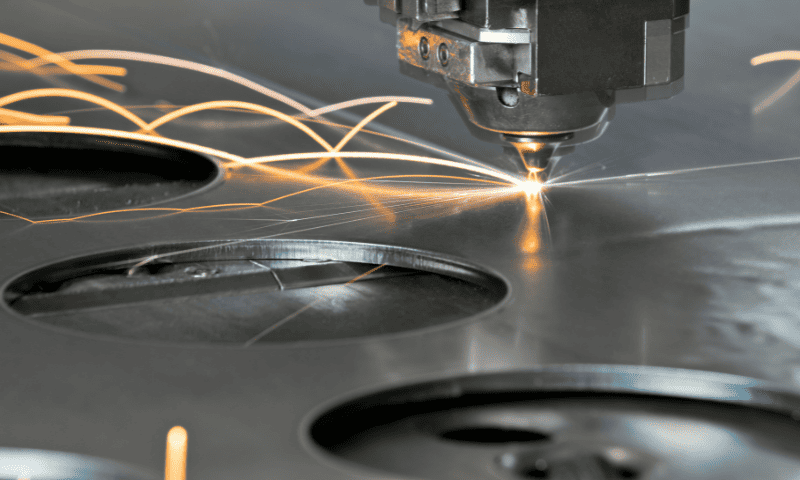
These gases, such as nitrogen and oxygen, are not just present for showing. They mean business. By preventing oxidation and ensuring clean cuts, assist gases help achieve impeccable results. Their presence during the process is like having a trusty sidekick that guarantees top-notch performance. Regard for assist gases cannot be underestimated.
What Is Assist Gas in Laser Cutting?
Assist gas in laser cutting refers to the gas that is used in conjunction with the laser beam during the cutting process. It plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and quality of the laser cutting process.
The primary purpose of assist gas is to remove the molten material and debris from the cut zone. It helps to blow away the melted material, preventing it from interfering with the cutting process and reducing the risk of the material re-solidifying and causing issues such as slag or dross formation.
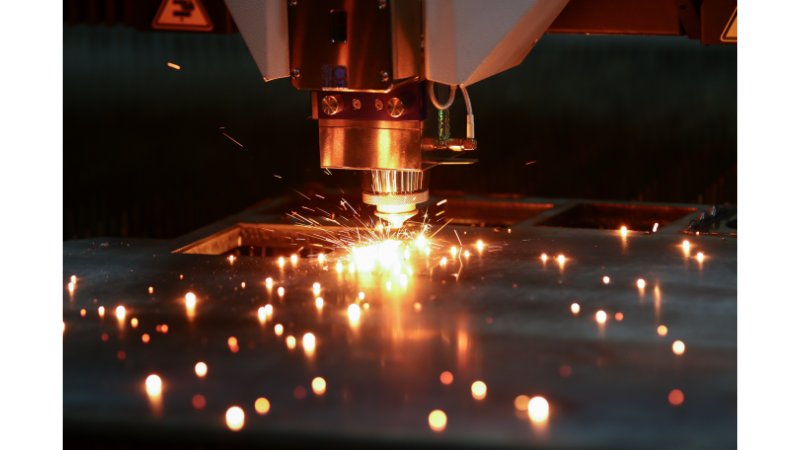

Commonly used assist gases in laser cutting include compressed air, nitrogen and oxygen. The choice of assist gas depends on the material being cut and the desired outcome.
The assist gas jet is typically delivered through a nozzle located near the laser beam. The assist gas flow rate and assist gas pressure can be adjusted to optimize the cutting process and achieve the desired results.
Types of Different Gases for Laser Cutting
There are several types of gases commonly used in laser cutting, each with its own specific properties and applications. The choice of gas depends on the material being cut and the desired outcome. Here are some of the most commonly used gases in laser technology.
Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is often used for cutting carbon steel. When the laser beam reacts with oxygen, it creates an exothermic reaction that helps to facilitate the cutting process. Oxygen cutting is highly reactive and can produce a clean, oxide-free cut edge. However, it can also cause oxidation and create a rougher edge on some materials.
Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen is commonly used for cutting stainless steel and laser cutting aluminum. It is an inert gas that helps to prevent oxidation during the cutting process. Nitrogen produces clean, oxide-free cuts and can provide high-quality edges. It is also used as an assist gas to blow away molten material and debris from the cutting zone.

Compressed Air: Compressed air is often used for cutting non-metallic materials such as wood, plastics, and acrylics. It provides a cooling effect and helps to remove debris from the cutting area. Compressed air is readily available and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for certain applications.
Argon (Ar): Argon is an inert gas commonly used for laser cutting applications that require a high level of precision. It is often used for cutting thin materials or when a clean, oxide-free cut is desired. Argon helps to prevent oxidation and produces high-quality edges.
