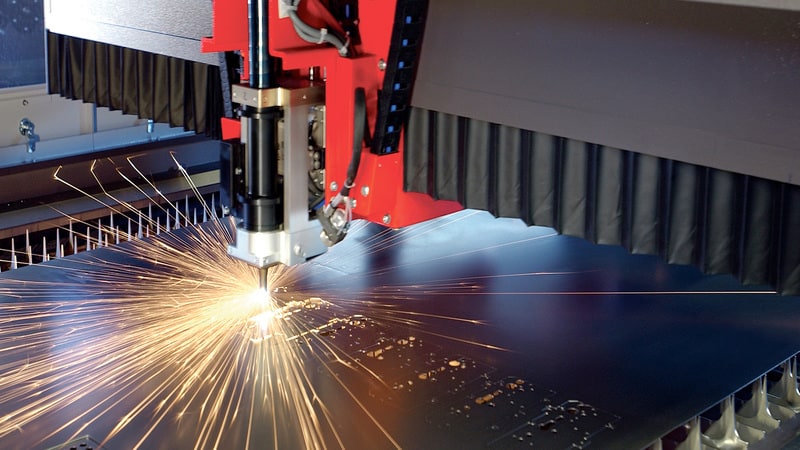
Laser-cutting machines are crucial systems in various industries, allowing manufacturers to achieve precision and efficiency in production. However, these machines utilize thermal processes during operation, generating a significant amount of heat that can lead to reduced productivity, decreased precision while cutting, and reduced cut quality.
The good news is that these risks can be alleviated using cooling systems that can significantly improve the machine’s performance and enhance longevity by maintaining optimal temperature levels.
This blog post explores how to cool down the laser cutting machine using different cooling methods. We’ll also discuss each method’s pros and cons and potential factors that can cause your machine to overheat. Let’s dive in.
What Is a Laser Cutting Machine?

A laser cutting machine is a type of Computer Numerical Controlled (CNC) machine that uses an intensely focused, high-powered laser beam to precisely mark, cut, or etch out designs on different materials.
This laser technology concentrates an intense light beam on a work surface, rapidly increasing the heat density and causing partial or total heat dissipation on the material.
Laser machines are generally categorized based on the state and medium of their active laser medium. The three most common types are CNC crystal laser cutter, CNC CO2 laser cutter, and CNC fiber laser cutter. Others include Excimer laser machines, UV laser cutters, and Nd: YAG Laser cutters.
By the way, if you are interested in laser-cutting machines, click the button below!
How Does a Laser Cutting Machine Work?
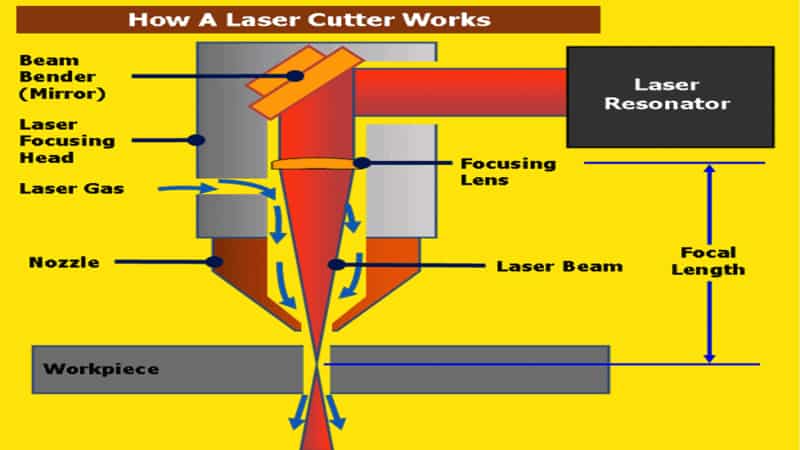
The laser machine works by inputting design instructions for the cutter using a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) which it uses to direct the laser beam. A CNC interprets the design and guides the beam along the intended work path.
The laser beams utilize a thermal-based process generated using carbon dioxide (CO2), fiber, UV, or crystals. The beam is then passed through a series of nozzles, mirrors, and focusing lenses contained in the laser tube and focused and aligned onto a small focal point on the material.
