW, especially in cases that need fine detail.
- Plastics: Laser welding’s capabilities extend beyond metal due to its versatility especially when applied to join some thermoplastics. This has been vital in certain industries such as medical devices and electronics whereby some small and precise plastic welds are essential.
SMAW Welding VS. Laser Welding: Actual Visible Differences
Here is a deeper dive into practical differences in SMAW and Laser Welding beyond fundamental techniques.
The table showcases the inherent contrasts between SMAW and Laser Welding, two techniques which, despite sharing the common goal of joining materials, show many differences in their approach and outcomes.
1. Material Compatibility
SMAW is a seasoned veteran, Chen et al., (2023) notes this traditional technique has the capability of handling a wide range of metals with particular excellence with iron and steel. that SMAW is a versatile choice in numerous traditional projects. While Laser Welding on the other hand brings in a unique ability of fusing certain plastics. Laser’s prowess in lighter metals also showcases its more specialized applications.
2. Speed of Operation
SMAW is manual in nature and the constant need for electrode manipulation makes it slower compared to Laser. Laser Welding’s ability to deliver focused energy at incredible speeds gives it an advantage in repetitive and large-scale tasks.
3. Material Thickness
SMAW is more adaptable to both thin and thick materials and isn’t intimidated easily by the density of the material.
Laser Welding on the other hand specializes in thinner materials and excels in precision to produce perfect weld without excessive heat dispersion.

4. Application Scenarios
SMAW works well in challenging environments whether it’s windy outdoors at a construction site or a simple indoor repair task. It’s resilience is one of it’s greatest assets. Laser Welding on the other hand is best suited in controlled environments where accuracy and minute detailing are vital.
5. Working Methods
SMAW heavily relies on the expertise of the welder so it is vital that skilled labor is applied for optimal results. The skills are honed over decades which ensures reliable and robust welds. Laser Welding on the other hand employs a blend of manual and automated operations.
Pros and Cons of Laser Welding
In order to understand laser welding more comprehensively, let’s take a look at its advantages and disadvantages.
Pros of Laser Welding
- Precision: The focused beam makes the results highly accurate with little to no margin of error.
- Clean Welds: The precision of the laser beam means that the area of focus is the only one affected. Thereby there are fewer inclusions and contaminants.
- High Speed: Laser welds are synonymous with faster work due to the direct energy focus by the use of laser beam
- Minimal Heat Effects: The precision of the laser beam ensures that there is lowered thermal distortion hence the material properties mainly stay the same.
Cons of Laser Welding
- Expensive: The initial equipment costs can be very high.
- Material Limitations: Laser can struggle with some reflective metals since it uses light to generate heat. Reflective metals can lead to distortion of the light which might lower precision.
- Risk of High Radiation: Safety measures when using laser beam requires the use of specialized equipment because of the high levels of radiation.
Pros and Cons of SMAW Welding
After understanding the advantages and disadvantages of laser welding, the following are the advantages and disadvantages of SMAW welding.
Pros of SMAW Welding
- Versatility: From old and rusted surfaces to newer ones, SMAW is one of the most adaptable techniques and works with a wide range of metals and under many different conditions.
- Portability: SMAW’s equipment is more mobile and suited for both onsite tasks.
- Economic: The equipment is not as costly and therefore accessible to more people.
- Toughness: SMAW’s resilience in handling contaminants and impurities is an advantage over other techniques.
Cons of SMAW Welding
- Depends on Welder Skills: SMAW highly depends on the skill of the welder which can me it’s results inconsistent. Quality can vary based on the welder’s expertise.
- Slower: SMAW falls short in terms of speed to the laser.
- Cleanliness: SMAW might require post-weld cleaning since it can leave spatter or slag.
Which is Better – SMAW or Laser Welding
The notion of better in the realm of welding is often subjective and contingent on the specific demands of a project. SMAW and Laser have both carved out their niches in different sectors, mainly driven by their inherent strengths and limitations. To be able to decide between these two techniques, one must assess the project’s objectives, challenges, and desired outcomes.
Scale of Production: SMAW VS. Laser welding
Laser Welding: In industries where high volume production is required, Laser Welding is often the obvious choice. The method hails in precision which ensures that every weld whether the first or the thousand meets exact same standards.
This consistency is vital in electronics manufacturing and the automotive sector where slight deviations can lead to inefficiencies or product failures. When Laser Welding is automated, it’s the best choice for mass production lines.
SMAW: This methodology thrives in environments in which adaptability is vital. It is efficient for repair tasks, bespoke projects, and construction work with unpredictable conditions while the volume isn’t necessarily high.
The manual nature of SMAW allows for on-the-spot adjustments thereby catering to varied and unique project demands. SMAW’s manual nature distinguishes it from other arc welding which can be semi-automated such as Gas Metal Arc Welding. This is a comparison article about SMAW and GMAW.

Budget Constraints: SMAW VS. Laser Welding
SMAW: One of the main advantages of SMAW is cost-effectiveness. The equipment for SMAW welding is pretty straightforward and doesn’t have high initial costs when compared to laser systems. This is why it is more suited for individuals and businesses with tight budgetary constraints. In the case where a project doesn’t really benefit from the advanced Laser Welding capabilities, SMAW becomes a better choice.
Laser Welding: Although the initial costs of laser welding are considerably high, the long-term returns make up for it. For industries where operations require precision, speed, and consistency is offered almost exclusively laser welding, is an obvious choice. Laser Welding consistency ensures that products are high-quality and production rates are much higher which saves money over time.
Environmental and Safety Considerations: SMAW VS. Laser Welding
SMAW: When this technique is used, slag, fumes, and splatters are produced which makes it a requirement to use appropriate safety gear. It also means that there will be post-weld cleanup and treatments. Training is also required when working with open arcs to ensure safety.
Laser Welding: This is a cleaner technique with less residue and emissions. Nevertheless, the intense light from the laser can lead to potential eye damage. So it is non-negotiable to wear protective equipment, especially for the eyes.
Conclusion
To compare SMAW to Laser is evidence of how much the industry has evolved. SMAW stands testament to the robust underpinning of welding while laser represents it’s precise, cutting-edge future. Find the technique that suits your needs because both have evolved over the years to meet your demands.
Baison Laser: Simplifying Your Laser System Selection
Selecting the ideal laser system for your business can seem overwhelming given the numerous factors at play. It’s crucial to identify a system that aligns with both your needs and budget. Enter Baison. We provide excellent laser welders like handheld laser welding machines and welding robots.
Baison provides laser system quotations tailored to businesses of all scopes and scales, ensuring you receive the most competitive offer. Just send us your requirements, and our dedicated team will respond with a customized quote.






