For the application of metal laser cutting machines, cutting quality is the first condition to be considered. Metal laser cutting machines with good cutting quality can create value for metal fabricators. Therefore, it is necessary to master the problems often encountered in the cutting process and their solutions.
Now let’s get down to brass tacks and talk about some typical quality defects and how to prevent them—because ain’t nobody has time for subpar cuts! And find the most suitable laser cutting machine in Baison.
Understanding Laser Cutting
Laser cutting in metal fabrication offers several advantages, including high precision, versatility, speed, and minimal heat-affected zone. Laser processing is widely used in industries such as manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and more.
Understanding the types of laser cutting machines and the working principles of laser cutting can help in selecting the right equipment and optimizing the cutting process for specific applications.
Types of Laser Cutting Machines
There are several types of laser cutting machines, each designed to cut different materials and workpieces. The main types of laser cutting machines include CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and neodymium-doped YAG lasers.
These machines use different laser powers of high quality cut through various materials, such as metal, plastic, and wood. The laser beam is focused through a lens to create a concentrated light signal that can accurately cut through the material surface.
CO2 Laser Cutting Machines: These machines use a carbon dioxide gas laser to generate the laser beam. CO2 laser cutters are versatile and can cut through a wide range of materials, including wood, acrylic, plastics, fabrics, leather, and some metals. They are commonly used in industries such as signage, packaging, and textiles.
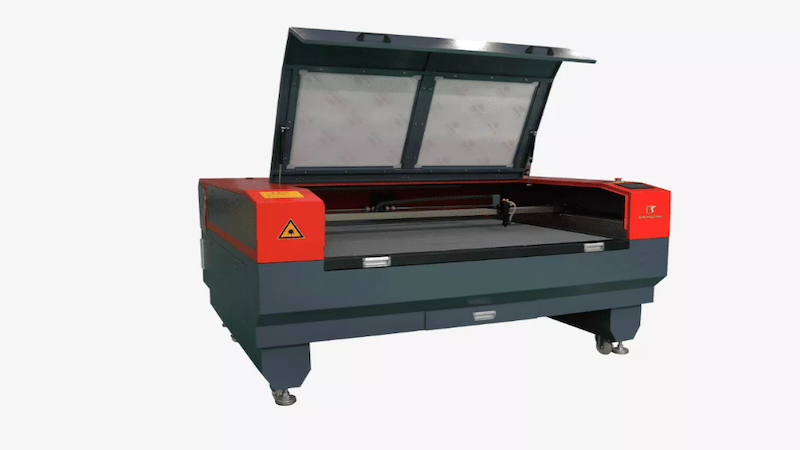

Fiber Laser Cutting Machines: Fiber laser cutting machines use a solid-state laser source, typically a fiber optic cable, to generate the laser beam. Fiber lasers are highly efficient and are primarily used for cutting metals, such as stainless steel, mild steel, brass, and copper. They offer high cutting speeds and are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication. The light signal is emitted through the focusing lens onto the workpiece.
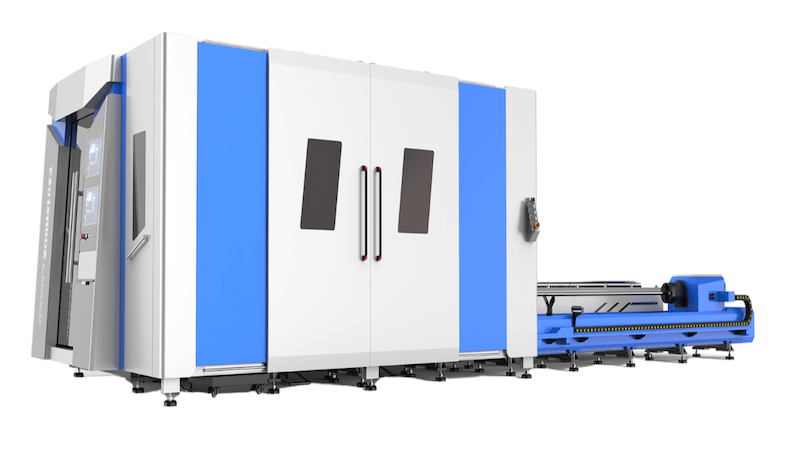