Helium (He): Helium is sometimes used in laser cutting, particularly for applications that require very high energy density or when cutting thick materials. Helium has excellent heat transfer properties and can help to achieve faster cutting speeds and improved cut quality.
It’s important to note that the choice of gas and its settings (flow rate, gas pressure) can significantly impact the cutting process and the quality of the cut. It’s advisable to consult with the laser machine manufacturer or experts in fiber laser cutting to determine the most suitable gas for your specific application.
Importance of Assist Gases for Laser Cutting Efficiency
Assist gas plays a crucial role in laser cutting applications. It serves as a facilitator for the entire process, ensuring optimal results and a smooth finish. Here’s why assist gases are so important:
Blowing Away Molten Material
The primary purpose of assist gas is to blow away molten material from the cut. This prevents re-deposition, where the molten material solidifies again on the surface, leading to rough edges and an uneven finish. Ensuring a smooth finish is especially important when working with delicate materials or intricate designs that require precision. The assist gas pressure helps in achieving this by reducing the cutting kerf width.
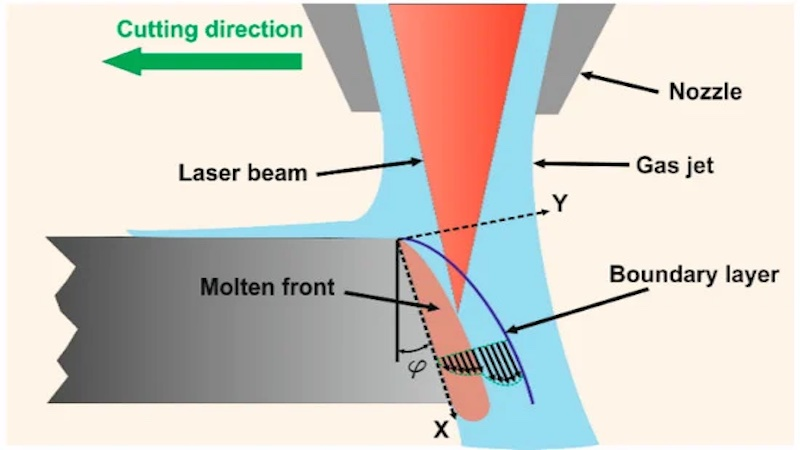
Heat Dissipation
Laser cutting generates intense heat, which can cause the material being cut to warp or distort. Assist gases help to dissipate this heat, preventing excessive heat buildup and minimizing the risk of material deformation. This allows for more accurate and controlled cutting, especially when working with delicate or heat-sensitive materials.
Oxidation Prevention
Certain assist gases, such as nitrogen, are used to prevent oxidation during the cutting process. Oxidation can lead to the formation of undesirable oxides on the cut edges, affecting the quality and appearance of the final product. By creating an inert environment, assist gases help to maintain clean, oxide-free cut edges.
Improved Cutting Speeds
Assist gases can help to increase cutting speeds by improving the efficiency of the laser beam-material interaction. For example, oxygen reacts exothermically with carbon steel, enhancing the cutting process and allowing for faster cutting speeds. This leads to higher productivity and reduced production time. The gas jets of compressed gas can facilitate this process.
Enhanced Cut Quality
Assist gases contribute to achieving high-quality cuts in laser fusion cutting with smooth edges and minimal burrs. They help to control the melting and vaporization of the material, resulting in precise and clean cuts. The choice of the appropriate assist gas and its settings can significantly impact the cutting performance and cutting kerf width, ensuring optimal results.
Overall, assist gases are essential for maximizing the efficiency and effectiveness of laser cutting processes. The selection of the appropriate assist gas depends on the material being cut and the desired outcome, and it is crucial to optimize the assist gas parameters for each specific application.
Factors Influencing Assist Gas Selection in Laser Cutting
Choosing the right assist gas is crucial for achieving optimal results in laser cutting applications. Several factors come into play when deciding which assist gas to use. Let’s explore these factors and their influence on the selection process.
Material Type
The type of material being cut has a significant impact on the choice of assist gas. Different materials require different gases to achieve desired outcomes. For example:
- Metals like steel often benefit from oxygen as an assist gas due to its ability to react with the material and enhance the cutting process.

- Non-metallic materials such as acrylic or wood may require nitrogen or compressed air, as they do not react well with oxygen assist gas. Gas jets or cutting nozzles can be used to deliver the mixed gas.
Thickness of the Material
The thickness of the material being cut also plays a role in assisting gas selection. Thicker materials typically necessitate high assist gas pressure and assist gas flow rates to ensure efficient cutting. Conversely, thinner materials may require lower assist gas pressure and flow rates to avoid damaging the surface.
Cut Quality Requirements
The desired quality of the cut is another critical consideration when choosing an assist gas composition. Factors such as smoothness, precision, and minimal heat-affected zones influence which gas will yield the best results for a particular application.
