What Is Resistance Spot Welding?- An Overview
Resistance Spot Weld (RSW), as the name suggests, utilizes strong heat concentration caused by high electrical resistance to fuse two metal pieces at a fixed spot. It’s easy to perform and has a simple working principle.
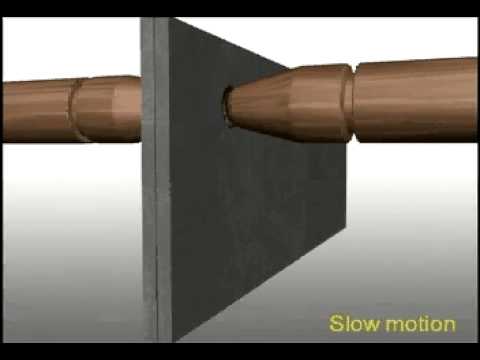
RSW welding machines have two electrodes, like prongs, that grab the metal piece together. These electrodes are made of copper, which is a great conductor. In contrast, sheet metal or a thin plate is a poor conductor of electricity.
Once the electrode is in place, the circuit closes, and high ampere current start to flow. Steel is a poor conductor and resists this flow, creating intense friction between the molecules. This raises the temperature to 2000℃ (3632 ℉), which melts and fuses the metal pieces at the spot. Also known as the “Weld Nugget.“
The current passes for a few seconds and then stops, but the pressure is still applied at the spot. This further fuses the parts as the pressure holds. Once cooled, the electrodes are dispatched, and the spot weld is achieved.
Power Source
The type of electric current greatly influences the output of RSW welding. The current that comes into our power socket is mostly an Alternating Current (AC) of 120 or 220 V with a frequency of 50-60 Hz.
You may notice that AC passes through the zero amplitude line at least two times in one cycle. In RSW welding, this effect translates into the pulsating supply of current and causes energy losses. To reduce this effect, modern machines resort to two options.
The first is to use three-phase AC power instead of a single phase. With this, three peaks are in one cycle, and the pulsating effect is reduced, resulting in smoother spot welds. However, it’s still not enough.
Researchers have deduced another way to supply constant power supply. The supply is converted into a high-frequency square wave by passing a three-phase current through an inverter technology.
After that, these waves move through a “Diode Rectifier” that converts them into an even higher frequency Direct Current (DC) power supply. This new power source is perfect for smooth current supply and produces high welding quality.
There are essentially two types of RSW machines you can buy. One is your everyday manual spot welder. It’s suitable for small businesses or backyard projects.
Another is a “Robotics” spot welding machine seen in large industries. In this case, spot welding is carried out by an automated robotic arm.
What is Laser Welding? – An Overview
Laser welding is a modern technique that is getting popular in the modern manufacturing industry. It involves the use of high-powered laser beams to melt and fuse two workpieces with or without the use of filler material.
The source of their power categorizes multiple laser machines. The most common is “Fiber laser” and “CO2 laser” machines.
Fiber laser, also called solid-state laser, is generated when light is introduced in a “Neodymium Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet, (Y3Al5O12) -YAG” (solid crystal), which excites the atoms within the crystals.
And by using optical fibers and mirrors, the newly excited photons are amplified to become a functional beam. This beam travels to the welding head, which performs the required operation. It’s also known as YAG laser welding.
CO2 works similarly, but instead of solid crystal as a source, it uses a gas chamber filled with carbon dioxide as a gain medium. A high current passes through it, which excites the atoms, and infrared energy is released, which is then amplified to use for different purposes.
Fiber laser welding is powerful and multi-purpose. It’s suitable for small businesses and large industries alike. Unlike traditional welding, fiber lasers are compatible with many materials, such as sheet metal, steel, carbon steel, aluminum, thermoplastics, etc. It also produces less heat overall, which results in decreased thermal deformations. This saves costs in post-production and positively affects profits.
You can use it for thin and thick plates though the welding speed differs with shape. There are tons of welding settings in a typical laser welding machine that can help you produce the best weld with limited power.
Laser welding can be done with or without the filler material. This increases its practicality in terms of welding performance. Wire and powder fillers are typically used when there is a gap between two workpieces.
You can use laser welding for tack/spot welding and long seams. The welds are strong and have minimum welding defects. Laser welding is easy to master and is very low maintenance. These days, manufacturing plants are using welding robots that are much more efficient and increase production.
