What Is Laser Welding?
Welding is a critical process used to join materials permanently, but traditional welding methods can be time-consuming, imprecise, and lead to deformities. Contrarily, the accuracy, speed, and efficiency of laser welding have transformed the welding industry.
Several industries use laser welding, including automotive, aerospace, and medical. The joining of materials of various types and thicknesses uses potent and cutting-edge laser welding technology.
This process is becoming increasingly popular due to its precision, speed, and cost-effectiveness. High-powered lasers are used in laser welding to melt and fuse various materials, creating a solid, high-quality connection.
This comprehensive guide aims to give readers an in-depth understanding of laser welding, including its history, different types, process, thickness, quality assurance, applications, advantages, disadvantages, cost, and how to choose a suitable laser welding machine.

The History of Laser Welding
Scientists first used laser welding technology in the 1960s after learning that a laser beam could heat and melt metal. At the time, neither the technology nor the cost of the technique allowed for the production of welds of a high caliber.
Laser welding, however, became more practical and started to be employed in various applications as laser technology advanced. The aerospace industry began using laser welding in the 1970s to join titanium and other high-strength materials.
The car industry began using laser welding in the 1980s to join pieces together. The aerospace sector now uses laser welding to join titanium components.
Over time, advancements in laser technology, including the development of solid-state lasers, have made laser welding more accessible and affordable for a wide range of applications.
The Fundamentals of Laser Welding
A highly concentrated light beam is focused onto the materials to be connected following the fundamentals of laser welding. The materials absorb the light energy, melting and uniting as a result. The computer software that ensures precision and accuracy in the welding process typically controls the laser beam.
Certification and Standards for Laser Welding
Certification and standards ensure that laser welding meets certain quality and safety requirements. There are different certification and standards organizations in Laser welding, such as ISO and ASTM, and the requirements for certification in laser welding. The benefit of being a certified Laser welder is numerous.
How Does Laser Welding Work?

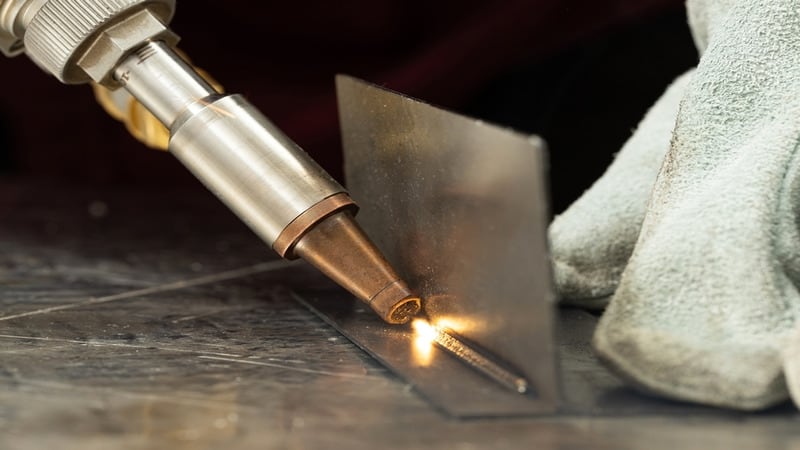
A laser beam is used in laser welding to combine two materials. Due to its accuracy and effectiveness, this cutting-edge welding technique is gaining popularity. In contrast to conventional welding techniques like gas or electric arc welding, laser welding melts the material using a focused beam of light rather than heat.
High-powered lasers are used in laser welding to melt and fuse materials. The substance melts and forms a puddle of molten metal due to the laser beam’s extreme heat generation. The molten pool solidifies as the laser beam passes, linking the two materials.
Laser welding differs from traditional methods in using a highly focused beam of light to deliver heat to the material rather than an electric arc or flame.
What Are the Different Kinds of Laser Welding?
Conduction, keyhole, and deep welding are the three main varieties of laser welding.
- Low-power conduction welding involves heating the material’s surface to the point where it melts and fuses.
- Keyhole welding, often called penetration welding, creates a hole in the material using a strong laser beam filled with molten metal to create a weld.
- Deep welding is a powerful technique that produces a narrow, deep weld with a less heat-impacted zone.
There are several types of laser welding, including CO2 laser welding, Nd: YAG laser welding, and fiber laser welding.
- CO2 laser welding is best suited for welding thicker materials
- Nd: YAG laser welding is better suited for thinner materials.
- Fiber laser welding is the most sophisticated type, which can quickly and accurately join various materials.
- What Is the Process of Laser Welding?
A laser beam is focused onto the material’s surface to be fused for laser welding. The substance is subsequently heated up and melts due to the laser beam being absorbed by it. The dissolved components merge to form a solid connection. The process is managed by modifying the laser beam’s power, speed, and focus point.
Suitable Materials for Welding
A wide variety of materials, including metals, polymers, and ceramics, can be joined together by laser welding. Stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and copper are typical metals in laser welding. Metals and polymers can be joined together by laser welding if they are of different compositions.
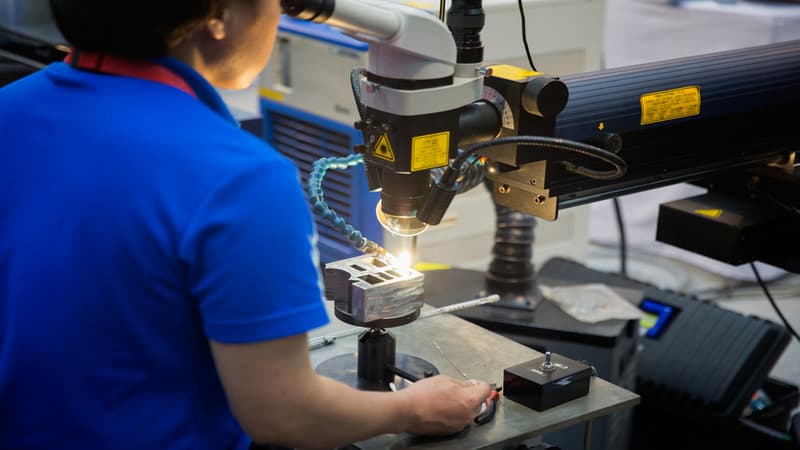

