Laser welding is a high-precision welding process that utilizes lasers, high-tech machines, and advanced technology to focus a concentrated beam of light. This beam of light is generated by a laser and used to fuse together metals or thermoplastics.
Fusion welding technology utilizes lasers to create weld seams by directing a highly focused laser beam onto the surface of the materials to be joined. The welded materials melt and form a strong bond upon cooling. This process is also known as swing welding.
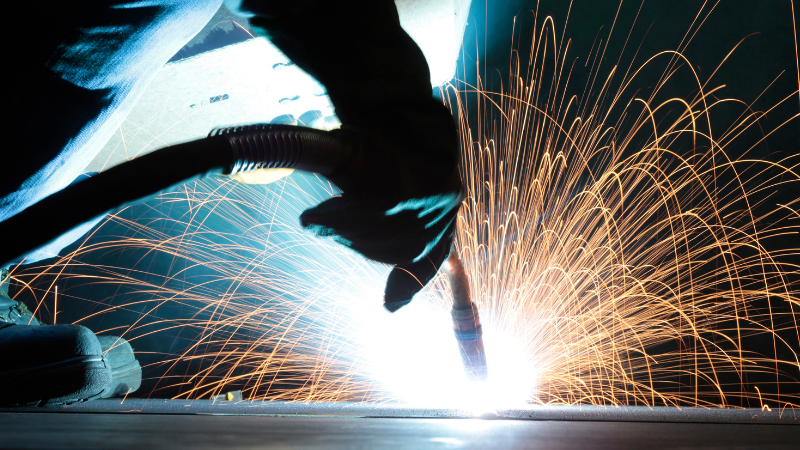

The laser welder with high-power lasers offers exceptional control and accuracy, making it particularly suitable for applications that require intricate and precise welds on the workpiece. The laser beams allow for precise and controlled heating, resulting in precise and accurate welds.
Types of Laser Welding Processes
Laser welding is a versatile method used in various industries to join sheet metal and other materials. There are different types of laser welding processes that use lasers to create a focused beam for processing the workpiece. Each process has its own unique characteristics and applications. Let’s explore some of these welding methods:
Fiber Laser Welding
- Employs laser beam welding with high energy density for longer periods.
- Fiber lasers provide faster welding speeds and deeper penetration.
- Commonly used in industrial applications.
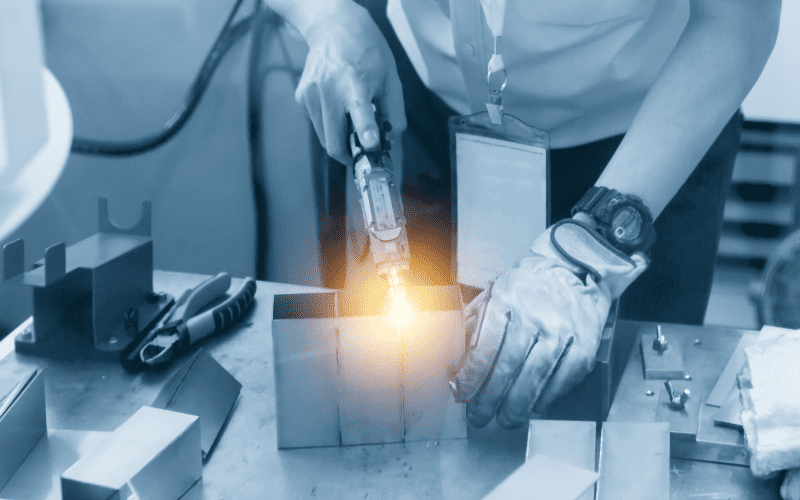

Conduction Welding
- Suitable for thin sheet metal.
- Uses low power density to melt the material surface.
- The heat is conducted through the metal, creating a solid weld joint.
Keyhole Welding
- Ideal for thicker materials.
- High power density creates a deep penetration weld.
- Forms a keyhole-shaped cavity in the material, allowing molten metal to flow into it.
Pulsed Laser Welding
- Utilizes short bursts of high-energy laser pulses.
- Offers precise control over the welding process.
- Suitable for delicate or heat-sensitive materials.
