But cutting hard transparent material like glass has its own challenges. It can shatter under sudden impact and lead to large and dangerous shards.
This article lists the top ten things you need to know about laser-cutting glass and its machines for maximum profits.
The Basics of Laser Glass Cutting
Laser-cutting glass uses a concentrated and focused laser beam to selectively melt the glass. The laser beam makes contact with the glass surface for less than a second.
In this short period, the laser imparts all its energy into the glass without causing it to warp or crack. With the expectation of a few handheld units, all laser cutters use CNC controls to direct the cutting head. Ensuring accurate and precise cuts every single time.
Glass is difficult to cut, as it is very brittle and cracks under sudden shocks. Traditional methods of cutting glass involve an extremely sharp material (diamond, tungsten carbide, or hardened steel ) scoring the surface of the glass and a calculated shock to the side.
While the traditional methods are a tried and true process, they lack versatility and can’t produce complex shapes. Laser-cutting glass is faster, safer, more versatile, and requires little to no staff training.
Research shows that processing glass materials using laser-cutting machines doesn’t affect its material strength or thermal stability. Laser-cutting glass holds several advantages of the mechanical cutting process.
Types of Laser Glass Cutting Machines
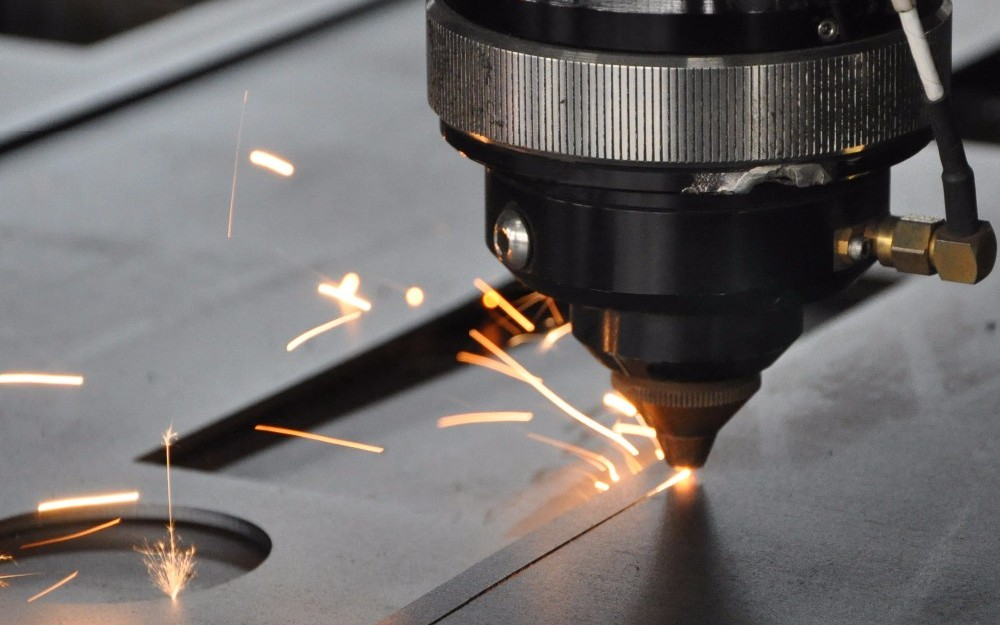

Laser-cutting machines are primarily categorized based on the type of laser sources. The following are the four most common types of laser machines available for glass cutting.
- CO2 Laser Cutters
CO2 lasers use a glass chamber filled with a gas mixture that gets excited by high-voltage electric current. The gas molecules radiate light energy, which gets amplified into a laser beam.
- Fiber Laser Cutter
Fiber lasers are modern laser-cutting machines that use optic fiber as a gain medium. They take existing light and bounce it inside a fiber optic cable until it transforms into a laser.
- Crystal Laser Cutters
Crystal lasers use an Nd: YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet) crystal as a gain medium. These lasers are primarily used in medical devices.
- Diode Laser Cutters
Diode laser cutters work by exiting a semiconductor diode until it releases light, which is then amplified into a laser. Diodes are low-power electronics and thus cannot produce high laser power.
Top 10 Things to Know About Laser Cutting Glass and Its Machines
Laser-cutting glass is a complex process requiring the machine operator to know several important things beforehand.
We’ve compiled a detailed list of the top ten things you should know about laser cutting and its machines.
1 – Soda Lime Glass Is Easier to Cut
The glass comes in several varieties, and each is meant to enhance its natural material properties.