It has been observed that laser welding produces less toxic smoke than traditional welds; however, eye protection gear is crucial during welds.
Laser Welding vs. RSW Welding
Let’s dig deep into the differences between these two welding types.
Benefits of RSW Welding Over Laser Welding
Low Cost
When it comes to handheld spot welding machines, the price is lower than similar laser welding products. The operational cost is also low compared to laser welding. It’s especially good for thin steel plates. It has lower thermal conductivity, so the heat remains concentrated in the spot between the electrodes.

However, the operational cost is affected by the material at hand. For example, aluminum alloys have a higher thermal conductivity, which requires greater amperes of current. Bigger transformers are needed to supply such high amperes, which can increase the overall cost.
Easy and Quick
Spot welding is easy to handle, and handheld machines are readily available. You can quickly do spot welds in succession and get relatively consistent results. It doesn’t require much skill, too, so it’s perfect for a novice.
Many automobile workshops have a spot welder to fix small damages and join spare parts. Laser welding machines are relatively new, so many small-scale businesses can’t afford them.
Semi-automotive and automatic machines are popular in larger industries. Robotic arms incorporated with spot welding electrodes are used in large manufacturing plants. They are extremely quick and make production much faster.
Reduced Distortion
Both laser welding and resistance spot welding dissipate less heat. RSW welding, however, releases an even lesser amount of heat. And by the very nature of this welding process, the resulting joint produces less distortion. The electrodes remain clenched for milli-seconds as the current passes and melt the metal.
Afterward, the pressure remains intact, and the weld is allowed to cool. This restriction while cooling prevents the mechanical stresses from propagating, which is why we see less overall distortion.
Although, laser welding, compared with traditional techniques, isn’t very far behind in preventing thermal distortions.
Benefits of Laser Welding Over RSW Welding
Practical Applications
Laser welding is miles ahead of RSW welding when it comes to practicality. First, RSW welding is only good for spot welding, and that’s it. You can’t do continuous welding with it. On the contrary, laser welding can do both spot and continuous welding.

Another restriction is that RSW can only do lap joints between overlapping workpieces. So you can’t perform butt joints or any other kind with it.
RSW welding can’t work with a workpiece thickness greater than 6 mm, which is another hindrance. It’s particularly suited for sheet metal work only. However, fiber lasers can easily work with sheet metal and thin and thick plates.
Laser welding is much more practical, and there is no restriction regarding the type of joints, position of welds, and materials.
Lasers welding can also form joints using filler metal suitable for pieces with spaces in between.
Laser welding is used in aircraft manufacturing, shipbuilding, micro-machining, construction, and many more industries. However, the automotive industry primarily uses spot welding. It’s said that a typical car has 4500 spot weld joints.
Precision
Laser welding is much more precise than spot welding. It’s because fiber lasers use amplified light which can target the workpiece in the most precise manner. A specialized field called “Precision Welding” uses lasers to weld intricate shapes at the micro level. This unique property of Laser technology is utilized in the medical industry, micro-machining, jewelry making, etc.
Range of Materials
Both laser welding and RSW welding need preliminary preparation of material. But lasers can do away with a simple cleaning. Whereas for RSW, a weld-thru-primer is recommended for longer life.
There is no comparison regarding the range and size of material the fiber laser can handle. You can use it for sheet metal, aluminum, carbon steel, plastics, brass, etc. However, RSW works best with steel sheet metal and struggles with other materials.
According to research, laser spot welding produces stronger welds than RSW welding. The results show that the laser weld had a strength of 63.60 N compared to RSW, which had 39.6 N. It’s almost double the strength in absolute terms.
Adaptability
Laser welding is highly flexible in terms of laser power, welding position, weld shape, and type of welding. It’s because of the inherent nature of light that can be controlled easily.
The most popular feature of the latest welding machines is “ Beam Shaping Optimization,” which lets you control the shape of a laser beam projected on the workpiece. By optimizing it, the splatter and porosity of the welds can be reduced.
The computer numeric controls allow the user to select from many welding options. A welder can experiment with the settings and produce the best weld possible.
Automation
Both welding types have a good level of automation; frankly, it’s a tie. Research is being done on making robotic laser welding and RSW welding better and faster through robotics. Robotic arms are most commonly seen using RSW welding. Similarly, CNC technology is mostly adapted by fiber lasers.