YAG Laser Cutting Machines: YAG (yttrium-aluminum-garnet) lasers are solid-state lasers that use a crystal medium to generate the laser beam. YAG lasers are known for their high output power and are capable of cutting through thicker materials, such as metals, ceramics, and some plastics. They are commonly used in industries that require high precision and accuracy, such as jewelry making and electronics. The YAG laser’s ability to cut through thick steel and workpiece makes it ideal for industrial applications.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
Laser cutting is a precise and efficient process that utilizes a high-powered laser beam to cut through various materials. Here’s how it works.
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a focused laser beam to cut through materials. The laser beam is generated by a laser source and directed through a series of mirrors or fiber optics to the laser head. The laser head contains a lens that focuses the laser beam to a small spot size, increasing its intensity.
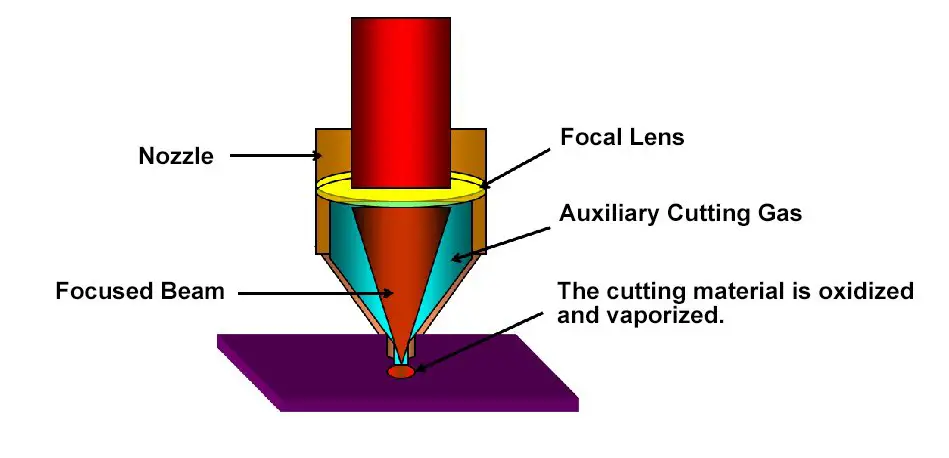
When the laser beam interacts with the workpiece, it heats and vaporizes or melts the material, creating a narrow cut. The focused laser beam provides high energy density, allowing for precise and controlled cutting. The movement of the cutting head, guided by CNC (Computer Numerical Control), determines the shape and light path of the cut.
Advantages of Laser Cutting
Compared with other thermal cutting methods, laser cutting has many significant advantages. The following are specific advantages.
- Precision: Laser cutting offers high precision and accuracy, allowing for intricate and detailed cuts. It can achieve tight tolerances and produce complex shapes with minimal distortion.
- Versatility: Laser cutting machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, fabric, leather, and more. This versatility makes laser cutting suitable for various industries and applications.
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser cutting is a fast and efficient cutting method. It can quickly process materials, reducing production time and increasing productivity. Additionally, it eliminates the need for secondary processing steps like deburring or finishing.
- Non-contact Process: Laser cutting is a non-contact process, meaning there is no physical contact between the cutting tool and the material. This eliminates the risk of material deformation or damage, especially for delicate or sensitive materials.
- Minimal Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): Laser cutting produces a narrow and concentrated heat-affected zone due to laser irradiation, minimizing thermal distortion and reducing the risk of material warping or discoloration. This is particularly important for materials that are heat-sensitive.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
Introduction to 10 Laser Metal Cutting Quality Defects and Prevention Methods
Laser metal cutting is a widely used technique in various industries, offering precise results and increasing production efficiency. However, it is not without its challenges. The process can encounter several quality defects that may compromise the integrity of the final product.

1. Burr Formation
Burrs are raised edges or rough surfaces that occur during laser cutting. They can affect the aesthetics and functionality of the cut parts. Burr formation can be caused by factors such as improper laser focus, excessive cutting speed, or inadequate assist gas pressure.
Prevention methods:
- Optimize laser focus and beam quality.
- Adjust the laser focus position, power density, and feed rate on the laser cutter machine to ensure a clean cut.
- Use an appropriate assist gas (such as nitrogen gas) and maintain proper air pressure to aid in the removal of molten metal.
2. Heat-affected Zone (HAZ)
Laser cutting generates heat, which can lead to a heat-affected zone around the cut edge. This zone may have altered material properties, such as increased hardness or reduced ductility, affecting the performance of the cut parts.