Stained glass changes the refractive index and color of glass by introducing metal additives.
Borosilicate glass has exceptionally high thermal and chemical resistance from the addition of boric oxide.
Soda lime glass is less resilient than borosilicate but is considerably cheaper and easier to work. It can also be tempered after processing for better thermal resistance.
Due to borosilicate’s resistance to thermal energy, it cannot be cut using most laser-cutting machines. Meanwhile, soda lime glass melts under the laser beam but still resists cracks and unwanted melting.
2 – Laser Cutters Are Faster than Traditional Glass Cutting Methods
A skilled craftsman can cut glass quickly and precisely. Years of experience have allowed them to hone their skills to perfection.
But even the most skilled person can’t compete with the exceptional cutting speed of a laser cutter. Complex shapes and designs are still a challenge for expert glass cutters. The risk of crack formation prevents them from cutting glass at high speeds.
Luckily, laser-cutting machines lack any such restrictions. The only moving part in the laser cutting process is the cutting head. Thus, the glass workpiece experiences no vibrations, shocks, or accidental jerks, mitigating the risk of cracks.
With zero risk of the glass cracking, the laser beam can cut shapes faster than any human.
3 – Laser Cut Glass Doesn’t Need Sanding
Traditional glass cutting requires a sharp tool for scoring and a calculated light tap to initiate a crack. This method leads to rough edges around the cut glass, which is quite hazardous.
Therefore, all mechanically cut glass shapes must go through a sanding process to smooth out the edges.
As the laser beam melts the edges, it creates a much cleaner and smoother outer edge, negating the need for post-cut sanding.
4 – A High Powered Laser Beam Results in Burning Marks
High-power lasers are useful in cutting metals but have become redundant in glass cutting. If you can’t cut a sheet of glass using a sub 1kW laser, then the odds are you will not have any further success by increasing the laser power.
The glass reflects most of the visible laser energy. Therefore, excess energy will bleed to the sides, resulting in the glass sheet burning instead of cutting.
Laser wavelength plays a higher role in the glass-cutting process. Ultraviolet (UV) intense light (laser) at a lower wattage is far more capable than a visible light laser at higher wattage.
5 – Avoid Handheld Laser Cutters
Handheld lasers are an excellent solution for quickly cutting large and simplified shapes. But with glass sheets, handheld laser machines can introduce unknown variables and human error.
For small businesses, a handheld machine offers less value over time. After all, small businesses can’t fully benefit from the portability and high wattage of handheld fiber laser systems.
The precision and accuracy of a CNC glass laser cutter are more valuable than the portability of a handheld laser machine.
6 – Use Short Pulses When Laser Cutting Glass
Glass sheets aren’t well suited to long periods of laser exposure. The excess energy doesn’t penetrate the glass layer. Instead, it radiates to the sides.
Short pulses of a laser beam deposit just enough energy to melt thin materials, and repeat passes allow even low-power lasers to cut through thick glass plates.
Studies have shown that lasers only need to make contact with the glass for a femtosecond for precise cuts. A femtosecond is one quadrillionth of a second that’s 14 zeros after the decimal point.
7 – Laser Wattage Isn’t as Important
The most common types of glass laser cutting machines use only a 30-40W CO2 laser. Any more power, and you’re spending additional money for zero additional benefits. After all, most glass cutting in the industrial environment is for sheets under 0.2 inches (6mm) in thickness.
Most businesses are not cutting half-inch (12mm) thick glass materials, and even if they were, a weak laser with multiple passes would be more than adequate.
A laser cutter works by maximizing the laser light’s output and minimizing its contact period. Pulsed lasers were designed for this exact purpose.
8 – You Can Cut Glass with CO2, Diode, & Fiber Lasers
The type of laser cutting machine isn’t a major factor for glass cutting. As laser wattage isn’t a big deal, even diode-based laser cutters are an acceptable solution.
Laser types are less important to the actual cutting functionality of the machine. But choosing the right type of laser will help you save on maintenance and energy costs.
CO2 lasers have the lowest lifespan of the bunch, and diode lasers have the highest electrical. However, fiber lasers offer the best of both worlds regarding efficiency, longevity, and performance.
9 – Quality Servo Motors Result in Precise Cuts
Laser spot diameter, lens quality, and laser source are not the only metrics for measuring precision. At the end of the day, the laser light is controlled by servo motors and gear belts.
The XYZ motion of the laser also needs to be precise. Otherwise, it would negate the precision of the laser beam.