The laser beam then heats the material, melting and cutting it into different shapes. Additionally, these lasers use compressed gases, such as oxygen or nitrogen, ejected through the nozzle to blow away vaporized or molten material from the work area to clear a beam path for the laser and produce cleaner cuts.
What Metal Materials Can a Laser Cutting Machine Cut?
Laser machines can cut various metal materials, including aluminum, brass, stainless, steel, copper, carbon steel, titanium, nickel alloys, silver, bronze, gold, and galvanized steel. Asides from metal, these machines can also cut wood, leather, and even cardboard.
As a result, this laser cutting technology has applications in several industries requiring high accuracy, such as aerospace, medical, architectural, chemical, engineering, construction, marine, automotive, manufacturing, and even musical.
However, you should note that these laser cutters have different capabilities based on the thickness and type of material being cut, especially regarding metal. This can affect their speed, power, and output.
Signs of Overheating in Laser Cutting Machines
Laser cutters generate a significant amount of heat while working and after using them for an extended period of time. If they aren’t allowed to cool effectively, they can overheat, develop faults and reduce the longevity of the machine and the quality of their cuts. Here are some signs to look out for when your laser machine is overheating:
Increased Temperature Readings
This is the most apparent sign of overheating in your laser machine. If you notice a drastic increase in the temperature compared to the normal operating temperature range, your cutter might be overheating.
Strange Sounds and Vibrations
Excess heat generation can cause the parts of your laser equipment to expand, allowing them to grind up against one another and malfunction. They then begin to generate range noises or vibrations and might produce a burning smell due to excess friction.
Automatic Shutdown
Some of these laser cutters come with in-built protection structures programmed to automatically turn them off once they begin to experience thermal stress. If this happens frequently over a short period, it might be a major sign of overheating.
Reduced Cutting Speed or Inconsistent Operations
Excess heat production can cause a reduction in your laser cutter’s performance level, which can be characterized by slower or inconsistent cutting speeds or reduced productivity. This can, in turn, affect the quality of cuts produced.
Error Messages
Like automatic shutdowns, you might begin to receive automatic error messages when the temperature of your cutter is high due to the in-built protection mechanism.

Common Factors That Affect Laser Cutting Machine Temperature
Each laser machine comes with its own set of instructions and specifications provided by the manufacturers regarding temperature, maintenance, and operation. The machines might overheat if conditions are not met. Some factors that can lead to this are mentioned below.
Incorrect Laser Setting
There are specific parameters recommended for using your laser machines on different materials. Not sticking to the appropriate speed or laser power can produce excess heat.
Prolonged Operation Time
Operating your laser cutters beyond their recommended duty cycles without enough breaks between use can cause them to overheat. These duty cycles indicate how long the machines can operate continuously before needing to cool down.
Lack of Cooling System
Cooling systems are responsible for the heat dissipation of laser cutters during operation. If you don’t have an effective cooling system, or yours is not maintained correctly, it can result in insufficient heat dissipation, leading to overheating.
Faulty Parts
Damaged components of the laser cutter, such as faulty cooling fans or optics, can prevent the release of heat and cause overheating. Broken or worn-out parts can also rub against each other, causing friction and increasing heat generation.
Irregular Maintenance and Cleaning
Without proper cleaning and maintenance, dirt and debris can accumulate on essential parts of the laser machine, hindering heat transfer and preventing the laser cooling system from functioning properly.
Why Is Cooling Important for a Laser Cutting Machine?
Cooling is vital to guarantee the longevity of your laser cutter. Operating these machines for an extended period of time causes excess heat to build in the laser tube and other optical elements, such as the laser tube.
This can lead to issues that can reduce the quality of the cuts and marks and eventually damage the laser tube. Cooling helps to protect these crucial components, ensuring they operate within the appropriate temperature and prolonging their lifespan.
Cooling also prevents material distortion by maintaining the beam’s precision to achieve the desired quality. This is particularly important in industries with high-tolerance applications. Adequate laser cooling ensures safety in your work environment.
Regulating the heat generated by these laser machines reduces the risk of workers obtaining burns or scalds from accidental contact with the hot components.
Five Common Practices for Cooling Down the Laser Cutting Machine

You can use several methods to cool your laser machines, and by implementing these systems, you can ensure they operate at optimal capacity and prolong their life span. These include:
Water Cooling System
A water cooling system is an effective way to dissipate heat while using laser cutters. This works by using cooling water to absorb the heat the machine generates, heating up in the process.