The Process of Laser Welding
The process of laser welding involves several steps, including preparing the materials, focusing the laser beam, heating the materials, cooling, and finishing.
- Preparing the Materials: The materials to be welded must be thoroughly cleaned and prepared before the welding process begins. Any contaminants on the surface can interfere with the welding process and result in a weak bond.
- Focusing the Laser Beam: A lens or mirror directs the laser beam onto the material’s surface. The beam’s focal point must be exact to guarantee that the material is uniformly heated.
- Heating the Materials: The laser beam is aimed at the material’s surface after being focused. The material is heated by the laser beam, which melts it and causes it to melt together to produce a weld.
- Cooling: After welding, the material must be allowed to cool slowly to prevent any distortion or cracking.
- Finishing: Once the material has cooled, the weld is inspected to ensure that it meets the required specifications. Any excess material or burrs are removed, and the surface is smoothed and polished if necessary.
Can a Laser Welder Weld Tough Materials?
The thickness of a material that a laser welder can join relies on the laser’s power. The normal power range of handheld laser welding devices is 1500–3000W, and they can weld materials up to a thickness of 4-5mm. Yet, stronger laser welders can fuse materials that are at least 20 mm thick.
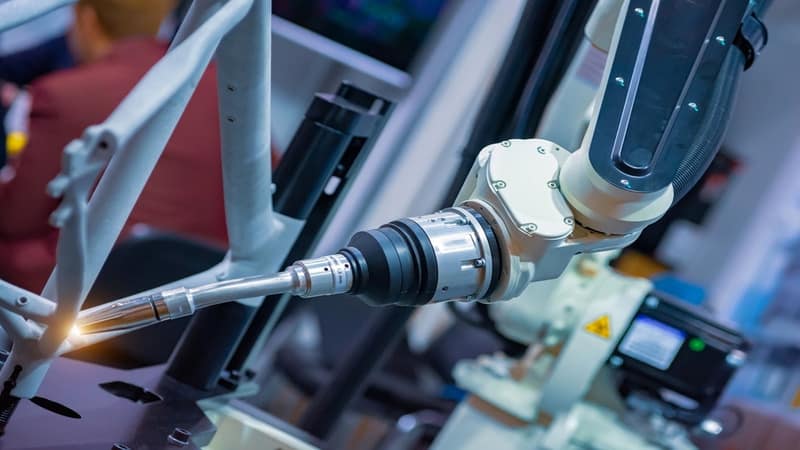