Quick Breakdown
| RSW Welding | Fiber Laser Welding | |
| Type of Welds | Spot Weld | Spot, tack, continuous filler weld, Butt weld, etc. |
| Preparation Need | Higher | Moderate |
| Automation | Compatible | Compatible |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Moderate |
| Maintenance Cost | Moderate | Lower |
| Thickness of Material | < 6 mm | All compatible. |
| Types Materials | Steel, Aluminum. | Steel, Aluminum, Carbon Steel, Titanium, Nickel, Thermoplastics, etc. |
| Industry Applications | Restricted | Vast |
| Skill Level | Easy | Easy |
| Precision | Moderate | Higher |
How To Choose The Right Welding Method For Your Project
Before investing in a welding machine for a project, you may want to consider the following things:
Application
Taking into account the application is the first and most crucial step. There are many welding options out there, and most have multiple applications. However, some are better suited for particular applications than others.
If you are strictly in the business of automobiles, then spot welding is better suited. Many car parts, like bumpers, door frames, fenders, hoods, etc., can be efficiently welded using RSW.
If you require other types of welds, like continuous welding, it’s better to invest in laser welding. That way, you’ll have a multi-purpose welding system at your disposal. Examples include sheet metal work, thin plates, thick plates, repair works, etc.
Type of Material
Another advantage of laser welding is that it’s compatible with many materials. Such as die steel, stainless steel, titanium, nickel, copper, brass, thermoplastics, magnesium, and aluminum alloys. It’s even possible to weld dissimilar materials together.
On the contrary, RSW is best suited for steel and nickel allows. You can weld aluminum, too, but it requires a higher-power spot welder for better performance. Another restriction is the thickness of the said material. RSW only works for thinner workpieces. Otherwise, it gets harder to get full weld penetration.
Skill Level
Even though RSW is easy and has a fairly simple working principle, the actual skill takes time and effort to master. There is a need for skillful labor for maintaining and controlling RSW spot welding machines.
Laser welding is an easy skill to master and doesn’t need highly skilled labor for proper operations.
Production Rate
When it comes to automation, the production rates of both RSW and Laser welding are comparable. It depends on what kind of work parts your industry produces. Robotic spot welding machines are expensive and require extra care while operating. You’ll require greater space as these machines move in 3D space. Also, the investment would be feasible if the applications were limited to car parts and frames.
Examples Of Projects That Would Be Best Suited For RSW Or Laser Welding
Automotive Industry
RSW welding is only suited for the automotive industry, and the evidence backs it. Most car manufacturers go for spot welding because it’s functional and low-cost. Also, car parts, frames, and structures don’t need continuous welds. Laser welding still has uses and can replace traditional RSW welding. Other popular techniques are electric arc welding, gas metal arc welding, and tungsten inert gas welding.
Sheet Metal Industry
Fiber laser welding is better suited for this industry. First, it doesn’t have limitations like RSW welding. Fiber lasers can weld a variety of materials in many shapes and sizes. It’s not restricted to welding positions, either.
Oil and Gas Industry
Oil and Gas industry has a lot of demand for strong welds. Fiber lasers can perform longitudinal and orbital welding on fuel pipes precisely. The welds are strong enough to withstand extreme pressures.

Aerospace Industry
The use of laser welding in aerospace is on the rise. Due to its vast practicality, fiber laser is used for welding the titanium skin of the aircraft fuselage. Another reason for its use is that the welds have higher absolute strength than traditional methods.
Final Thoughts
Now that you have a holistic view of RSW and Laser welding techniques and how they stand against each other, it will be easier for you to make an informed decision. Make sure you factor in all the above points before investing in machinery. RSW is far better suited to car manufacturing and repair, while fiber lasers have broader applications. Fiber lasers are continuously advancing, and they are going to change the welding industry forever.
Get The Best Welding Solutions From Baison Laser
Save your resources and invest in high-quality laser welding machines by Baison Laser. Our machines are designed by expert technicians and engineers using premium technology as they last longer and save a lot on operational and maintenance costs.
Also, our machines are equipped with the latest laser controls that can adapt to any industrial application.
You can also get customized orders suitable to your needs at competitive market rates. We serve our clients all around the globe and help them grow their businesses. So what are you waiting for? Click the button below and get in touch with us NOW!