A pump then takes the heated water through a radiator or heat exchanger, which releases the heat into the atmosphere, or an external cooling system, a water loop, or refrigerant.
This laser cooling system is highly efficient because water absorbs high heat energy, ensuring the laser machine operates at stable temperatures.
Proper Ventilation
Placing your laser machine in a well-ventilated location can help regulate the temperatures and maintain them within reasonable limits. Adequate air circulation can help dissipate heat by creating an air cooling system that prevents hot air from accumulating around the laser machine.
Using a Laser Chiller
A laser chiller is a specialized cooling device that automates cooling systems for laser cutters. The chiller typically contains a cooling unit for circulating a coolant or coolant mixture, an in-built water pump that circulates the liquid through the laser components, and an active heat exchanger that releases the heat the coolant absorbs into the atmosphere.
Note that only pure or distilled water must be used for your cooling liquid. Deionized water is also acceptable, but whichever you use, ensure the water is cleaned regularly.
The laser chiller might also have a temperature control mechanism featuring thermometers, thermostats, and sensors to regulate and maintain the appropriate operating temperature.
Freon-cooled chillers
A freon chiller is a laser chiller that uses a refrigerant, freon, as the cooling liquid for heating carbon dioxide (CO2) or fiber laser cutters. A compressor increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant by compressing it.
The refrigerant, already at high pressure and temperature, is pushed to a condenser that releases the heat to another cooling system or the environment.
The liquid then passes through an expansion valve to reduce pressure and temperature into an evaporator to reabsorb heat from the laser tube. And back into the compressor for the cycle to continue.

The Pros and Cons of These Cooling Methods
Water Cooling System
Pros
- Precise temperature regulation
- Quiet operation
- Compact design for easy integration into laser cutters
cons
- Water issues, such as contamination, impurities, leaks, corrosion, or scaling, can arise.
- Increased energy consumption
- Require additional components such as filters, reservoirs, and pumps, which might be expensive.
Proper Ventilation
Pros
Removal of harmful emissions from the work environment.
It helps prevent fire hazards and increases air quality
It doesn’t require any additional costs
cons
Limited cooling capabilities and heat dissipation
It does not provide precise temperature control
Using a Laser Chiller
Pros
A laser chiller is energy efficient as it consumes low energy
It helps to provide efficient cooling for the laser cutters
Minimizes the risk of machine failure and prolongs the lifespan
cons
Initial installation and maintenance costs are high
The laser cutter might not function properly when the chiller has a downtime.
Requires specialized training or expertise due to the chiller’s complexity.
Freon-cooled Chillers
Pros
These chillers come in a compact design allowing them to be installed where space is limited.
They are easier to maintain compared to other cooling systems.
Available in a range of cooling capacities to suit your production needs
Pros
Freon is a chlorofluorocarbon contributes to the ozone layer’s depletion when released into the atmosphere.
They can only achieve a limited temperature range.
Possibility of refrigeration leaks which can create a health hazard if inhaled
Other Factors That Affect Laser Cutting Machine Temperature
Machine Setup
Factors such as misalignment and improper calibration can lead to faulty cuts and increased temperature within the laser cutter. This can also cause the material to absorb excess energy, producing heat.
Ensuring all components, such as the laser tubes, nozzles, lenses, and mirrors, are correctly aligned and calibrated ensures the machine performs optimally and regulates the temperature.
Environment
Positioning your laser cutter in a ventilated location with adequate airflow is crucial. These conditions aided the release of heat produced during cutting, preventing heat buildup and increased temperature due to insufficient circulation.
Material Being Cut
Every material has its own absorption and dissipation rates. Some materials have higher thermal conductivity, allowing absorption and dissipation and preventing a rapid increase in temperature. However, thicker materials require prolonged cut time, increasing the amount of heat produced.
Conclusion
Cooling systems play a crucial role in ensuring the efficiency and accuracy of your laser cutters. Throughout this post, we have provided valuable information and insights into how you can cool your machines, including water cooling systems, proper ventilation, Freon-cooling chillers, and laser chillers.
By implementing these methods, you can take your laser-cutting processes and, in turn, your business to greater heights.
You can also visit our website for more information and additional resources on cooling methods for your laser-cutting machines to boost your business and production processes.