Cost Considerations
Cost considerations can impact the decision between using readily available compressed air or generating nitrogen on-site. While compressed air is more economical, nitrogen (n2) offers specific advantages in certain scenarios, such as reducing oxidation during cutting processes. Additionally, gas jets, including CO2 and assist gas jets, can further optimize cutting performance.
By taking into account factors like material type, thickness, cut quality requirements, and cost considerations, manufacturers can make informed decisions regarding assist gas selection in laser cutting applications. This ensures optimal performance and efficiency while achieving desired outcomes for each unique project.
Maximizing the Benefits of Assist Gases in Laser Cutting
To maximize the benefits of assisting gases in laser cutting, here are some key considerations:
Choose the Right Assist Gas: Selecting the appropriate assist gas for the material being cut is crucial. Consider factors such as the material’s composition, thickness, and desired cut quality. Different gases have different properties and react differently with various materials. Consult with experts or the laser machine manufacturer to determine the most suitable assist gas for your specific application.
Optimize Gas Flow Rate and Pressure: The flow rate and pressure of the assist gas can significantly impact the cutting process. It’s important to optimize these parameters to achieve the desired results. Too low of a flow rate or pressure may not effectively remove debris, while too high of a flow rate or pressure may cause excessive turbulence or material blowout. Experiment with different settings to find the optimal balance for your specific application.
Maintain Clean Assist Gas: Ensure that the assist gas supply is clean and free from contaminants. Contaminated gas can lead to poor cut quality, nozzle clogging, and reduced efficiency. Regularly inspect and clean the gas supply system, including filters and nozzles, to prevent any blockages or impurities from affecting the cutting process.
Proper Nozzle Alignment and Maintenance: An optimum nozzle diameter can achieve maximum cutting speeds, so make certain to choose the ideal nozzle. Ensure that the assist gas nozzle is properly aligned with the laser beam. Misalignment can result in uneven gas distribution and compromised cutting quality. Regularly inspect and clean the nozzle to prevent any blockages or damage that may affect the assist gas flow.
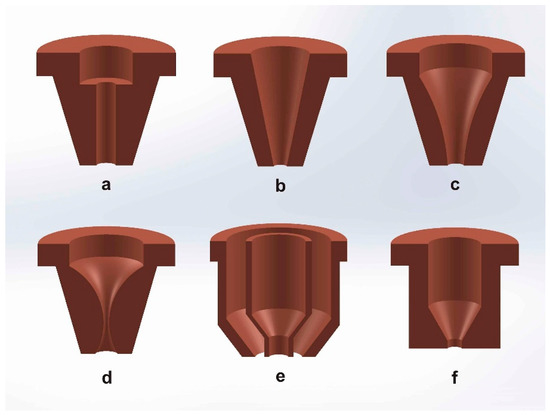
Experiment and Fine-tune: Laser cutting is a complex process, and the optimal settings for assist gases may vary depending on the material, thickness, and desired outcome. Experiment with different gas settings, flow rates, and pressures to find the optimal parameters that maximize the benefits of assist gases for your specific application.
By considering these factors and fine-tuning the assist gas parameters, you can maximize the benefits of assist gases in laser cutting, achieving clean, precise cuts with improved efficiency and cut quality.
FAQs
Can I use compressed air instead of nitrogen as an assist gas?
Compressed air can be used as an alternative to nitrogen; however, it may result in lower cut quality compared to nitrogen due to its higher oxygen purity. Assessing your specific needs and evaluating the cost-effectiveness is essential when deciding between compressed air and nitrogen.
What are the advantages of using nitrogen as an assist gas?
Nitrogen offers several advantages, including improved cut quality, reduced oxidation, and enhanced process control. It also allows for faster cutting speeds and minimizes the heat-affected zone, resulting in better overall performance.
Are there any cost-effective alternatives to nitrogen generation for assist gas?
While nitrogen generation provides long-term cost savings, alternative options such as bulk supply or cylinder delivery of compressed gas (N2) can be considered based on your production volume and budget constraints. Evaluating the pros and cons of each option will help determine the most cost-effective solution for your specific needs, taking into account factors such as gas flow and gas pressure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, maximizing the benefits of assist gases in laser cutting is crucial for achieving optimal efficiency and precision. By understanding the role of assist gases and considering various factors in their selection, you can significantly enhance your laser cutting process.
Air can work on mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and brass, but the edge quality is poor in laser fusion cutting, which can be compensated by low operational costs. Remember to do a detailed analysis of the gas jet and gas pressure before making any decision because it’s a recurring cost that can make or break your project.
Baison Laser Provides the Best Laser Cutting Solutions
It is undoubtedly very important to purchase a laser machine that can work perfectly with the auxiliary gas. Baison Laser offers products that are at the forefront of the market such as the fiber laser cutting machine and CO2 laser cutting machine. if you are unsure of the specifications of your machine, feel free to try our free application evaluation, where our experts will guide you 24 hours a day.