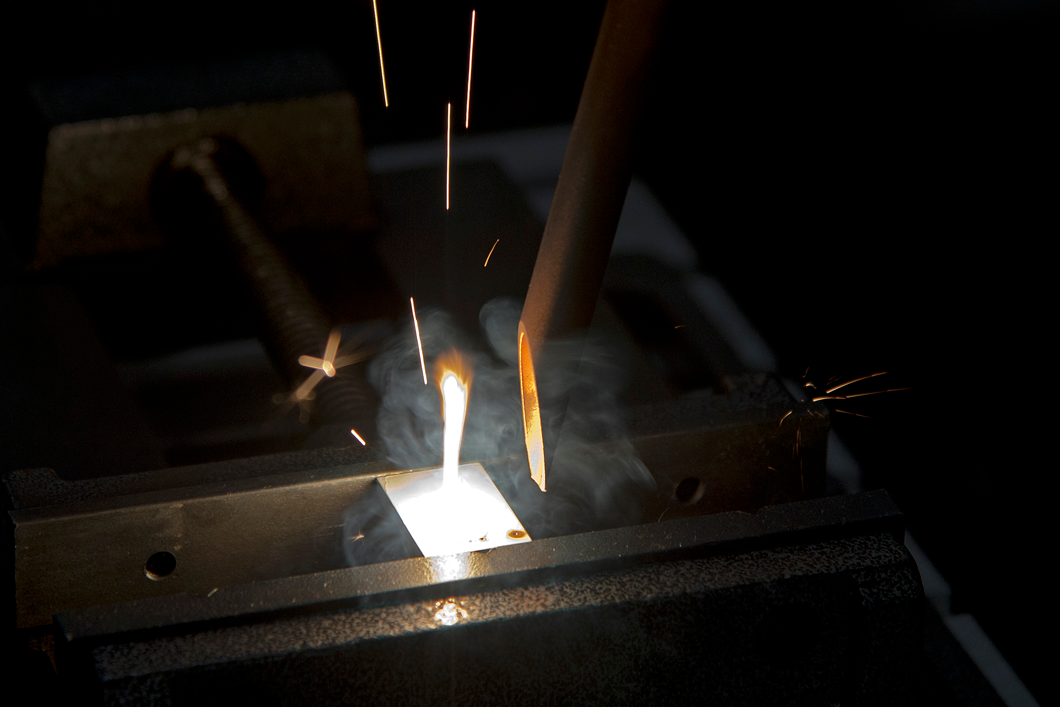
Each type of laser welding process, utilizing lasers as the primary technology, has its own advantages and limitations, making them suitable for specific applications. Laser processing machines are used in this advanced technology. For instance, heat conduction welding is commonly used in electronics manufacturing, while keyhole welding finds application in automotive and aerospace industries where thicker metals are welded.
Sheet Metal for Laser Welding
Not all types of sheet metal are suitable for laser welding. The material properties and thickness of material play a crucial role in determining the weldability of thin sheet metal. The welding effect and welding speed are affected by the sheet metal welding process and thin sheet metal welding techniques used. Here are some key points to consider when working with sheet metal for laser welding.
Types of Materials
Common materials used in laser welding sheet metal include stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, and titanium alloys. This process requires the use of specialized equipment and machines that utilize advanced technology for efficient processing.
The Surface of Sheet Metal
Surface condition plays a crucial role in determining the quality of welds, especially when using fusion welding techniques like traditional arc welding. The welding effect and welding speed are directly influenced by the surface condition of the sheet metal. Proper preparation, cleaning, and positioning are essential for successful laser welding.
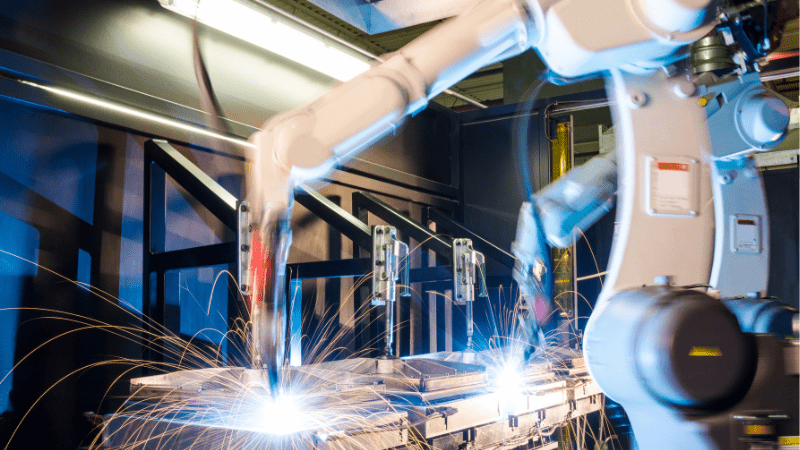
The Thickness of Sheet Metal
Different types of sheet metal require specific techniques and considerations during the welding process. Thin sheet metals may require different approaches compared to thicker ones.