Prevention methods:
- Optimize cutting parameters such as laser power density, cutting speed, and focus to minimize heat input.
- Use a high-quality laser cutting machine with precise control over parameters, including the nozzle, focus lens, and light.
- Consider post-cut treatments like annealing, or stress relieving to mitigate the effects of the HAZ.
3. Dross or Slag Adherence
Dross or slag refers to the molten material that solidifies on the bottom surface of the cut. Adherence to dross can affect the quality of the cut and may require additional post-cut cleaning.
Prevention methods:
- Optimize cutting parameters to minimize dross formation, such as reducing cutting speed or increasing assist gas pressure.
- Use assist gas with appropriate composition and flow rate to aid in the expulsion of molten material.
- Implement post-cut cleaning methods, such as grinding or sandblasting, to remove any adhered dross from the cutting slit. This is especially important after laser welding, as it helps maintain the desired cutting speed and prolong the lifespan of the machine.
4. Edge Roughness or Striations
Laser cutting can sometimes result in rough or uneven edges, which can affect the aesthetics and functionality of the cut parts.
Prevention methods:
- To achieve a smooth and clean cut, optimize the cutting parameters of the machine, such as power, speed, feed rate, and assist gas pressure.
- Use a laser cutting machine with high-quality optics and precise control over cutting parameters.
- Implement post-cut treatments, such as deburring or polishing, to improve edge quality if necessary.
5. Material Discoloration
Laser cutting utilizes powerful light to feed laser energy into the material, resulting in precise cuts. However, this process can sometimes lead to discoloration or oxidation on the cutting edge, impacting the overall appearance and surface quality of the parts.
Prevention methods:
- Optimize cutting parameters, such as power, laser focus position and speed, to minimize heat input and reduce discoloration.
- Use assist gas with appropriate composition and flow rate to protect the material from oxidation during laser cutting. The laser power supply provides the necessary laser power, while the laser tube emits a focused beam of light for precise cutting. This ensures a laser focus on the material and enhances the overall cutting quality.
- Implement post-cut treatments, such as passivation or surface coating, to restore the original appearance and prevent further oxidation.
6. Gas Pressure Fluctuations
Inconsistent gas pressure can result in variations in the cutting process, leading to irregularities in the cut quality, such as taper or angle deviations.

Prevention methods:
- Use a laser cutting machine with a stable and accurate gas pressure control system.
- Regularly calibrate and maintain the gas pressure control system to ensure its accuracy and stability.
- Monitor and adjust gas pressure as needed during the cutting process to maintain consistent cutting conditions.
7. Warping or Distortion of Thin Materials
Laser cutting thin materials with high power can sometimes result in warping or distortion due to the intense heat input.
Prevention methods:
- Use a laser cutting machine with high power and a high-frequency pulsing feature to minimize heat input and reduce the risk of warping.
- Implement proper clamping or fixturing techniques to minimize material movement during laser cutting. This ensures a laser focus position, while also optimizing the performance of the laser tube and laser power supply.
- Consider using a heat sink or cooling system to control the temperature of the material during cutting with a laser power supply. This is important for maintaining the optimal performance and longevity of the laser tube. Additionally, it is crucial to ensure the laser focus position remains accurate for precise cutting results.
8. Kerf Width Variation
Kerf, the width of the cutting slit made by the laser, is crucial for accurate dimensions and proper fitment of parts. A narrow kerf allows cut patterns to be nested as close as one beam diameter apart, an effective way to reduce scrap metal. Inconsistent kerf width can negatively impact the cutting surface and cutting seam. Therefore, it’s important to optimize the cutting speed to ensure precise results.