What must Be Taken into Account While Laser Welding Certain Materials?
The importance of quality control is essential to laser welding. The power, speed, and focus of the laser beam, as well as the preparation and cleanliness of the material, all affect the weld’s quality. The weld can be checked in real-time to ensure it meets the parameters using quality control procedures.
Various laser welding parameters are needed for various materials. For instance, welding aluminum requires a lower laser power and a faster welding speed than welding stainless steel. The wavelength and kind of laser beam used during the welding process can also have an impact.
It is crucial to consider the material’s particular qualities and the required laser welding parameters to obtain a high-quality weld.
Laser Welding’s Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Laser welding creates welds of exceptional quality with little distortion or deformation. Automating the welding process reduces labor costs and saves time. Welding is a quick and effective process.
- Laser welding can join dissimilar materials, such as metal and plastic, which are challenging to weld with traditional welding methods.
- Laser welding generates lesser waste and is an environmentally friendly process.
Laser Welding is gradually replacing traditional welding methods, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), and shielded metal arc welding (SMAW). This change is because Laser Welding is safer and also produces stronger and well-welded results.
Disadvantages:
- Specialized equipment and qualified operators are necessary for laser welding, which can be expensive.
- Not every material and thickness is appropriate for laser welding
- Laser welding results in a narrow weld that might not be appropriate for large or complex components.
What Does Laser Welding Cost?
The type of laser welding machine, the material being welded, and the necessary welding settings are some of the variables that affect the price of laser welding. Hand-held laser welding machines range in price from $10,000 to $50,000, while larger, industrial-grade machines can cost over $1 million.
How Do I Pick the Right Laser Welding Machine?

The ideal laser welding machine must be selected for the best results and efficiency. While choosing a laser welding machine, keep the following things in mind:
- Needs: Consider the specific welding requirements, such as the type of material to be welded, the thickness of the material, and the welding speed required.
- Material: Different materials require different laser welding parameters. Make that the laser welding equipment is appropriate for the material being welded.
- Budget: Determine the budget for the laser welding machine and associated equipment, such as ventilation systems and safety gear.
- Size and Capacity: Choose a machine that can accommodate the size and capacity of the components to be welded.
- Customer Service of the Manufacturer: Consider the manufacturer’s reputation, customer service, and support.
- Decide on the Laser Welding Machine: Choose the type of laser welding machine that best suits your needs, such as hand-held or industrial-grade machines.
- Consider Ease of Use and Training Requirements: Choose an easy machine to operate and maintain, and ensure that training and support are available.
What Are the Applications of Laser Welding?
Electronics Industry: Laser welding is frequently employed in the electronics business, especially when producing cutting-edge products like smartphones, laptops, and tablets
Laser welding can be applied in several cases, such as welding micro components, wire bonding, and soldering. Laser welding has increased the dependability and efficiency of electrical gadgets.
Additive Manufacturing: Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, is a growing industry that is using laser welding as a key technology. Laser welding can be used in the additive manufacturing of goods such as 3D images and decors.
High-Power Applications: Laser welding is not limited to small-scale applications. Laser welding can be used for high-power applications, such as welding ship hulls and large machinery components. Though it is not yet popular in this industry, it has created a starting point.
Emerging Trends in Laser Welding Technology
As laser welding technology continues to evolve, new trends and innovations are emerging. The latest trends in laser welding technology include fiber lasers, additive manufacturing, and robotics. These trends can impact the future of Laser welding and the industries that rely on it.
As technology continues to advance, the future of laser welding looks promising. Researchers are exploring new materials and applications for laser welding, including the use of lasers to weld dissimilar materials.
Additionally, there is growing interested in using robotics and automation in laser welding to increase efficiency and reduce costs. The future of laser welding is exciting, and we will likely continue to see advancements in this field.

Conclusion
Laser welding is a fast and efficient process that produces high-quality welds with minimal distortion or deformation. Laser welding can join dissimilar materials and is used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical.
Choosing a suitable laser welding machine and ensuring proper preparation and quality control measures are critical for achieving high-quality welds.
Are you interested in laser welding? Baison laser offers different models of machines. Contact us to learn more about our laser welding machines and how they can benefit your business.