Sheet Metal Fabrication
Laser welding is often employed in various applications involving sheet metal fabrication. It allows for precise and efficient joining of different parts to create complex structures.
Tips for Successful Welding
To achieve optimal results when laser welding sheet metal, it is important to follow these tips:
- Ensure proper alignment and fit-up between the parts being welded in the sheet metal welding process. This is crucial for fusion welding, especially in arc welding, when working with thin sheet metal welding.
- Use appropriate shielding gases or protective environments to prevent oxidation or contamination during the process.
- Adjust laser parameters such as power, speed, and focal length based on the specific material being welded.
- Consider using automatic laser welding machines or equipment for consistent and efficient production.
Laser welding offers numerous advantages in terms of precision, speed, and versatility when working with sheet metal. By understanding the properties of different materials and employing suitable fusion welding techniques, manufacturers can achieve high-quality welds in their sheet metal parts using laser welding machines and laser welding equipment.
Benefits and Applications of Laser Welding Sheet Metal
Laser welding of sheet metal offers an array of advantages that have revolutionized manufacturing processes across industries. The precision, efficiency, and quality of laser-welded joints using machine technology have opened up a multitude of applications that benefit from this advanced welding equipment.
Advantages of Laser Welding
- Precision and Accuracy: Laser welding excels in producing intricate and precise welds, even in complex geometries. This precision is essential for applications requiring fine detail and tight tolerances.
- Minimal Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ): The focused laser beam generates localized heat, resulting in a smaller HAZ compared to traditional welding methods. This minimizes material distortion and reduces the need for extensive post-welding corrections.

- Clean and Strong Welds: Laser welding produces clean, spatter-free welds with minimal porosity. The fusion achieved is strong and reliable, ensuring the integrity of the joint.
- Speed and Efficiency: The concentrated energy of the laser beam allows for rapid heating and cooling, enabling quick welding processes. This efficiency contributes to higher productivity in manufacturing.
- Reduced Material Waste: Laser welding’s precision minimizes the amount of material affected by the heat, leading to less waste during the welding process.
Applications of Laser Welding in Sheet Metal
- Automotive IndustryBody Assembly: Laser welding is used to join body panels and components with precision, ensuring structural integrity and improving vehicle aesthetics. Here is an article about the automatic application of laser welding.Laser-welded exhaust components, created using advanced welding equipment, demonstrate exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, significantly prolonging the lifespan of vehicles. This makes them an ideal choice for sheet metal welding in exhaust systems.
- Aerospace IndustryLightweight Structures: Laser welding aids in creating lightweight and sturdy structures for aircraft, enhancing fuel efficiency without compromising safety.Precision Components: Critical aerospace components requiring intricate welding, such as turbine blades and engine parts, benefit from the precision of laser welding.
- Electronics IndustryHermetic Sealing: Laser welding ensures airtight and reliable seals for electronic components, protecting them from moisture and contaminants.Microelectronics: Laser welding’s ability to work on a small scale is valuable in assembling microelectronic devices with delicate components.
- Medical Device ManufacturingLaser welding is used to create seamless and biocompatible welds in implantable medical equipment, ensuring patient safety and comfort.Medical Instruments: Fine welding capabilities of lasers are utilized in assembling complex and delicate medical instruments.
These applications merely scratch the surface of the vast range of possibilities that laser welding offers in sheet metal fabrication. The versatility, reliability, and quality of laser-welded joints continue to drive innovation and excellence in numerous industries, especially in the field of welding equipment and sheet metal welding.
Factors Affecting Laser Welding Quality
Achieving high-quality laser welding results requires careful consideration of various factors. Let’s explore the key elements that influence the quality of laser welding.