Prevention methods:
- Ensure proper alignment and calibration of the laser cutting machine.
- Regularly inspect and maintain the focus lens and laser source to ensure consistent beam quality and spot size.
- Implement closed-loop feedback systems that monitor and adjust cutting parameters in real-time to maintain consistent kerf width.
9. Material Re-solidification or Re-melting
Laser cutting has the power to cause re-solidification or re-melting of the material along the cut edges, leading to rough or uneven surfaces.
Prevention methods:
- Optimize cutting parameters, such as laser focus position, power, and speed, to minimize the risk of re-solidification or re-melting caused by the laser tube.
- Use assist gas with appropriate composition and flow rate to aid in the removal of molten material.
- Implement post-cut treatments, such as grinding or sanding, to smoothen any rough or uneven surfaces.
10. Gas Composition Optimization
Different materials may require specific gas compositions to achieve optimal cutting results. Using the wrong gas composition can lead to poor cut quality, increased dross formation, or excessive heat input.
Prevention methods:
- Consult the material specifications and laser cutting machine manufacturer’s guidelines to determine the appropriate gas composition for the material being cut.
- Adjust the gas composition as needed to achieve the desired cutting results, such as using a nitrogen-oxygen mixture for stainless steel cutting.
- Regularly monitor and analyze the gas composition to ensure its accuracy and consistency.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
Solutions for Nonnormal Spark When Cutting Low Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel
Nonnormal sparks during laser cutting of low carbon steel indicate poor cut quality and potential defects. To rectify this issue, several solutions can be implemented:
- Adjust the focal length and cutting speed: Modifying the focal length can help improve the quality of the cut by ensuring precise focus on the material. It is important to consider the cutting speed when making these adjustments. This will optimize the performance of the laser tube and enhance the overall laser cutting process.
- Increase assist gas pressure: By increasing the pressure of the auxiliary gas, a more controlled cutting process can be achieved, resulting in better quality cuts.
- Modify nozzle design: The design of the nozzle plays a crucial role in directing the assist gas flow. Modifying it to optimize gas distribution can help eliminate nonnormal sparks.

Insufficient shielding gas coverage on the cut metal surface may result in nonnormal sparks during laser tube cutting. Here are some solutions to address this issue and improve cutting speed.
- Increase nitrogen flow rate: Increasing the flow rate of nitrogen as an assist gas can enhance shielding and prevent nonnormal sparks while cutting stainless steel.
- Utilize a protective film: Applying a protective film on the stainless steel surface before laser cutting helps maintain proper shielding, reducing the occurrence of nonnormal sparks.
By implementing these solutions, manufacturers can effectively address nonnormal spark issues when cutting low carbon steel and stainless steel using laser technology.
FAQs
1. How do I prevent excessive heat from affecting my cuts?
Excessive heat during laser metal cutting can be prevented by using suitable cooling techniques such as air or water cooling systems. Optimizing laser power settings and controlling the speed of the cutting process helps manage heat generation.
2. How can I prevent tapering in my cuts?
Tapering, where the cut width varies along its length, can be mitigated by optimizing cutting parameters such as focal point position, cutting speed, and assist gas pressure. Ensuring proper alignment of the laser beam also helps maintain consistent cut quality.
3. Are there any precautions for cutting reflective metals?
When cutting reflective metals like aluminum or copper, it is essential to use appropriate wavelength lasers and specialized optics. Implementing a back reflection protection system further ensures safe and efficient cutting.
4. How can I avoid distortion in delicate materials?
Delicate materials prone to distortion during laser metal cutting can benefit from using lower power settings and slower cutting speeds. Employing a smaller focal laser spot size also aids in minimizing heat-affected zones and potential material deformation.
Ready to Get Your Own Laser Machines?
Boost your operations with Baison Laser's advanced, customized technology!
Conclusion
Metal laser cutting is an extremely flexible manufacturing process that provides high-speed, high-quality cutting for parts used in a variety of applications.
To ensure high-quality laser metal cutting, it is crucial to address and prevent common defects that may arise during the process. By implementing effective prevention methods, you can enhance the overall cutting performance and achieve optimal results.
Baison Helps You Get the Best Cut!
The important factor of cutting quality is the quality of the metal laser cutting machine itself, so you must choose a strong manufacturer when buying equipment. Baison Laser has nearly 20 years of experience in the laser cutting machine manufacturing industry. With strong technical strength, we have established a good reputation in the industry. Welcome to consult more details and get the application evaluation today!