As the laser cutter moves across the glass surface, the moment of the laser head prevents it from making sudden stops. Hence you will often see a laser cutting machine advertise its X/Y positional accuracy.
A small laser spot diameter and a higher positional accuracy are essential to accurate laser cutting.
10 – The Cost of a Laser Machine is Variable
The cost of a laser cutter isn’t always easy to estimate. Laser type, machine work area, laser power, precision, and after-sale services all affect the final price tag.
Since the price of a laser machine is all over the place, you won’t always benefit from the most expensive model. Always choose a laser cutter that best suits your glass-cutting needs.
Applications of Laser Glass Cutting

Laser-cut glass has slowly started taking center stage in the tech sector. Glass is a premium transparent material with several key advantages over other materials.
With the demand for glass as high as ever, laser-cutting machines have stepped in to ensure quality cutting and processing services.
Following are just some of the many applications cases of laser cutting glass.
Smart Device Displays
The biggest innovation of the past two decades has been premium quality glass displays. Premium smartphones and tablets utilize the latest and greatest glass displays that require millimeter precision to cut.
Laser cutting has allowed manufacturers to produce high-quality glass displays rapidly, resulting in lower costs and even lower defect rates.
With the explosive growth of smart wearables like AR headsets, smartwatches, and more, we see a greater demand for precision-cut glass displays using a laser cutter.
Micro Electronic Devices
Glass is also a highly sought material in microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Glass’ non-conductivity, see-through appearance, and corrosion resistance are all highly valued in the construction of sensitive electrical equipment.
Thin sheets of glass are used as a substrate (backplate) for MEMS devices. Laser-cutting machines enable manufacturers to ensure consistent microscopic level accuracy for all sensitive electronics.
Medical Equipment
The medical industry also loves glass for its inert nature, heat resistance, and easy sterilization capabilities. Laser cutting has been instrumental in pushing medical advancements to the next stage.
We can see laser-cut glass prominently used in microscope slides, coverslips, and cover glass.
Optical Devices
Optical devices are now present in every industry. From cameras to laser cutter focus lenses to delicate electronic sensors.
Laser-cutting machines allow operators to make precise cuts to thicker materials as well. Meaning regardless of the lens size or thickness, laser cutting glass should be an easy process.
Laser Engraving and Etching
Glass laser cutters also come with additional features like engraving and etching. Marking surfaces is a necessity in many performance applications. Important details about the product or its surrounding environment should be displayed clearly.
Solutions like paints or printed stickers don’t have good longevity. Rain, dust, or abrasion can remove markings from glass surfaces over time.
Etching and Engraving allow manufacturers to permanently mark their products without fear of wear and tear. Etching is a huge positive for sensitive laboratory equipment, which demands minimum interference from outside elements.
3 Factors to Consider When Choosing a Laser Glass Cutting Machine
For most businesses, any glass laser cutter from a reputable brand should do the trick.
But for consumers looking to maximize the value of their laser-cutting machine, here are a few factors to consider.
- Type of Glass
Laser cutting can be used to process all types of glass materials, from tempered to borosilicate to soda lime. Choose a laser-cutting machine that is best suited to your specific glass-cutting needs.
Borosilicate and tempered glass require specialized laser operating modes.
- Cutting Precision
Pay extra attention to the quality of the motors. A high-quality laser cutting machine using quality rotary parts will have higher cutting precision.
- Cost and Maintenance
Laser cutters come with a direct cost and an indirect cost. Direct cost is the one-time investment and shipping costs.
Maintenance, electrical efficiency, and part replacements comprise the bulk of the indirect costs.
Conclusion
Laser-cut glass is amazing for several reasons. It’s faster, more accurate, and more convenient. But the process is very different from laser cutting other materials like metals, fabrics, plastics, and wood. The same attributes of glass that make it an attractive material also contribute to cutting challenges.
Learning the basics of laser cutting will help businesses make more well-informed purchasing decisions that will directly result in increased profits and productivity.
Why Choose Baison Laser for Your Laser Cutting Needs
Baison Laser is one of the industry’s most capable fiber laser solutions manufacturers. With over 20 years of manufacturing experience and a wide network of global shipping partners, Baison has established itself as a major player in the laser cutter game.
Our excellent product catalog includes everything from Fiber Laser Cutters to Handheld Fiber Laser Welders. We understand the importance of a good customer experience and are committed to customer satisfaction through exceptional custom training.
Let Baison boost your business to new heights with its industry-leading laser-cutting machines. Contact us Now!