- Welding Process Parameters: The laser power, beam focus diameter, travel speed, and pulse duration are critical parameters that significantly impact weld quality. Proper adjustment of these factors ensures optimal heat input and penetration depth, resulting in a strong and reliable weld.
- Gas Shielding: To protect the molten pool from oxidation during the welding process, gas shielding is employed. This technique creates an inert atmosphere around the weld area, preventing any detrimental effects on the joint’s integrity. The choice of shielding gas depends on the specific application and material being welded.
- Joint Design: The design of the joint plays a crucial role in achieving high-quality welds with minimal defects. Factors such as joint geometry, fit-up accuracy, and edge preparation directly affect weld strength and overall quality. Careful attention to joint design ensures proper fusion and enhances mechanical properties.

- Alignment: Proper alignment between the laser beam and workpiece is essential for accurate heat distribution during welding. Precise alignment guarantees consistent energy delivery throughout the joint, minimizing distortion and ensuring uniform fusion. Maintaining alignment is particularly crucial when dealing with complex or intricate structures.
By considering these factors – welding process parameters, gas shielding, joint design, and alignment – you can achieve superior laser welding quality in your sheet metal applications. Understanding their effects allows you to optimize each aspect of the process for exceptional results.
Remember to fine-tune your settings based on specific materials and requirements to ensure excellent weld quality every time.
Controlling Distortion in Sheet Metal Welding
Distortion is a common challenge that arises during laser welding of sheet metal. It occurs due to the thermal expansion and contraction of the metal, resulting in unwanted changes to the shape and dimensions of the welded components. However, there are several effective techniques for controlling distortion and ensuring high-quality welds.
Fixturing Techniques
- Proper fixturing plays a crucial role in minimizing distortion by controlling heat distribution during welding.
- Strategically positioning fixtures can help distribute heat evenly, preventing excessive localized heating that leads to distortion.
Preheating or Post-weld Heat Treatment
- Employing preheating or post-weld heat treatment methods can alleviate residual stresses within the sheet metal welding structure. By using a laser welder, these methods can be effectively implemented.
- These techniques help reduce distortion by relieving built-up stresses caused by rapid cooling after welding.
Adjusting Heat Input
- Using lower heat input or pulse duration can effectively control distortion in sheet metal welding.
- By reducing the amount of heat applied during welding, it becomes easier to manage thermal expansion and contraction, minimizing distortion.
Controlling distortion in sheet metal welding is essential to ensure precise and accurate results without compromising structural integrity. By implementing proper fixturing techniques, employing preheating or post-weld heat treatment methods, and adjusting the heat input, welders can achieve successful outcomes while maintaining control over the welding process.
Remember, excessive heat can have detrimental effects on traditional arc welding as well, making it crucial to understand how to mitigate this issue when working with various welding methods.
FAQs
What types of materials can be welded using laser welding?
Laser welding is versatile and can be used on various materials such as stainless steel, aluminum alloys, titanium alloys, carbon steels, and more. It provides excellent results across different thicknesses of sheet metal.
Is laser welding suitable for high-volume production?
Yes! Laser welding is highly efficient and well-suited for high-volume production due to its speed and accuracy. It allows for the rapid joining of components with minimal heat input.
Can laser welding replace traditional methods like spot or TIG welding?
While laser welding offers numerous advantages over traditional methods like spot or gas metal arc welding, it may not completely replace them in all applications. Each method has its strengths depending on factors such as joint design, welding material thickness, and production requirements.
Does laser welding produce a clean finish?
Yes! Laser welding produces clean and precise welds with minimal spatter or distortion. This makes it particularly suitable for applications where aesthetics are important, such as automotive or electronics industries.
Conclusion
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of laser welding for sheet metal fabrication, it’s time to put your knowledge into action. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or just starting out in the field, don’t hesitate to explore the possibilities that laser welding offers. By leveraging the advantages of a laser welding machine, such as enhanced precision and improved productivity, you can elevate your sheet metal welding projects to new heights while reducing distortion. So go ahead and embrace this cutting-edge welding technology – it’s time to weld like never before!
What Can Baison Help You?
If you still have questions about laser welding of sheet metal, please contact Baison for our help. Baison is a leading supplier to the laser industry. With our years of industry experience, we can help you find the best welding equipment for your business and get you up and running as soon as possible.






